A responsible approach to the environment is not only related to corporate ecology, but is also increasingly reflected in the design and construction of buildings, which is closely related to the concept of sustainable construction of buildings. With the development of sustainable construction, the need arose to evaluate buildings and their impact on the environment. For this reason, environmental certifications of buildings have been developed, which assess how a building affects its surroundings during its life cycle.
The aim of this article is to find out which environmental certifications exist in the world and which of them are most often used in the Czech Republic. Finally, the certifications are compared and their main differences are described.
Archiv článků od 25.1.2021 do 30.4.2021
Increased stresses occur near the supports of glass structures, which can be decisive for design of glass member. Recommendations for minimum distance of bolted connection from the edge can be found in current standarts. For verification of details are used FE-models. Influence of the edge distance and material thickness on the maximum stress value at the edge of the hole in glass loaded in its plane is compared in this paper.
This article deals with the possibility of using masonry aggregate from construction and demolition waste. The article summarizes the properties of concrete with a laboratory-optimized recipe with a full replacement of natural aggregate with recycled masonry aggregate. Testing of concrete samples was carried out according to valid standards. The result is a mixture with optimized properties for the production of construction parts.
Very quick process of digitalization in civil engineering is progressing also in the branch of geotechnical engineering. BIM is a part of this process. Mutual interconnection of the 3D model of ground with the 3D model of the geotechnical structure can help to give more clear view on the interaction of this structure with ground. However, at the same time it makes possible better control for all participants of the construction process, particularly if all conditions of this mutual interaction are fulfilled. Whether the main aim of the construction process – that the care devoted to the individual phases of the structure design and execution correspond to the risk with which this structure and ground are connected. Within this context a closer specification of the Eurocode 7 of the second generation will be specified, as it counts with different models.
Internal erosion is one of the most common causes of failure of hydraulic structures. A special case is a backward erosion piping during which an exceeding of critical hydraulic gradient occurs on the edge of the structure foundation interface. This becomes especially dangerous for the structure when the foundation consists of sand or very sandy soil that is very easy to erode. The sand property of erodibility is not yet fully described. In this paper, an experimental device used for the rate of erosion determination for a picked sand is presented as well as a calculation of the erosion coefficient which is usually used to describe soil erodibility. Furthermore, the paper contains critical hydraulic gradients during which the erosion occurred.
This task deals with the properties and the possibility of recycling of thermal insulation materials such as polystyrene and mineral wool, not only from buildings after demolition but also from discarded materials left over after the construction of new buildings. This newly developed material is being tested as a filler for ultra-lightweight concrete where it fills the cavities of ceramic hollow bricks, as a filler for self-compacting concrete (SCC) and for the production of acoustic facing.
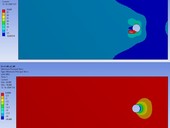
The paper offers an overview of the performed analyses, which evaluated the leakage into underground garages in the densely built-up area of the Prague city centre. Only after a comprehensive reassessment of geological conditions, the project and other available information was it possible to determine the probable causes of leakage into large underground parking spaces.
The aim of the paper is to summarize and evaluate individual diagnostic procedures that diagnose reinforced concrete structures damaged by fire. Based on our experience, we tried to design a methodology for the selection and use of individual diagnostic methods and procedures. Knowledge of the objective state construction after a fire is the basis for determining the procedure of its subsequent remediation.
The Helmholtz resonator is one of the most widely used low and medium frequency attenuation acoustic absorbers. While commercial products usually offer efficiency across almost the entire spectrum under consideration, in many cases only the specific natural resonance of the room needs to be suppressed. In such cases, it is necessary to proceed with your own design. This paper presents one of the possibilities of calculating a perforated resonator using the electro-acoustic analogy and the transfer matrix method. This method is not demanding on computing power, but nevertheless it is rarely used in current building-acoustic practice. This paper focuses on the comparison of the calculation of the sound absorption coefficient by this method with the data measured in the reverberation room.
The paper deals with the energy balance of windows for different combination of glazing parameters in connection with their orientation. Sum of solar gains through the transparent surfaces of a building envelope depends mainly on the size, their orientation and the g-value. Large glazed surfaces with correct orientation ensure large solar gains, but they are also the weakest part of the thermal isulating building envelope.
The influences of various U-value (Ug) and g-value of glazing on the energy performance of selected passive house were calculated by the use of computer simulation.
