Results of the measurement ultrasonic pulse method are influenced by numerous factors. The influence of humidity and the method of sounding, direct and semi-direct on the measurement results was monitored. The influence of moisture and the method of transmission the bricks influences the measurement results by varying degrees. The least is influenced by the results of measurements on calcium silicate bricks and, on the contrary, on clay bricks made of plastic dough. Here shows synergistic effects of the state structures and defects in the head.
Archiv článků od 26.2.2018 do 13.8.2018
Replacing a concept “types” of the landscape by the concept “landscapes” in the content of the graphical part of the territorial development principles (ZÚR) presents a substantial change of content in the expression of conception of the regional development, because for these landscapes the target qualities including territorial conditions for their preservation or accomplishment are established in the territorial development principles (ZÚR). The original definition of the types of landscape, which divided the territory according to the characteristic features and properties, must be gradually replaced by the definition of (real) landscapes. It is a great change, because a type of landscape expresses the characteristic properties, but real landscapes in the sense of landscape itself = specific, characteristic, have substantially different sense – they express most of all individual properties of the landscape. Therefore it is necessary to describe and give reasons for importance and the method of individual (not typological) zonation of the territory of the region into landscapes (real landscapes) corresponding to the sense of the European Landscape Convention.
In the paper the refurbishment of riding`s hall roof structure is presented. The combined steel-timber load-bearing structure had visible and high horizontal deformations and the gable wall was pushed out of the building.In the frame of refurbishment the diagnostic survey, structural calculations of the original and the new stage of the structure and the proposal of refurbishment works were worked out.
The work is focused on the investigation of the formation of gaseous thermal degradation products of retarded firwood. Samples of firwood were impregnated with solutions of 6 inorganic salts, thermally loaded and the arising gaseous products analyzed by SPME-GC-MS. There were 20 compounds identified, the highest amount was achieved for acetic acid and 2-furaldehyde as typical representatives of wood degradation. Most compounds were identified by degradation of samples treated with boric acid solution, at least with ammonium dihydrogenphosphate. The smallest amount of acetic acid and 2-furaldehyde was determined by treating of fir samples with sodium tetraborate solution, which appears to be a very suitable wood treatment agent for fire protection.
This paper shows the process of restoration, of a historic wooden ceiling, using a “dry method” – interaction between historic timber joists that are mechanically jointed with wood-based boards.The paper describes reasons for choosing the method and principles of a good design. The experience of using this method on site is also described in this article.
This paper aims to outline basic requirements for the creation of the mediating institution in the urban planning process. It applies the work of the Austrian School of Economics on the urban planning system. It reviews the current state of the system of urban planning, it’s hierarchy. Decision-making process, the role of public, and the role of private investors and developers. To increase the quality of the urban planning process, it establishes the principle of mediation, which aims to change the positions of all sides involved. The core of the mediation principle is to use the unique knowledge and position of the three main sides of the process, being developers, public, and public administration. Establishing of a productive dialogue between all sides can create a more effective urban development.
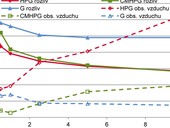
Long-term physical-mechanical characteristics of aerial-lime based mortars with guar gum derivatives
This paper studies the possibility of usage of the guar gum and its derivatives as admixtures for aerial lime-based mortars. The influence on the properties of mortars was studied on the aerial lime–based mortars prepared with quartz fine grained sand and doses of admixtures ranging between 0,5 and 10 ‰. The hardened bulk densities, flexural and compressive strength, carbonation rate, workability though flow table test and air content in fresh mortar were studied. The addition of the hydroxypropyl guar (HPG) lowered the bulk density (due to an air intake), improved workability, slightly increased the strength and slowed carbonation rate. The addition of carboxymethylhydroxypropyl guar (CMHPG) does not impact the bulk density and air content in the fresh mortar, the strengths were increased similarly to HPG: it does not impact carbonation rate significantly, so the long term strengths were comparative with the HPG. The pure guaran was found not to be beneficial for the lime mortars.
Wood and the materials on its basis fulfil the requirements of an ever-evolving and accelerating society. In addition to naturally grown wood, wood-based materials are frequently used as a basic material for production of furniture and for building constructions as well. Looking at changes in waste management, a significant shift from the waste to the circular economy can be observed. The valuable raw materials are kept in the production cycle instead of landfilling or burning. Wood and wooden products can be efficiently separated in waste management, reused and recycled. The so-called wood waste – old furniture, wooden pallets, window and door frames, demolition wood, used lumber, bark and other wood residues can be reused in particleboard production. Particle board manufacturers in the Czech Republic have adopted progressive waste management and currently use 60% of recycled wood into particle boards. A completed life cycle analysis (LCA) of OSB demonstrates that replacing of 50% of natural fibres with recycled wood has significant environmental benefits. The objective is to push furthermore on effective legislation to promote waste material utilization and thus lead to a more sophisticated waste wood collecting.
