Contemporary architecture often works with glass facades, roofs or even glass columns and beams. The problematic part of a glass structure design is usually a connection between the glass elements and the rest of structure. In order to achieve as much transparency as possible, various mechanical point fixing systems, adhesive connections and their combinations were developed. Although being widely used, the design procedure is mostly based on experiments. There is ongoing research at the Czech Technical University in Prague focusing on characteristics of an embedded laminated connection under various types of loads. Within the initial phase of experiments, small scale specimens consisting of different glass and foil types were tested. The experiments revealed the tensile, eccentric shear and compressive short-term load-bearing capacity of the connection and a dominant mode of failure. Data obtained from the tests are going to be used for further numerical simulations and a parametrical study.
Archiv článků od 17.5.2022 do 27.2.2023
The test results show that both TORRENT and ISAT methods can be used to assess the durability of both concrete and fibre concrete with dense aggregate. In the case of concrete containing concrete recyclate, however, the TORRENT method was not effective. Also the method of determining the permeability for CO2 was not suitable for the concrete with concrete recyclate.
The rapid growth of the world's population and its concentration in large cities represents a major impact on the construction industry and the production of building materials. It is the recycling of building materials that is an effective solution to meet the requirements for the construction of new buildings and at the same time achieve sustainable development on earth.
The article deals with the issue of punching shear of flat slabs without shear reinforcement weakened by openings near the supports. The paper compares the predictions of punching shear resistance of flat slabs weakened by openings and supported by square and wall columns. The predictions were calculated using the design model prEC2 for prediction punching capacities that are introduced in the second generation of Eurocode 2. The obtained results of punching shear capacities were compared with experimentally measured results. The standard-recommended model of reduction of the control perimeter length using steering by a radial projection of the opening show that the prEC2 model significantly underestimates punching capacity when the opening is located at the face of support or near the shorter side of the wall column.
The article presents individual procedures for the selective demolition of a panel house intended for demolition. The procedure for inspecting the building for the purpose of identifying waste materials or end-of-life products intended for recycling is given. Furthermore, the contents of the project documentation for the demolition work and the progress of the preparatory work associated with the dismantling of the building are presented. The following is a description of the prefab house intended for selective demolition, the procedure for the demolition work and a sample of the summary list of waste during the selective demolition of the prefab house.
The article provides an overview of the development of construction and demolition waste recycling in the Czech Republic in the period between 2007 and 2020. Waste group 1701 concrete, bricks, tiles and ceramics analyzed in more detail. Recycled C&DW from this group are assessed in terms of the possibility of their use as concrete filler. Attention is also paid to group 170504 – soil and stones without hazardous substances. A significant increase in recycling has been demonstrated for this group in recent years. In conclusion, the ratio of recycled C&DW and extracted natural mineral raw materials in the construction industry is analyzed.
This post was posted on XXX. International Scientific Conference of Forensic Engineering ExFos 2022 [1]. We would like to present natural gardens and their benefits for both the owner and society. They are provided for free and therefore, we tend to overlook them. The literature refers to these benefits as ecosystem services. We are also thinking about possibilities so that the benefits of natural gardens can be valued financially, which would support their further development. We were inspired by a new book by V. Cílek, V. Mačura et al., called Trees Know Me by Name [2].
The article deals with sealing of cement-based materials and tensile properties of the sealed joint. Aquapanel cement board was chosen as the base material, which was treated with a primer. Then two sealants were applied, one representative of acrylic and one of polyurethane sealants. After curing, the resulting test specimens were tested according to the valid European standard ČSN EN ISO 8340, which defines the parameters of the test specimen and subsequent test procedures. The evaluation of the test, which took place visually and with a caliper measurement, showed that only polyurethane sealant could be recommended for sealing Aquapanel. This putty, unlike acrylic putty, did not show any defects after the test, so it can be stated as suitable for sealing Aquapanel cement board.
Part 2 covers buckling lengths of three-hinged arches both with the crown hinge of a fork type (in the arch plane) and a full type (both in and out of the arch plane). The article follows the Part 1 [1] which deals with two-hinged and built-in arches. All studies present three uniform loading patterns (vertical along the arch length, vertical to the arch plan or radial to the arch axis). Buckling lengths of the equivalent straight (Euler’s) column with the constant axial force corresponding to maximal axial arch force in the arch bases are presented in the form of graphs for CHS (circular hollow sections), various open rolled IPE and HEB sections.
Results of extensive study concerning buckling lengths of circular steel arches are presented. The study in Part 1 covers two-hinged and built-in arches, in Part 2 three-hinged arches with the crown hinge of a fork type (in the arch plane only) and a full type (both in and out of the arch plane). All studies present three uniform loading patterns (vertical along the arch length, vertical to the arch plan or radial to the arch axis). Buckling lengths of the equivalent straight (Euler’s) column with the constant axial force corresponding to maximal axial arch force in the arch bases are presented in the form of graphs for CHS (circular hollow sections) and various open rolled IPE and HEB cross-sections. The study is a follow-up of the author’s article Stability of Steel Circular Arches [1], embodying the preliminary stability analysis of two-hinged arches.
