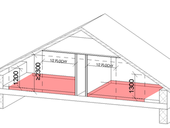
Floor area in living spaces with slanting ceilings has an ambiguous interpretion in czech national regulations. It has an effect on a building approval process and this article describes how to determine this area in both architecture and civil enginnering.
Archiv článků od 16.11.2015 do 20.6.2016
The paper describes a system of FBG (Fiber Bragg Grating) sensors and their integration into the beams of glued laminated timber for continuous monitoring and diagnostics of mechanical stress in building structures. The possibility of gluing the optical fibers into the timber structure and influence on manufacturing process of glued laminated timber on the glued fibers is studied. Laboratory tests including mechanical loading of examined samples were carried out to verify the correct operation of the sensors. Based on the measurement, a timber beam with embedded FBG sensors for the monitoring of the real construction have been manufactured.
The world exhibition EXPO 2015 proved from the creative and useful perspective that wood is a promising building material. We could see the use of wood on a number of exhibition objects representing countries from around the world. Even in the recent past that was not quite realistic. This was enabled by technological advances which created conditions for the implementation of bold ideas of architects associated with this renewable raw material. Along with the exhibition buildings, wood was used for the service utilities which provided comprehensive facilities of the exhibition grounds. In addition to wood, other natural materials such as rattan, bamboo and natural fibres were applied in some exhibition halls.
The article introduces the new method “Lapped Scarf Joints for Historical Structures Repairs” that deals with design of the lapped scarf joint suitable for the reconstruction of valuable historical timber structures, with help of making the prosthesis for the damaged parts of the beams. The method is a result of the four-year research project supported by the Czech Ministry of Culture within NAKI program. Institute of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics AS CR, Faculty of Civil Engineering CTU and Faculty of Forestry and Wood Technology of Mendel University participated in the research.
The study is focused on evaluation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (N-TiO2) impact on photocatalytic properties of concrete surface. Specimens made from ordinary white cement with no TiO2 particles, specimens made from commercially available photocatalytic cement and specimens made from white cement covered with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanotextile containing N-TiO2 were compared with respect to their ability to decompose rhodamine B dye when exposed to direct UV radiation. PVA nanotextile was prepared by electrospinning method. The solution exploiting the nanotextile was not found to be prospective in this phase of the research. However, the method of preparation of enriched nanotextiles as well as their application on the surface of concrete elements was tried and can be adjusted for different purposes.
The paper will describe the technical requirements for the choice of the material for the steel structures and bridges. They are specified by the steel structures designer in the different deign stages. However, the tender design is the stage, where the full material specification should be given. The paper will be divided to several parts, that will describe all specification for the design, testing and checking of material.
Preface – Helping data (continuation): Compression design strength at an angle to the grain – Columns: buckling coefficients for solid timber and for homogeneous glued laminated timber – Stability of members: Beams subjected to bending without compression force – Tilting factors – Laterally loaded joints with dowel type fasteners.
Timber and glass are the materials that have excellent aesthetic qualities. In current architecture, glass, as well as wood, are increasingly used for the visually exposed structures. Since glass is a brittle material, various types of hybrid structures are developed. Glass in hybrid element is combined with other material (eg. concrete, timber, steel, aluminium etc.) to increase load-bearing capacity and stiffness of the element, achieve safe failure behaviour together with high level of transparency. Nowadays, several European universities and research centres deal with the glass-timber load-bearing elements. This article provides an overview of the developed hybrid timber-glass structures including an experimental analysis of adhesive timber-glass joints, which was performed at Czech Technical University in Prague.
Transparency and also smooth, glossy and reflective glass surface give special importance of this material in the contemporary architecture. Connections between two glass elements or glass pane and other part from a different material are very important issue for structural applications of glass. Moreover, there are many types of hybrid structures that combine glass and different materials to achieve safe failure behaviour and high degree of transparency at the same time. Connection of brittle glass and reinforcing material is an essential part of these structures, where composite action between two parts is beneficially ensured by a glued joint. Experimental determination of mechanical characteristics of various adhesives applied in planar connections under shear loading is a main topic of current paper.
This paper presents methods to enhance the punching shear resistance of existing flat slabs (enlargement of supported area, enhancement of flexural resistance of slab, post-installed shear reinforcement and prestressed solutions). In case of post-installed shear reinforcement, systems based on steel and CFRP are mentioned. Static, technological and economic advantages and disadvantages are analysed. Differences between the systems are mainly due to the requirement to access the upper face of the slab, resistance-decrease in case of fire and deformation capacity of the strengthened slab.
The corrosion of steel reinforcement is the most important factor in degradation of the concrete structures. The use of the new composite materials as reinforcement in concrete structures has expanded in recent years. These concrete structures are often exposed to extreme environmental loads. The fibre reinforced polymer (FRP) materials are an alternative to the steel reinforcement. It is a durable material, which has corrosion resistance, high tensile strength and low density. The manufacturers use various kinds of fibers in the FRP reinforcement, especially carbon (CFRP), glass (GFRP), aramid (AFRP) and basalt (BFRP). The present article describes the application of the FRP reinforcement as a replacement of the steel reinforcement in new structures, respectively for strengthening of existing concrete structures.
This paper proposes statistical methods for evaluation quantitative performance determinated by tests of building products for objective decision during conformity assessment / certification in a fire protection field. The procedure is applicable for other types of products, and research / development of new material products.
Concrete exposed to high temperature considerably changes its properties down to total destruction. The paper describes renovation of concrete floor damaged by a fire of a factory building. Individual steps of determination of damage of concrete floor structures caused by high temperatures are described. Structure of damaged floor was technically analyzed, redevelopment was designed and renovation works were carried out.
zpět na aktuální články