Wood and the materials on its basis fulfil the requirements of an ever-evolving and accelerating society. In addition to naturally grown wood, wood-based materials are frequently used as a basic material for production of furniture and for building constructions as well. Looking at changes in waste management, a significant shift from the waste to the circular economy can be observed. The valuable raw materials are kept in the production cycle instead of landfilling or burning. Wood and wooden products can be efficiently separated in waste management, reused and recycled. The so-called wood waste – old furniture, wooden pallets, window and door frames, demolition wood, used lumber, bark and other wood residues can be reused in particleboard production. Particle board manufacturers in the Czech Republic have adopted progressive waste management and currently use 60% of recycled wood into particle boards. A completed life cycle analysis (LCA) of OSB demonstrates that replacing of 50% of natural fibres with recycled wood has significant environmental benefits. The objective is to push furthermore on effective legislation to promote waste material utilization and thus lead to a more sophisticated waste wood collecting.
The article is devoted to extraction of some mode-shapes from measured data during the operational state. The measured bridge is in Bratislava and connects two city districts: The Old Town and the Petrzalka district. The structure is an asymmetric cable-stayed steel bridge with an orthotropic 2-box beam supported in one plane by cables from an inclined pylon. The bridge was measured twice, firstly in 2016 and secondly in 2017. Ambient vibration data were acquired during the measurements. The FEM model has been prepared before the measurements. Some mode-shapes were identified from the data and then compared to the calculated ones.
Wood and the materials on its basis fulfil the requirements of an ever-evolving and accelerating society. In addition to naturally grown wood, wood-based materials are frequently used as a basic material for production of furniture and for building constructions as well. Looking at changes in waste management, a significant shift from the waste to the circular economy can be observed. The valuable raw materials are kept in the production cycle instead of landfilling or burning. Wood and wooden products can be efficiently separated in waste management, reused and recycled. The so-called wood waste – old furniture, wooden pallets, window and door frames, demolition wood, used lumber, bark and other wood residues can be reused in particleboard production. Particle board manufacturers in the Czech Republic have adopted progressive waste management and currently use 60% of recycled wood into particle boards. A completed life cycle analysis (LCA) of OSB demonstrates that replacing of 50% of natural fibres with recycled wood has significant environmental benefits. The objective is to push furthermore on effective legislation to promote waste material utilization and thus lead to a more sophisticated waste wood collecting.
The paper deals with the experimental analysis aimed at function verification of fiber optic sensors (Fiber Bragg Gratings). The sensors are used for mechanical stress measurement in wooden load-bearing structures. Glued laminated timber beam with built-in fiber optic sensor system was mechanically loaded during two bending tests. The data obtained using the fiber optic sensors were compared with the results of reference measurement method and analytical calculation.
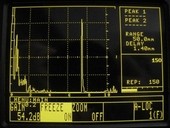
Diagnostics of building structures are used in non-destructive and destructive methods for evaluation of selected properties of building materials. Structural elements but also selected parts are assessed. Ultrasonic method, which is among the non-destructive testing methods, is being used for the diagnosis of concrete and steel structures for many years. The paper presents possibilities of carrying out inspections of selected elements of steel structures.
Sintering activity (dependence of porosity, flexural strength and firing shrinkage on the firing temperature) of feldspar dust (Casial) which is generated during the milling of potassium feldspar in Halamky quarry was determined. Potassium industrially milled feldspar Z75K13 as a reference material with similar granulometry and mineralogical composition with Casial was used for comparison. More intensive sintering activity showed dry pressed samples based on Casial in comparison with feldspar Z75K13 (about 30 °C lower sintering temperature – 1180 °C). Casial created red body after firing thanks to higher content of Fe2O3.
The magnitude of the load on the walls of tall wooden constructions can be assembled according to the existing standards according to the valid combination equations in several ways. There are differences between the results. Determining the appropriate procedure for determining vertical strength from construction in different parts of building preparation and comparing it with other options is the subject of this paper.
Within this work possibility of using four kinds of waste glass as a replacement for the commonly used filler, silica sand DORSILIT, to epoxy based polymer concrete (PC) is experimentally verified. Determination of compressive and flexural strength, chemical resistance and thermal resistance is examined in order to find out if PC containing waste glass as filler can be used for rehabilitation of concrete structures. Even based on the results of the tests it will be assessed whether it is possible replace DORSILIT by waste glass.
There are applications of refractory concretes for places where these are exposed to corrosive environments. This text deals with both description the corrosive effects and methodology of their testing. One of the most important properties of materials, affecting the chemical corrosion resistance, is their density. The second part of this text is focused on testing the refractory concretes which are currently used for applications. The aggregates were tested for the resistance to sulfuric acid.
Adding structural fibres into concrete has an impact, both positive and negative, on the long-term durability of concrete. Polymer fibres do not resist shrinkage of the concrete, steel fibres, on the other hand, create a tough skeleton preventing deformation. Porous structure of fibre concretes exposed for a long time in the environment of CO2 is estimated using the method of determining the coefficient of diffusion resistence and the method of determining the capillary hight. Comparison of measured capillary hight and diffusion coefficient of fibreconcrete samples bring the knowledge, that close correlation between both quantities does not exist, due to the physical difference between determination of both quantities.
With strengthening of damaged concrete linear elements have been engaged since 2003. It is a co – ÚSTARCH SAS Bratislava, FCE University of Zilina, STU Bratislava. Repaired the damaged components – new the coupling plate with reinforced contact, the coupling plate without reinforcement – replacing the geometrical condition of contact. The use of GFRP panels. The effect of the time factor on both the MS.
zpět na aktuální články