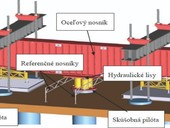
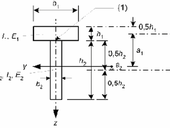
In connection with the natural disaster that hit the Břeclav and Hodonín regions in June last year, more than a thousand houses, buildings, halls and other structures were damaged or completely destroyed. Real estate was owned by both natural and legal persons, as well as by cities, municipalities and state institutions. Several state and non-state, for-profit and non-profit organizations came with financial help. To determine the amount of support, subsidy or loan, it was required to document the estimated costs of compensation. The estimated costs were determined on the basis of several methods, taking into account the type and type of real estate, ownership, and the extent of damage. The methods used to determine the estimated costs of compensation are described below.
Archiv článků od 25.9.2021 do 3.5.2022
One of the very essential aspects to ensure adequate durability of composite materials that combine cementitious matrix and wood is the stabilization of the wood structure. Stabilization of the wood structure is particularly important in relation to the moisture effect on the wood-cement composite mechanical properties. Stabilization of the wood matrix is generally carried out by means of suitable types of additives. This paper deals with a detailed analysis of the influence of the wood-cement materials composition in relation to the effect of liquid water. Another essential area of the presented research is the analysing the ability of the modified matrix (by different types of industrial wastes) to fix sugars in the structure of the wood mass, with regard to the possible affecting the hydration process of the cement matrix.
The article is focused on the evaluation of the static load test of piles by various methods. The aim of the evaluation is to obtain design values of the experimental bearing capacity of the piles. The analysis contains evaluated 10 static load tests performed on large-diameter piles of various lengths, which are located in the same engineering geological district and are made as drilled piles with a casing. Each test is evaluated according to STN 73 1002, according to the Brinch Hansen method 80% criterion and according to the Davisson method of ultimate strength.
The current way in drainage of roads is the concentration of rainwater in the subsoil of roads, so that rainwater does not drain into the sewer system, but freely infiltrates into the subsoil. The aim of this research is to optimize the structural layers of green parking lots with AS-TTE grassing blocks. During the design of structural layers and new types of materials, will be optimized to allow maximum water infiltration into the subsoil and at the same time keep the requirements for load-bearing capacity of structural layers according to ČSN 72 1006. Laboratory tests will be performed focusing on basic physical and mechanical properties, water permeability and adsorption of oil drips.
In this contribution, experimental and numeric analysis of slender stair tread model made of an ultra-high performance concrete, is described. Task of the analysis is to determine the behaviour of the model under acting load. The experimental part is represented by the static load test with the use of a vacuum method. Besides that, nonlinear numerical analysis in the environment of the ATENA Science software, is described. Gained results from both parts of the analysis are compared and unusual behaviour of the model is discussed.
Stairs are an integral part of multi-storey buildings and must meet a few ones based mainly on technical standards. One of the basic requirements for buildings is mechanical resistance and stability, which is currently often verified by calculation methods. If the calculation methods are insufficient, the experimental methods of loading the structures described in this publication must be used. The paper summarizes the course of static loading of prefabricated stair assemblies made of composite materials based on cement and reinforcing organic fibers. The applied methods are based on European standards and guidelines for technical technical approval.
Producers and suppliers of construction materials are dealing with rising prices of raw materials, semi-finished products and lots of different types of products. Insecurity of input raw material supplies for production is on the rise as well. This is due to the concurrence of many unfavourable circumstances.
Plastics are now being directed primarily to healthcare, mainly for the production of protective aids against virus transmission. A large amount of plastics is used for disposable food containers or packaging of goods, which is now more than ever ordered online. The outage of production capacity of global plastics producers in the USA has the biggest impact on plastics prices. Lack of plastics in the US influences significantly the quantity of plastics available on European markets. The subsequent withdrawal of plastics from China and Europe significantly contributes to logistics complications. Insufficient capacity of transport ships, aircraft and rail transport makes delivery times longer.
Reduction or termination of production of some smelters in Europe, rising emission allowance prices, tariff restrictions and a shortage of metals from Asia are contributing to raise metal prices. It is seen on the London Metal Exchange.
Although the long-term bark beetle calamity is not at its end yet, foresters have succeeded in stopping it in many places in the Czech Republic. Logging of bark beetle timber is decreasing and its price increases. The increase is caused not only by the decrease in logging, but also by export of this timber abroad, particularly to China, which is a phenomenon of the last two years.
Pandemic restrictions have impact on availability of workers for materials production, products logistics, sale and on-site assembly. There was a slowdown in construction output in spring and summer 2020. However, a recovery phase has been seen recently and demand for many materials exceeds supply.
The construction industry is the primary source of environmental impacts, especially the carbon footprint. Life cycle assessment (LCA) as an analytical method is used for quantifying the environmental impact of the investigated residential building. Life cycle costs (LCC) from the point of view of the circular economy create an economic model prioritizing reuse and recycling. The aim of this paper is to assess the residential building in terms of carbon footprint, using LCA analysis and circular economy, using LCC analysis. The residential building emits 1 756 tons of CO2e , which represents 41.35 kg CO2e/m2/year. The total estimated life cycle cost of the building in nominal terms is 1 694 699.61 €. This is the average total life cycle cost of 1 995.21 €/m2.