The article deals with experimental investigation of the influence of openings orientation on the punching resistance of flat slabs. Within the experiments, two isolated fragments of flat slabs were tested. Both specimens were weakened by two symmetrically placed openings with dimensions of 240 mm × 150 mm adjusted to the shorter side of the elongated column with cross-section of 950 mm × 150 mm. The specimens differed from each other by the orientation of the openings in relation to the support. In addition to the comparison of deformations, the actual control perimeter lengths of the tested specimens were calculated based on the results. Compared to the theoretical lengths of the control perimeters according to EC2, the reduction of the control perimeter appears to be conservative.
This paper discusses the feasibility of long-term monitoring using modern sensors and systems. New technologies are making long-term monitoring more accurate simpler and more successful. Currently there are many buildings that are monitored for a long time with its subsequent condition assessment, and thanks to the installed sensors and systems it has been possible to detect hidden and emerging defects and damages. Based on the current condition of the structure, it has been possible to carry out timely repairs or maintenance of the building which ultimately saves economic and time costs for the building, ensures safety and increases the life and durability of the building.
This paper deals with experimental verification of semi-rigid timer connections using modern timber connectors Rothoblaas Alumidi. The experiment consists of the loading of timber bracket of structural wood. There are 4 alternatives of connection prepared. Each alternative has 4 specimens. So far, 4 specimens out of a total of 16 specimens have been verified. The paper describes the preparation of the experimental set-up, the loading procedure, the preliminary findings and the results of the performed experiments. These results are confronted with numerical calculations and assumptions of previous theoretical research. Experiment research continues with the testing of additional specimens.
In preparing an expert opinion, estimate or valuation of any real estate, account should be taken not only of the type of property and the purpose of the valuation, but also of all factors which more or less affect their value or may affect it, in such a way that the slightest influence is incorporated. as a result of the award. One of these influences is tourism, in terms of the number of tourists who visit this locality. The impact of tourism on the market value of recreational facilities, residential real estate and other commercial purposes has already been partially mapped. However, the impact of tourism on the market value of residential properties has not yet been mapped and there are currently no relevant valuation procedures that can assess this impact. The following text contains an evaluation of one, as yet very little explored, intangible factor that may affect the price of real estate.
The paper deals with the methods of checking the performed sealing works in its second part. Measurements of the permeability of the grouted environment in the field are evaluated, the findings of the grouting records are analyzed and the cement content in the taken samples of the grouted soil was determined in laboratory conditions. Finally, the recommendations for remediation are summarized.
The ever-recurring high levels of the river Danube have forced Bratislava to be protected from floods. In the western part of the city, it was necessary to ensure the sealing of the heterogeneous fills located just on the banks of the Danube. The performed sealing works did not take into account the actual properties of the subsoil. The first part of the paper deals with the factual situation at the site and the shortcomings of subsoil injection.
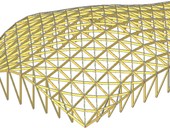
The paper deals with the theoretical shape and stability analysis of a timber grid-shell structure. The peculiarity of the approach to the analysis of this type of construction is manifested in several parts of the design process due to the complicated shape of the roof plane. These specifics can be applied to the initial phase of creating the shape of the structure, which is directly related to the resulting static efficiency of the final design. Other important parts of the structural analysis that deviate from the standard-defined procedures are the determination of the design load by external climatic influences and the stability analysis with the need to apply a geometrically nonlinear calculation with the influence of initial imperfections.
Ukraine has a strong influence on prices and availability of some construction materials. Steel products are the most hit by the war. Rising prices of energies and fuels are influencing the prices of construction materials, too. These unfavourable conditions are seen not only by small investors, but also by municipalities when announcing public tenders. The original price that won the public tender usually rises during the project’s preparation phase and subsequent construction phase. The author of this article analyses the construction materials’ price developments during a period of several years. In the article you can find a pricing of a particular public tender by indicative prices of construction materials and work in different periods.
Computer simulations require appropriate input data to match the relevant calculated results with those of experiments. The true stress-strain curve suitable for finite element analysis is describing the non-linear behaviour of the steel with a proper relationship from beggining of loading to failure of the test specimen. The pre-peak part of the curve can be easily covered by an analytical method, but the necking part of the curve cannot be described by such a relationship between the normalized and the true stress-strain curves. Simple numerical tensile test of a steel specimen was performed to establish the true stress-strain curve in ANSYS software. Stress and strain from the computer analyses were compared with the results of the experimental tensile test.
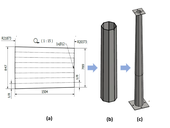
This paper deals with geometrical tolerances in the conical hollow tubes used in slip joints. Tubes are circular or polygonal cross-sections. The contribution includes standards concerning the tolerances. Based on the standards the imperfections in experimental specimens are evaluated. It is possible to say that it is not simple to state the shape and the allowed value according to standards. It is also possible to conclude that the experimental specimens include non-considerable imperfections.
zpět na aktuální články