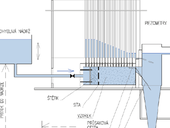
Internal erosion is one of the most common causes of failure of hydraulic structures. A special case is a backward erosion piping during which an exceeding of critical hydraulic gradient occurs on the edge of the structure foundation interface. This becomes especially dangerous for the structure when the foundation consists of sand or very sandy soil that is very easy to erode. The sand property of erodibility is not yet fully described. In this paper, an experimental device used for the rate of erosion determination for a picked sand is presented as well as a calculation of the erosion coefficient which is usually used to describe soil erodibility. Furthermore, the paper contains critical hydraulic gradients during which the erosion occurred.
Archiv článků od 14.9.2020 do 18.4.2021
This task deals with the properties and the possibility of recycling of thermal insulation materials such as polystyrene and mineral wool, not only from buildings after demolition but also from discarded materials left over after the construction of new buildings. This newly developed material is being tested as a filler for ultra-lightweight concrete where it fills the cavities of ceramic hollow bricks, as a filler for self-compacting concrete (SCC) and for the production of acoustic facing.
The paper offers an overview of the performed analyses, which evaluated the leakage into underground garages in the densely built-up area of the Prague city centre. Only after a comprehensive reassessment of geological conditions, the project and other available information was it possible to determine the probable causes of leakage into large underground parking spaces.
The aim of the paper is to summarize and evaluate individual diagnostic procedures that diagnose reinforced concrete structures damaged by fire. Based on our experience, we tried to design a methodology for the selection and use of individual diagnostic methods and procedures. Knowledge of the objective state construction after a fire is the basis for determining the procedure of its subsequent remediation.
The subject of the complex repair of the ceiling structure of the water reservoir Pasohlávky was the remediation and static provision of the unsatisfactory reinforced concrete structure. The original condition was inadequate, parts of the concrete structure were dropped due to steel due to steel corrosion and small cover layers of concrete.
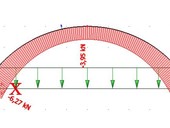
The article presents a stability analysis of circular arches under various uniform loadings (vertical to the arch plan, vertical to the arch length or radial to the arch axis). Linear bifurcation analysis resulted into critical loadings used for determination of the arches buckling length factors. With the exception of the radial loading the variable axial arch forces need to be taken into account also for the relative Euler basic strut. The analysis covers various boundary conditions of the arches in supports. The study embodies arches with both closed and open cross sections and proved the significant impact of the cross-sectional shape on out-of-plane buckling values. The article outcomes are tables with correct buckling length factors of arches.
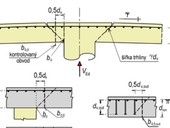
This paper deals with new methodology of design and verification of the limit state of punching of ceiling slabs in the prepared prEN 1992-1-1 [2]. The current methodology does not described with sufficient accurancy and with sufficient reliability the behavieur of the slabs structures in the area of supporting on columns and on ends and corners of walls.
The circular economy in construction is currently absolutely essential in the context of limited primary resources. This applies in particular to the use of inert mineral materials created during the demolition of buildings. It is proven that in the period from 2011 to 2018, the share of recyclates from C&DW in the total production of inert mineral materials more than tripled. One of the barriers to higher production of recycled aggregates is the low level of demolition of buildings, which often makes it impossible to carry out quality recycling.
The paper deals with the new Czech standard ČSN 731004 Geotechnical Design – Foundations, Requirements for calculation methods, published in July 2020. The subject of this standard ase simple calculation methods for the design of foundation structures based mostly on conventional analytical methods validated by long-term use not only in the Czech Republic. The standard applies to flat foundation structures, bored piles and displacement piles, micropiles and jet-grouted columns for axial loading. The standard is primarily intended for structures falling under 2. geotechnical category.
The paper is focused on the current issues of protection and strengthening of wooden structures. The wood used for them is a construction material whose mechanical properties are shaped by the nature and because it is also an organic material, it is subjected to various degradation processes. Types of wood protection includes all measures which would protect wood from influences of fungi, insect, weather (temperature, humidity, wind, fire etc.) and can be divided into chemical protection and radiation protection. Chemical protection can be further divided into protection against weather, biological pests and against fire. In our paper the solution of this weakness by photocatalytic materials (namely TiO2) is presented. Those materials are efficient UV absorbers and they are able to destroy biological aggressors as well. Nowadays, there is not enough information about the interactions between wooden surface and non-photoactive or photoactive form of TiO2. TiO2 exists in many morphological forms. The planar particles were chosen for purpose of the experimental investigation. This material was applied on wooden surface for creating a transparent layer. The results are presented in the first part of the paper. If it is necessary to increase the load-bearing capacity of wooden elements, one of the possibilities is to strengthen them by applying a high-strength layer containing carbon fibers. The second part of the paper is devoted to this procedure with a detailed description of how to implement and design this reinforcement.