The European standard ČSN EN 17037 Daylighting of buildings has been valid in the Czech Republic since August 2019. A year and a half is enough time for the first evaluation of its functioning in project practice. The author of the article deals intensively with this practice and in this paper he would like to share some of his findings concerning the assessment of solar exposure of buildings according to this new European standard. On the edge of this problem, the relationship between accuracy and uniformity in normative requirements is also discussed.
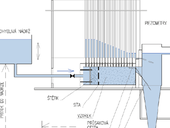
The subject of the complex repair of the ceiling structure of the water reservoir Pasohlávky was the remediation and static provision of the unsatisfactory reinforced concrete structure. The original condition was inadequate, parts of the concrete structure were dropped due to steel due to steel corrosion and small cover layers of concrete.
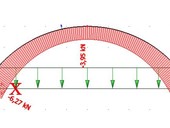
The article presents a stability analysis of circular arches under various uniform loadings (vertical to the arch plan, vertical to the arch length or radial to the arch axis). Linear bifurcation analysis resulted into critical loadings used for determination of the arches buckling length factors. With the exception of the radial loading the variable axial arch forces need to be taken into account also for the relative Euler basic strut. The analysis covers various boundary conditions of the arches in supports. The study embodies arches with both closed and open cross sections and proved the significant impact of the cross-sectional shape on out-of-plane buckling values. The article outcomes are tables with correct buckling length factors of arches.
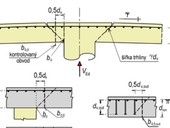
This paper deals with new methodology of design and verification of the limit state of punching of ceiling slabs in the prepared prEN 1992-1-1 [2]. The current methodology does not described with sufficient accurancy and with sufficient reliability the behavieur of the slabs structures in the area of supporting on columns and on ends and corners of walls.
Example of rehabilitation of sewerage facilities, shafts and chambers in an environment of the historic city center with increased loads of chemical-biogenic corrosion. Possible causes and consequences for both, original and newly constructed, building structures. Modification of the proposed solution, including the design of an appropriate construction structure and installation technology solution.
The circular economy in construction is currently absolutely essential in the context of limited primary resources. This applies in particular to the use of inert mineral materials created during the demolition of buildings. It is proven that in the period from 2011 to 2018, the share of recyclates from C&DW in the total production of inert mineral materials more than tripled. One of the barriers to higher production of recycled aggregates is the low level of demolition of buildings, which often makes it impossible to carry out quality recycling.
The paper deals with the new Czech standard ČSN 731004 Geotechnical Design – Foundations, Requirements for calculation methods, published in July 2020. The subject of this standard ase simple calculation methods for the design of foundation structures based mostly on conventional analytical methods validated by long-term use not only in the Czech Republic. The standard applies to flat foundation structures, bored piles and displacement piles, micropiles and jet-grouted columns for axial loading. The standard is primarily intended for structures falling under 2. geotechnical category.
The paper is focused on the current issues of protection and strengthening of wooden structures. The wood used for them is a construction material whose mechanical properties are shaped by the nature and because it is also an organic material, it is subjected to various degradation processes. Types of wood protection includes all measures which would protect wood from influences of fungi, insect, weather (temperature, humidity, wind, fire etc.) and can be divided into chemical protection and radiation protection. Chemical protection can be further divided into protection against weather, biological pests and against fire. In our paper the solution of this weakness by photocatalytic materials (namely TiO2) is presented. Those materials are efficient UV absorbers and they are able to destroy biological aggressors as well. Nowadays, there is not enough information about the interactions between wooden surface and non-photoactive or photoactive form of TiO2. TiO2 exists in many morphological forms. The planar particles were chosen for purpose of the experimental investigation. This material was applied on wooden surface for creating a transparent layer. The results are presented in the first part of the paper. If it is necessary to increase the load-bearing capacity of wooden elements, one of the possibilities is to strengthen them by applying a high-strength layer containing carbon fibers. The second part of the paper is devoted to this procedure with a detailed description of how to implement and design this reinforcement.
The paper describes special types of fiber optic point sensors based on FBG (Fiber Bragg Grating) and FP (Fabry-Perót) structures. First part of the paper deals with principle of FBG and FP and their exposition. Next part is focused on different types of FBG and FP sensors and principle of interrogation units. Finally practical examples of use are listed.
zpět na aktuální články