Timber-concrete composite structures which use advantages of both materials are suitable for new works and reconstructions of civil and residential buildings. There are described many methods of joining between timber beam and concrete slab in technical literature. Joints are more and more sophisticate which brings higher demands of work control and technology. Main goal of this paper is in design technologically low demanding method of joining with steel plates and nails, to test its shear strength and compare it with other similar joining method.
Archiv článků od 6.5.2013 do 30.9.2013
The paper is concerned with some selected defects and failures of timber structures and their rehabilitation. The paper summarises some conclusions from the construction and real behaviour of selected timber systems. Due to the fact that their load-carrying capacity and deflections are considerably affected by the load-carrying capacity of the joints, it was de-sirable to verify the influence of structural design of fasteners and connectors on the over-all behaviour of structural systems. Findings from behaviour of structures after their reha-bilitation are crucial for further research into real behaviour of timber structures.
The work describes the divisions of contemporary and traditional solid wood constructions. The introduction briefly explains the historical development of timber structures and the advantages that these structures provide. Individual structural systems are described according to the basic elements and usage possibilities. The requirements for the massive wooden houses are listed in the form of technical standards and laws that have to meet.
This paper deals with the basics of the so-called “Massive Timber Construction“ (MTC) system. The paper is focused to the design of MTC system (mainly design of floors, shear walls and connections) which is made from the relatively new wood-based product “Cross Laminated Timber” (CLT). CLT consists of several layers built-up with boards. Their assembly in orthogonal directions allow them to produce elements with big dimensions. Currently, no regulations for the design of CLT-elements are given in the European standards. Nevertheless mechanical parameters of CLT-elements can be determined on the basis of the properties of the single layers as is shown in the paper. It is expected that CLT will play an important role in the future use of wood in single and multi-storey buildings.
This paper deals with possibility of using recycled construction and demolition waste as aggregate for concrete. The European Standards describes tests and properties of recycled aggregate for concrete. The main aim of this investigation was determination of recycled aggregates properties and their comparing with properties of natural aggregate and requirements in Standards. Selected geometrical and physical properties were tested and results were used to design concrete mixture. It was found that the main differences between natural and recycled aggregate is water absorption. Water absorption of recycled aggregate was more than ten times higher.
A new type of circular wind bracing has been developed for stiffening of high-rise slender steel structures. This bracing can use pre-stress to modify its stiffness to achieve required properties. The models scalled 1/20 are subject to static and dynamic load laboratory tests in order to prove theoretical conclusions and to adjust optimal values of pre-stress.
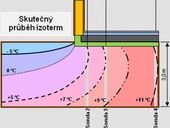
Existing procedures for determining heat transfer in the soil. Temperature measurements in the soil under the floor of the experimental house MSDK at the Technical University in Ostrava. The difference between the calculated temperatures and actually measured. Theoretical and real temperature field in the soil.
Blocks for masonry with integrated insulation material are known over 30 years. Especialy hollow clay bricks have low U value due to optimalization of their geometry with low thermal conductivity of ceramic body. Finaly integrated insulation material into the holes in bricks results to increasing of thermal insulation properties. Article is focus on behavior of hollow clay bricks with and without integrated insulation material in dynamic heat load.
The paper is focused on the results of testing of a key segment of the tunnel lining, which is important for the capacity of the tunnel lining itself. Strength parameters of the designed structural steel fibre reinforced concrete (SFRC) element are described. SFRC key segment with fibres dosages 50 kg/m3 are compared with ordinary RC key segment.
The article introduces the testing procedure of levelling instruments in construction. Generally described testing and validation procedure of levelling instruments (optical and digital as well) is supplemented by results and evaluation of four selected levelling instruments (Sokkia C40, Geo Fennell NO.10, Spectra AL100 a Leica Sprinter 150) used to work in technical levelling.
For reasons of failure to material detarioration have occurred to many premature or sudden failure of building structures. The quality of the design, execution and maintenance of building structures is a serious problem in the present. The paper presents probabilistic models of concrete deterioration that cause depassivation of reinforcement.
Forestry and forest management plays many roles in the landscape and in the socio-economic area. Forests represent a landscape stabilizer, the best preserved part of the landscape of predominantly natural character with significant application of natural, spontaneous process. It also serves as a source of material benefits to human society. The wood-producing function of forests was questuioned in this country in recent years. Above all, leaders of various environmentalist movement are demanding ever greater proportion of forests without economic activity. However, forestry is afflicted by such influences by decades and the aim of this paper is to demonstrate possible implications of these trends for forestry and subsequent economic sectors.
Building Act (Act. No. 183/2006 Coll.) in its regulations frequently uses the term of built up area, particularly in the context of built up area of building (hereinafter referred to as “built up area”). Correct determination of built up area is highly significant. Unfortunately, the Building Act did not contain a definition and a method of determining the built up area.
On January 1, 2013 came into effect an extensive amendment of the Building Act (Act No. 350/2012 Coll.). The aim of a legislature was to bring clarity and to provide clear way to determine the built up area. This is defined in § 2 clause (7) of this Act. This definition is not considered unambiguous, though.
The aim of this paper is to analyze the regulations of the Building Act in detail and to find a probable way of correct determination of the built up area. All facts presented in this paper should be taken as the opinions of the authors and should not be considered as a binding interpretation of the law, which is due only to the independent court.
Setting out and control of a vertical direction belong among often solved tasks in civil engineering. In order to setting out a plumb line the optical plumbing instruments are used. The most commonly used instrument for this activity is Zeiss PZL (Zeiss Zenitholt PZL 100). This contribution describes the procedure and results of testing according to STN ISO 17123-7: 2010 Optics and optical instruments – Field procedures for testing geodetic and surveying instruments. Part 7: Optical plumbing instruments.
In the second half of the last century the village changes in terms of demographics. First, the outhouses lose their importance, later, the living houses got empty. At best, the homesteads are used for weekend recreation. As a result of these changes, and due to improper construction impacts the houses dilapidate. There is material destruction and creation of static structural failure of the house.
zpět na aktuální články