This article deals with the properties of recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) from two-phase recycling. Specifically, it is the 8–16 mm fraction, which is already commonly used in practice in compliance with standard requirements, the 4–8 mm fraction, the use of which is problematic from the point of view of standard regulations. The article focuses mainly on the key properties of RCA that affect the design of concrete mixtures.
The increasing amount of construction and demolition waste is gaining the attention of research institutes that deal with the possibilities of using this waste. This article deals with the possibility of using masonry aggregate from construction and demolition waste in concrete samples. The most important are the properties of the aggregate as follows a suitable concrete recipe optimization with various number of replacements of natural aggregates with recycled masonry aggregates. The experiments in this paper are summarized in two categories - geometric and physical experiments.
This contribution deals with damage to buildings and building materials due to bad manage of rainwater regime. Effects are divided according to location of damage. First, the damage of roofs and roof trusses is presented, which are followed by examples of damage to the enclosure walls. The most attention, including numerical 3D modeling, is devoted to damage to foundation structures and foundations.
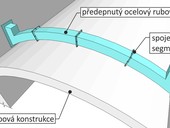
Many historic buildings are located in areas where there is a specific type of earthquake activity, the so-called earthquake swarms, during which a series of thousands of weaker tremors take place for several days or months. Sometimes these shocks are strong enough to be felt by people, and in some cases they can even cause material damage to buildings. Knowledge of the response, especially of vaulted structures of historic buildings to dynamic loads, is the basis of remediation interventions on monumental buildings exposed to these effects. Due to the increasing intensity of wheel and rail traffic, there is also an increase in the effects of the so-called technical seismicity on structures located near roads and tracks. The proposed system of additional stiffening of barrel, cross or of spherical vaults by means of prestressed flexurally rigid segmental ribs contributes to the increase of their resistance to the natural and anthropogenic dynamic effects.
Within the research project NAKI DG16P02M055, an extensive experimental and theoretical research of the influence of grouting on the physical and mechanical properties of brick and stone masonry is carried out. The focus of the research is to verify, in particular, the strengthening effect of selected grouting mixtures based on hydraulic lime (nano-lime), resins and silicates. The influence of grouting on the change of porosity, pore distribution, absorptivity and strengthening effect of grouting of historical brick, marl, sandstone, trachyte, limestone and mixed masonry with lime binder using various types of grouting mixtures in comparison with ungrouted masonry is evaluated. Particular attention is paid to the masonry damaged by cracks and cavities.
Many structural concrete elements of dams must withstand extreme frost stress and abrasion of fast-flowing water. At present, several reconstructions of concrete overflows, chutes of dams or weirs are underway or have already taken place with the requirement for increased resistance to abrasion. From the point of view of ČSN EN 206, abrasion-resistant concretes are determined by exposure class XM, but the evaluation criteria and testing methods are insufficient. The article deals with a closer presentation of the requirements for the properties and development of concrete with high resistance to abrasion and frost and its subsequent testing.
Textile-reinforced concrete is currently a newly developed material and can be used as an alternative to traditional reinforced concrete structures.It is a combination of high-performance concrete, textile carbon reinforcement, and its synthetic matrix. The main advantages of textile-reinforced concrete are its mechanical properties, while retaining a subtle structural character,and excellent resistance against atmospheric corrosion. Currently, textile-reinforced concrete is used mainly for non-load-bearing structures; however, more widespread usage in load-bearing structures is predicted. This article serves as an evaluation of textile-reinforced concrete in load-bearing structures from the fire safety of buildings‘ point of view as well asa stating prospective limitations resulting from the requirements of the set of standards series CSN 73 08xx.
The present experience has shown, that the most serious effect of the accidental load on prefabricated panel buildings in our conditions is a gas explosion. In addition to the explosion of gas, the effect of elevated temperature during a fire is also significant. During a fire, the mechanical properties of building materials may change. These may not return to their original value at the end of the temperature load. The article describes the design of repair of the load-bearing members the panel building after fire on the 11th floor of the panel system type T-06.
Article follows the previous treatise concerning prestressed steel tubes with just one crossarm (Machacek a Pichal [13]). A stayed column with two crossarms is investigated, while other parameters as those of tested and analysed stayed columns with one crossarm are identical. Critical loadings and decisive buckling modes of unprestressed stayed columns are solved by linear bifurcation. For prestressed stayed columns the analytical method is derived, which enables calculation of critical loading under an arbitrary prestress including the optimal one, resulting into maximal critical loading. The main study introduces geometrically, possibly also materially nonlinear analyses with initial imperfections, using software ANSYS. The nonlinear analysis is shown to be necessary even for critical loading of "ideal" stayed column, while for strength of "imperfect" stayed column, with given initial deflection, is absolutely essential. Finally are analysed impacts of material nonlinearity and numbers of crossarms, followed by practical design recommendations.
zpět na aktuální články