The subject of this paper is a comparison of two experiments of timber-fibre concrete floors in fire, which consist of steel fibre reinforced concrete boards and glue-laminated timber beams. Main aim of this project is to assess the using of steel fibre reinforced concrete board, which work together with glue-laminated timber beams to increase fire resistance and investigate its behaviour in loaded construction.
Archiv článků od 26.6.2016 do 30.1.2017
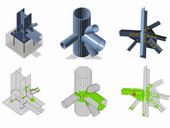
Steel frame structures are commonly analyzed three dimensionally by 1D elements. Connection of elements to joints is assumed to be perfectly rigid, nominally pinned or semi-rigid. The new CBFEM method allows to properly model the connection. The bending/deformation stiffness, resistance and deformation capacity of connections of individual members is evaluated. CBFEM model is loaded with appropriate internal forces obtained by global analysis. The article explains loading of a detailed 3D model of a joint. It also addresses situation where actual structural design of the joint does not match theoretical expectations of the global analysis.
The paper is focused on comparison of different types of compressive tests of samples exposed to high temperature. The tests could be divided into two basic types. The first type of the test is an ambient temperature testing to obtain residual compressive strengths and the second type is a hot state testing to obtain mechanical parameters of concrete exposed to high temperature.
The removal of unwanted material from the surface of historical artefacts is one of the most important and also the most delicate operations in the restoration of cultural heritage. In the Center for innovations in the field of nanomaterials and nanotechnologies a novel design concept of the cleaning microemulsions was developed based on a combination of the two functions, implemented by two components, namely a micellar solution or microemulsion of nonionic surfactants with the addition of co-surfactants and the specific solvents, which are selected according to the respective substances to be removed. The patented cleaning compositions can very effectively and selectively remove coatings of many substances important for the restoration practice, such as waxes, resins (e.g, Damara), paraffins, oils, water acrylate dispersions, hydrophobization coatings (both monomeric and polymeric) etc. Besides the efficient cleaning, the developed procedures have wider applications, such as in a new method of the hydrophobization of sandstone and limestone materials with a thin hydrophilic surface layer, which has been certified by the Ministry of Culture of the Czech Republic.
Non-aqueous dispersions of nanoparticles of calcium hydroxide and magnesium are principally suitable means for the consolidation of wall paintings and limestone materials because they are compatible with the material of historical artefacts. They are also suitable for the deacidification of paper and wood. In the Center for innovations in the field of nanomaterials and nanotechnologies procedures were developed which provide nanoparticles of calcium hydroxide and magnesium ranging in size from about 10 nm to about 200 nm. The procedures are relatively experimentally challenging and put them into practice will require further technological research. Thanks to the good stability of the dispersion a sufficiently long shelf life is ensured and premature aggregation on the surface or just below the surface of treated materials is prevented. There are several alternative methods of the consolidation stone, as exemplified by the use of alkoxides of calcium or magnesium. In converting the alkoxide to calcium carbonate, the sole by-product is alcohol, which naturally evaporates from the stone.
The paper introduces selected parts of the methodology for the technical state evaluation of the steel cylindrical tanks affected by the corrosion weakening. Technical conditions have been mainly worked out for the energetic company experts who are responsible for the realization and evaluation of the steel tanks diagnostics. Simplified analytical procedures have been developed to evaluate the influence of the measured corrosion weakening on the reliability of steel tank structures. The technical conditions serve mainly for a decision about the relevance of the corrosion damage: the corrosion weakening is insignificant with respect to the structural reliability or the corrosion failures are potentially dangerous with respect to the structural reliability and a detailed statistical assessment of the steel tank is necessary.
For rational design of concrete structures, it is necessary to take into account all types of loads to which the structure is exposed during the execution, operation and reconstruction. Biogas tanks belong to the group of constructions where the indirect and environmental loads represent a high risk to the reliability, particularly in terms of their serviceability and durability. The article analyses the effects of these loads as well as the causes of separation cracks formation.
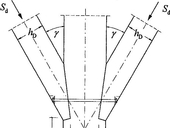
The paper introduces modified arrangement of the test in axial tension for cement composites. Specific shape of the specimen and special steel grips to fix the specimen in testing machine are described. The arrangement of the test enables recording of the load-deformation diagram in the central part of the specimen and direct derivation of the stress-strain diagram.
The floor system structure HURDIS is composed of a steel beam, of floor ceramic elements and of concrete. There are materials with different behavior in fire exposition. The paper deals with the analysis of the behavior of individual elements of floor structures affected by high temperatures. Knowledge is applied to the example of the assessment of the floor structure of the storehouses damaged by fire.
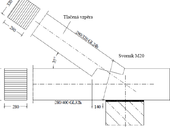
Checking the inner shell of tunnels during the construction phase as well as of existing tunnels is importand for their safe operation. Various non-destructive methods have been developed for this, which allow the control check to be carried out with experiences which were obtained using the new device, pased on an ultrasonic pulse echo method.
During the assessment of existing structures of monuments made from reinforced concrete is always necessary to verify the properties of concrete and placement of reinforcement. The paper deals with testing of concrete by non-destructive methods – especially by hardness test method and ultrasonic method. For testing of historical structures seems to be the most suitable ultrasonic method.
The aim of this article is to compare 3D numerical models of traditional timber joint. Numerical model of the subjected carpentry joint includes material nonlinearities. Material model of wood presume elasto-plastic behaviour and has orthotropic – transversal isotropic property. The finite-element meshes introduced herein differ one from other by element type and their quantity applied, type of mapping and local density of mesh. Number of nodes and elements, calculation convergence speed, FEM solution exactness, symmetry and mapping of elements are observed.
Building materials contains natural radionuclides, which comes from the earth's crust. In using secondary energy products as raw materials for production of building materials can increase the content natural radionuclides of products. This study focused on practical verification procedures proposed of radiation protection to optimize radioactivity of building materials. It measured the content of natural radionuclides in feedstocks and in final concrete mixtures. Measured values of natural radionuclides of concretes were compared with theoretical calculations.
This thesis deals with the water vapor permeability of wood for the most commonly used types of wood for construction work - Norway spruce (Picea Abies). Diffusion of water vapor is solved according to the density of the material, which varies depending on climatic conditions tree growth. These different conditions are in the Czech Republic mainly characterized by different altitude growing zones. Water vapor permeability is solved in the thesis by a method of measuring the diffusion resistance of materials. Specifically, the method of wet cup and dry cup, which is carried out using EN ISO 12572 knowledge and advices of previous researchers of that method. The results were compared with values reported in the Czech standard and later used for construction project of the typical timbered buildings with respect to contemporary legislation.
Presented text discusses the use of RPAS (Remotely Piloted Aerial System) in the building industry and heritage preservation. It provides information of various case studies and shows examples. For the purposes of building industry and technological area monitoring multicopter systems are mainly used. They have more complex control, but they can be successfully navigated in very low heights and low speeds around and above the object. Safe handling and ensuring the area after agreement with the owner or facility manager is crucial for their use.
Presented text discusses RPAS (Remotely Piloted Aerial System) in terms of history, legislation and its possible use especially in the civil sector. RPAS, often called UAV / UAS or “drones” in slang are a phenomenon of recent years. They present modern and popular technology that has undergone an unprecedented boom thanks to miniaturization of electronics, control and navigation equipment, high-performance battery development as well as individual components now available for affordable prices. Safe manipulation and current limits of applicability are indispensable and must be taken into account.
zpět na aktuální články