The paper deals with the principles of structure, function, use, disfunction and repairs of framework (part 1 to 4).
Archiv článků od 6.2.2017 do 14.8.2017
The cause of moisture in the masonry could by different. By old historical buildings is the problem in absence of hydro-insulation, which was made by flat stones or clay backfill. New buildings have a lot defect by application (for example: pipes penetration, join) or wrong design of hydro-insulation, which are the point infiltration of water in to the construction. This problems are made by wrong projection of hydro-insulation in the project. The project does not reflect all influences of the water. But they are also another cases, which can happened like river floods, flood by the neighbour. In those cases it is demanding to dry the building as soon as possible, to protect the property from the mold and return the function of the building. One of the method, which is suitable for this solution is microwave dehumidification, which realize all conditions in one. This aim include also the practice example of the microwave sanitation technique, used by dehumidification masonry, and the positive results.
The definition of what is a common part of a residential building is essential especially when modifying the building structures and eliminating defects that affect both a common part and residential units. How common parts are defined affects who finances the modifications and reconstructions of such structures and parts. The definition of common parts is based on the new Civil Code (No. 89/2012 Coll.) and on the already abolished Act on Ownership of Housing (No. 72/1994 Coll.).
At present, there is growing interest in the realization of multi-storey wooden buildings. In the case of multi-storey wooden buildings, their safety, stiffness and acoustics are of key importance. The submitted paper focuses on the issue of fire safety of multi-storey wooden buildings, which is currently the subject of major discussions.
A growing environmental awareness and desire for sustainable solutions and healthy living conditions, especially in Europe, lead to an increasing demand for timber structures. High speed, excellent cut quality and accuracy of CNC processing allows an effective produce of timber structures by traditional carpentry procedures. This article responds to current problem of load bearing capacity calculations of traditional carpentry joints. This way of structural joints has not sufficient support in current standards and therefore design relies on simple empirical relationships based on experience. This paper presents the experimental and calculation methods for investigation of static behaviour and load bearing capacity of carpentry joints.
The contribution dealst with the problematics of statical defects, or more precisely with the formation of cracks in the brickwork caused by the effect of technical seismicity. It further deals with the construction principles which can be used when designing reconstruction of buildings which are located within the reach of the effect of technical seimicity. The problematics of historical buildings and conservation areas is also mentioned.
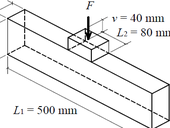
Computing models for structural behaviour and determination of traditional timber butt joints using analytical relations are presented in this paper. A component method is a base of the computing technique introduced herein. This method is usually used for steel joints design. The component method is based on dividing a joint into individual components. These are defined by partial joint component stiffness. An analytical solution includes a subsidence effect of wooden material in a close proximity of compressive loading. Analytical computation results are compared with the experimental outputs. A design procedure according to Eurocode 5 for a load capacity determination of perpendicularly loaded structural element is stated in the paper.
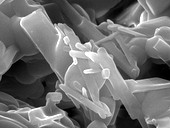
The article presents research into the effect of carbon nanotubes in the blended polymer-silicate matrix containing raw materials from alternative sources. The intention was testing of several variations of mixture composition at the laboratory and also extreme temperature ambient. Assessing the suitability of the matrix composition was carried out by using both basic physico-mechanical parameters and then microstructural analysis methods (on selected samples).
Utilization of fibre concrete in building structures, supported by technical standards in preparation, stimulates the development of methods for nondestructive analysis of its structure, crucial for mechanical properties, as fracture resistance under tensile loads. The paper presents an overview of available methods, based i) on image processing and ii) on measurements of electromagnetic quantities.
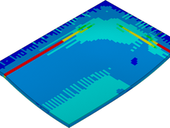
This report presents a new method for designing composite timber steel-fibre-reinforced concrete slabs with unprotected secondary timber beams subject to fire, taking tensile membrane action into account. The FE-model consists of material tests, push-out shear tests and beam tests, which had formed a preliminary study. The FE-model represents the behaviour of the floor slab tested in experiment, together with a collapse prediction for the slab. The FE-model with characteristic material properties includes a safety concept based on the Eurocode standards, and is applied to define the fire resistance of various types of timber steel fibre-reinforced concrete flooring.
This paper discusses the practical use of microwave technology in construction practice. Opinions on the use of EMW devices are not only among the general public quite different. From boundless praise, to the uncritical condemnation. The reason for this situation is the lack of awareness of experts and the public about what is and what is not possible to expect from this technology.The article conclusions which we reached on the basis of experiments conducted at the Faculty of Civil Engineering Brno and subsequently verified measurements in field practice. The aim is to provide basic information about how to use microwave technology. Their benefits but also the risks that this technology brings along.
Long-time study of fibre-reinforced concrete, i.e. a composite material with a cementitious matrix, whose structure is hardened by usually randomly distributed fibres (steel ones in the most frequent case), demonstrates good mechanical and other technical properties, which makes possible its utilization in bearing structures. This stimulates the development of methods, non-destructive or low-invasive if possible, for the analysis of its structure, which determines crucial mechanical properties, e.g. fracture resistance under tensile loads. This article, coming from research activities of the Faculty of Civil Engineering at Brno University o Technology, brings an overview of available methods, namely direct methods coming from image processing and indirect ones utilizing measurements of electromagnetic quantities.
The article deals with hot-air treatment of a historically valuable Rožnov town office, built in 1770, which was transported to the Wallachian Open Air Museum in Rožnov pod Radhoštěm in 1924 as the first building of the currently extensive premises of this national cultural heritage. The method of wooden structure hot-air treatment was used for the first time in the territory of the Czech Republic in 2010. It has been used in western European countries (especially Denmark and Germany) approximately since 1930. This comprehensive method is governed by the German standard DIN 68 800 – Part 4 [1] and it is especially used for historically valuable buildings where emphasis is put on the preservation of the original wooden structure attacked by wood-destroying insects, usually of the long-horn beetle family (Cerambycidae) oranobium beetle family (Anobiidae). The goal of the article is to explain the hot-air treatment method to professional public using an example of one of implementations.
Water vapour permeability is one of significant material properties. The value of water vapour resistance factor is necessary to know to be able to rehabilitate structures, mainly after floods. One thing is essential – to know what are the values of water vapour resistance factor of the used material to know how long the structure will take to be dried and users can come back to live there.
Sulfate attack is one of the major threats for durability of concrete in sewage collection systems where concrete sewer pipes are exposed to sulfates from waste water as well as from biogenic activity of bacteria. Damage due to sulfate interaction can result in the cracking and softening with loss of strength of concrete and it may lead to the concrete desintegration. Gypsum is the primary product of sulfate attack on concrete, after which ettringite is subsequently formed. Ettringite and gypsum are considerably larger in volume than the initial compounds, which leads to increased pressure within the concrete structure. This paper is focused on the sulfate attack on fine-grained concrete where the effect of 12 months contact of 0.5% sulfuric acid, simulating biogenic sulfuric acid corrosion, 5% sodium sulfate solution and solution simulating sewage water on various types of concrete has been investigated. The concrete specimens were characterized after exposition to the corroding media by their mechanical parameters, changes in pH and content of sulfates. It was found that after one-year exposure to sulfuric acid solution, the compressive strengths of all types of concrete significantly decreased. Sodium sulfate solution and the artificial waste water did not represent the significant corrosion environments for the concretes in terms of their strength reduction, increasing of sulfate ions content and the reduction in the pH of their aqueous leaches. The fine-grained concretes containing metakaolin and ground limestone showed the highest coefficient of corrosion resistance for the applied corrosive solutions.
zpět na aktuální články