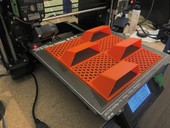
The paper discusses additive manufacturing in the building industry in terms of definition of terminology, application technology, machinery and materials to be used. It gives examples of executed buildings and discusses the possibilities of using natural materials for 3D printing of buildings. Current research and future prospects in the field of additive manufacturing are presented. The paper was created within the framework of specific research at the Faculty of Architecture of Brno University of Technology, where the possibilities of 3D printing from natural materials will be further analyzed.
Archiv článků od 8.8.2021 do 6.12.2021
Mobile laser scanning (MLS) is currently commonly used in many surveying applications. The refinement of MLS point clouds is usually done by increasing the number of control points (CP) equally distributed within the mapped area. The accuracy of point clouds can also be improved by multiple passes of the mobile mapping system (MMS). This paper deals with the proposal of a suitable procedure by which it would be possible to remove local deformations of MLS point clouds. The proposed approach is based on the comparison of point clouds from multiple MMS passes. Additional CPs are then added to the places where the more significant differences between the point clouds.
There are situations when it is necessary to determine the state of prestressing at a specific time on existing structures. In these cases, it is possible to use indirect methods for determining the state of prestressing. These methods consist of the observation of selected quantities on the investigated structure. Subsequently, based on obtained results it is possible to analytically calculate the actual state of prestressing. The observed quantities include e.g., strain, deformations, crack width etc. This paper presents an overview of possible indirect methods for determining the prestressing in the structure.
This paper deals with the possibilities of using modern measurement methods and technologies, i.e. ground-based laser scanning (TLS) and Image Based Modeling and Rendering (IBMR), Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Building Information Modeling (BIM) for processing, distribution and archiving of data collected during the Building Archaeology Survey (BAS). The paper tries to briefly summarize the current state of the author's knowledge and his practical experience with the issue.
The paper deals with the determination of strength characteristics of masonry composite. The MQI strategy, published by the staff of the University of Perugia, is presented. The calculation is based on a certain value analysis of several parameters, based on which the MQI masonry index is calculated. The index is then calibrated so that the strength characteristics of the masonry according to the new Italian standards can be determined from its value.
Modern composite materials are increasingly used in construction. One example is textile reinforced concrete (TRC), consisting of high-quality concrete and non-metallic reinforcing materials, most often in technical textiles. The current use of TRC is mainly in non-loadbearing structures such as facade panels and design elements. However, due to the excellent mechanical properties of TRC, it is possible to design subtle structures with high load-bearing capacity. Therefore, this material has a high potential in load-bearing structures. Consequently, it is necessary to comprehensively assess these materials in terms of load-bearing capacity at normal and elevated temperatures. For this reason, within the Faculty of Civil Engineering CTU in Prague and UCEEB CTU in Prague, research teams deal with the development and material research of TRC for use in load-bearing structures, including evaluation of its possible application in construction.
The aim of this paper is the modal analysis of a thin technical textile in shape of hyperbolic paraboloid. It is the geometrically nonlinear membrane structure, which can function only in tension. In this case, the structure was subjected to the natural vibration as a part of the overall dynamic analysis. All of this results in natural frequencies and mode shapes and deflections. Acquired results describe the dynamic behaviour of nonlinear system without affect of the external load. This part could represent a first step in the dynamic analysis and exactly the forced vibration as nonlinear time history analysis will have to be performed in a future to complete it.
The aim of this study is to find the dependence between the span and cross section area and other choose parameters of the timber-concrete composite beams. For analysis, we used coniferous wood C24 category and concrete C25/30 and C30/37 class with 50 mm thickness. We set the SFS Intec coupling elements. For calculation was used linear elasticity design method. Pliability of composite was take into account per γ-coefficient (γ-method).
As of 1st January 2021, an amendment to the Property Valuation Act and an amendment to the Valuation Decree also entered into force. With the amendment of these valuation regulations, there were fundamental changes in the valuation of easements. In this paper, we deal with the introduction of the new wording of these regulations concerning the valuation of easements and also the individual types of prices at which easements can be valued.
Good, well-functioning infrastructure signifies a well-run national economy and the overall state of development of the whole society. Buildings, bridges, roads, and other structures need to be regularly maintained if they are to last. In general, if a defect is detected early, the cost of its remediation is typically much lower than if it the structure is allowed to degrade for months or years. Early defect detection often means detecting one before it is visible to the naked eye. A key means of locating hidden defects are non-destructive testing methods. The article describes selected non-destructive methods that can be used in the diagnosis of bridge structures.