Reducing the consumption of non-renewable raw materials has become a growing issue in recent years. The construction of constructed treatment wetlands generates a significant consumption of natural aggregates, which can be classified as non-renewable raw materials. For this reason, it is necessary to try to find alternative materials to natural aggregates. A substitute for conventional aggregates may be recycled construction materials, which are still not as widely used as natural materials, mainly due to their low quality. The currently available materials should be evaluated in terms of replacing the main filter material of vertical filters, as this is where the consumption of natural aggregates is highest. The aim is to ensure financial savings by using more affordable recyclates, but also to preserve sufficient natural resources for future generations.
The paper deals with the behaviour of welded I-section duplex stainless steel members loaded by compression and major axis bending combination. The current beam-column design procedure is presented with its shortcomings described. To obtain the real behaviour data a set of conducted tests is presented, then numerical model created in Abaqus software with its validation is described. Furthermore, development of a unique pin-ended mechanism for member or member structure tests is given.
The new Eurocodes for basis of design and actions are almost completed and the final phases of their minor modifications are underway within the working groups of technical subcommittees SC1 and SC10. Their national availability for translations and preparation of national annexes is planned between 2023 and 2025, their implementation and withdrawal of the current Eurocodes in 2028. For the operational implementation of the new generation of Eurocodes, it will soon be necessary to prepare new national annexes and optimally set the values of nationally determined parameters, including calibrations of partial factors for loads and material properties, to ensure reliability, safety and economy of our buildings. It is expected to use the potential of our experts, as well as the considerable financial resources will be needed for the national implementation of the new Eurocodes and the publication of new manuals with practical applications.
This paper deals with the diagnostics of a timber load-bearing structure before planned renovation of covering structures. The roof and facade cladding can also change the load conditions, therefore, the inspection static design in this case is necessary. The planned object renovation is an opportunity for elaboration of diagnostic inspection of the supporting structure.
The paper discusses additive manufacturing in the building industry in terms of definition of terminology, application technology, machinery and materials to be used. It gives examples of executed buildings and discusses the possibilities of using natural materials for 3D printing of buildings. Current research and future prospects in the field of additive manufacturing are presented. The paper was created within the framework of specific research at the Faculty of Architecture of Brno University of Technology, where the possibilities of 3D printing from natural materials will be further analyzed.
There are situations when it is necessary to determine the state of prestressing at a specific time on existing structures. In these cases, it is possible to use indirect methods for determining the state of prestressing. These methods consist of the observation of selected quantities on the investigated structure. Subsequently, based on obtained results it is possible to analytically calculate the actual state of prestressing. The observed quantities include e.g., strain, deformations, crack width etc. This paper presents an overview of possible indirect methods for determining the prestressing in the structure.
The paper deals with the determination of strength characteristics of masonry composite. The MQI strategy, published by the staff of the University of Perugia, is presented. The calculation is based on a certain value analysis of several parameters, based on which the MQI masonry index is calculated. The index is then calibrated so that the strength characteristics of the masonry according to the new Italian standards can be determined from its value.
Modern composite materials are increasingly used in construction. One example is textile reinforced concrete (TRC), consisting of high-quality concrete and non-metallic reinforcing materials, most often in technical textiles. The current use of TRC is mainly in non-loadbearing structures such as facade panels and design elements. However, due to the excellent mechanical properties of TRC, it is possible to design subtle structures with high load-bearing capacity. Therefore, this material has a high potential in load-bearing structures. Consequently, it is necessary to comprehensively assess these materials in terms of load-bearing capacity at normal and elevated temperatures. For this reason, within the Faculty of Civil Engineering CTU in Prague and UCEEB CTU in Prague, research teams deal with the development and material research of TRC for use in load-bearing structures, including evaluation of its possible application in construction.
The aim of this paper is the modal analysis of a thin technical textile in shape of hyperbolic paraboloid. It is the geometrically nonlinear membrane structure, which can function only in tension. In this case, the structure was subjected to the natural vibration as a part of the overall dynamic analysis. All of this results in natural frequencies and mode shapes and deflections. Acquired results describe the dynamic behaviour of nonlinear system without affect of the external load. This part could represent a first step in the dynamic analysis and exactly the forced vibration as nonlinear time history analysis will have to be performed in a future to complete it.
The aim of this study is to find the dependence between the span and cross section area and other choose parameters of the timber-concrete composite beams. For analysis, we used coniferous wood C24 category and concrete C25/30 and C30/37 class with 50 mm thickness. We set the SFS Intec coupling elements. For calculation was used linear elasticity design method. Pliability of composite was take into account per γ-coefficient (γ-method).
Good, well-functioning infrastructure signifies a well-run national economy and the overall state of development of the whole society. Buildings, bridges, roads, and other structures need to be regularly maintained if they are to last. In general, if a defect is detected early, the cost of its remediation is typically much lower than if it the structure is allowed to degrade for months or years. Early defect detection often means detecting one before it is visible to the naked eye. A key means of locating hidden defects are non-destructive testing methods. The article describes selected non-destructive methods that can be used in the diagnosis of bridge structures.
The article presents the results of experiments of reinforced concrete walls with an opening, which have been tested for load carrying capacity in the diagonal direction. These are the walls that represent shear walls in multistorey precast concrete frame structures. The influence of various types of reinforcement on their load carrying capacity and deformation is studied on the designed walls. The data obtained by the experiment is then validated by computational models that represent the behavior of the samples during the experiment. The results of the models are compared between each other and pros and cons are assessed.
zpět na aktuální články