The article presents the results of experiments of reinforced concrete walls with an opening, which have been tested for load carrying capacity in the diagonal direction. These are the walls that represent shear walls in multistorey precast concrete frame structures. The influence of various types of reinforcement on their load carrying capacity and deformation is studied on the designed walls. The data obtained by the experiment is then validated by computational models that represent the behavior of the samples during the experiment. The results of the models are compared between each other and pros and cons are assessed.
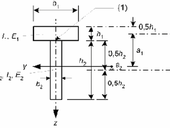
The paper presents the outputs of a computational parametric study investigating the influence of both reinforcement ratio and scheme of a cross-section reinforcement on a design value of the elastic module for the homogenized cross-section and the values of the stress redistribution coefficients. The design value of the elastic module represents the steel-concrete cross section in the calculations. The stress redistribution coefficients converts the state stress in the homogenized cross-section for the state stress in steel and concrete individually. The design value of the homogenized cross-section elastic module and the stress redistribution coefficients are determined from the theory of the cooperating rings and are computed by program HOMO. The result of a study is a set of the stress redistribution coefficients and a dependency of stress redistribution coefficients on the reinforcement ratio of a steel-concrete section.
Every element must meet design requirements for using structures in buildings. One of the requirements is the fire resistance. The required properties are presented in standards and laws according to type and way of using the building. The fulfilment of requirements is declared by resistance to fire classification report. This can be done in several ways. One of them are the fire tests. The article is focused on testing of fire resistance of structures in buildings.
The paper exposes knowledge referring a correspondence of stress states in the cross-section of steel concrete lining. The two different theories size the stress states. The first a theory of cooperating rings is pursued at department of geotechnics. The second referential is a reinforced concrete theory in use at building construction habitually. The correspondence targets the evaluation of suitability and the working condition of a cooperating rings theory to state the stress in the cross-section of steel concrete lining. An investigation was work out on a steel concrete section having been endorsing by lattice girder.
3D printing technology has contribution in building automatization. Today, printed buildings for everyday usage already exist. 3D printers movements are controlled by G-code. These buildings are described geometrically and then it's transformed in G-code by postprocessor. That one for building printing must respect the properties of printing mixtures. This work designs new postprocessor for building printing. It must include mathematical model of material according to which G-code for specific building geometry will be generated. In the work are proposed experiments to find out parameters for mathematical material model.
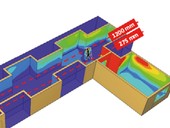
Fire safety assessment of a building is a process in which it is necessary to take into account a number of technical requirements and aspects prescribed by Czech legislation and technical standards. The requirements based on these documents are binding and form specific requirements for buildings and their solutions, which must be taken into account in the design phase of the project, both in its construction and in the technological part. As part of the fire safety assessment, the regulations allow for the possibility of using two basic design approaches, namely the standard approach and the engineering approach. The following work presents selected examples of the application of the engineering approach (specifically using the FEM and CFD methods) for fire safety solutions in comparison with the values obtained by the classical standard approach.
Fibre reinforcing of the soils is one of the methods used for improving the properties of the soils. The many research papers were interested in the fibre reinforcing however, used fibres were straight with smooth surface usually. These properties may not ensure sufficient interaction between soil aggregates and fibres. This disadvantage could eliminate by modification of shape or surface of each fibre and achieve a higher strength of the soil-fibre composite. In this paper is present the soil reinforcing by fibres manufactured by 3D printer. The fibres with the various shapes were made and tested. In the case of the modified fibres, the higher peak strength of the composite occurred.
This article examines the process for the synthesis of forsterite–spinel refractory ceramics from different raw materials. Raw materials were milled, mixed in different ratios and sintered at 1500 °C for 2 h. Sintered samples were characterized by XRD and SEM. Porosity, water absorption, bulk density, refractoriness, refractoriness under load and thermal shock resistance were also investigated. The impact of different raw material mixtures was investigated in accordance with the resulting properties and microstructure of all fired samples. Presence of spinel in fired samples led to improved microstructural and mechanical properties and thermal shock resistance. In particular, mixtures with 10–20 % of spinel had the most promising results.
The article describes the development of a prototype vegetation facade panel using parametric modelling. Parametric modelling was then most used for the design of individual parts of the panel, especially the visual part of the panel, which consists of a mathematically generated mesh, and also to create a supporting structure for vegetation. The production of individual prototypes of panels, their parts and components was performed with the help of FDM 3D printing. Individual prototypes were further subjected to testing in real conditions to verify the functionality of the proposed prototype and to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the panel, which will be used for further development.
zpět na aktuální články