The paper deals with special types of sensors that use optical fibers to measure various non-electrical quantities. The introduction describes the principle of light transmission in optical fibers and their applications. Main part is focused on fiber-optic sensors and their dividing. Special attention is paid to the distribution sensory systems and their practical application.
Archiv článků od 19.10.2020 do 20.1.2021
This article deals with the properties of recycled concrete aggregate (RCA) from two-phase recycling. Specifically, it is the 8–16 mm fraction, which is already commonly used in practice in compliance with standard requirements, the 4–8 mm fraction, the use of which is problematic from the point of view of standard regulations. The article focuses mainly on the key properties of RCA that affect the design of concrete mixtures.
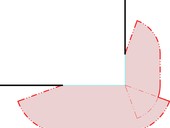
Fire separation distance is an area around a building where a risk of a fire spread to another building due to radiation is imminent. The article deals with the separation distances of corner window. Is It describes several methods of assessing, from using prescriptive methods of Czech legislation to CFD numerical simulations, and it also presents the limitations of particular methods. Finally, the method of corner window fire separation distance is proposed.
The increasing amount of construction and demolition waste is gaining the attention of research institutes that deal with the possibilities of using this waste. This article deals with the possibility of using masonry aggregate from construction and demolition waste in concrete samples. The most important are the properties of the aggregate as follows a suitable concrete recipe optimization with various number of replacements of natural aggregates with recycled masonry aggregates. The experiments in this paper are summarized in two categories - geometric and physical experiments.
This contribution deals with damage to buildings and building materials due to bad manage of rainwater regime. Effects are divided according to location of damage. First, the damage of roofs and roof trusses is presented, which are followed by examples of damage to the enclosure walls. The most attention, including numerical 3D modeling, is devoted to damage to foundation structures and foundations.
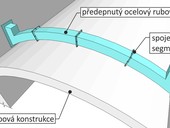
Many historic buildings are located in areas where there is a specific type of earthquake activity, the so-called earthquake swarms, during which a series of thousands of weaker tremors take place for several days or months. Sometimes these shocks are strong enough to be felt by people, and in some cases they can even cause material damage to buildings. Knowledge of the response, especially of vaulted structures of historic buildings to dynamic loads, is the basis of remediation interventions on monumental buildings exposed to these effects. Due to the increasing intensity of wheel and rail traffic, there is also an increase in the effects of the so-called technical seismicity on structures located near roads and tracks. The proposed system of additional stiffening of barrel, cross or of spherical vaults by means of prestressed flexurally rigid segmental ribs contributes to the increase of their resistance to the natural and anthropogenic dynamic effects.
Panels for openings in structures have always been an essential and integral part of buildings. Their importance in terms of a building´s functionality was not recognised. However, the general view on this issue has changed from focusing on big planar segments and critical details to sub-elements of these structures. This does not only focus on the forms of connecting joints but also on the supporting systems that keep the panels in the right position and ensure they function properly. One of the most strained segments is the threshold structure, especially the entrance door threshold structure. It is the part where substantial defects in construction occur in terms of waterproofing, as well as in the static, thermal and technical functions thereof. In conventional buildings, this problem is solved by pulling the floor structure under the entrance door structure and subsequently covering it with waterproofing material. This system cannot work effectively over the long term so local defects occur. A proposal is put forward to solve this problem by installing a sub-threshold door coupler made of composite materials. The coupler is designed so that its variability complies with the required parameters for most door structures on the European market.
Within the research project NAKI DG16P02M055, an extensive experimental and theoretical research of the influence of grouting on the physical and mechanical properties of brick and stone masonry is carried out. The focus of the research is to verify, in particular, the strengthening effect of selected grouting mixtures based on hydraulic lime (nano-lime), resins and silicates. The influence of grouting on the change of porosity, pore distribution, absorptivity and strengthening effect of grouting of historical brick, marl, sandstone, trachyte, limestone and mixed masonry with lime binder using various types of grouting mixtures in comparison with ungrouted masonry is evaluated. Particular attention is paid to the masonry damaged by cracks and cavities.
Development of the second generation of Eurocodes for climatic actions in the framework of the technical subcommittee CEN/TC250/SC1 is nearly finished. Revised Eurocodes should be more transparent, user-friendly and provide information about the basis of climatic actions and their effects on structures. National selection of the National Determined Parameters is expected to be given in the National Annexes including updated climatic maps.
Many structural concrete elements of dams must withstand extreme frost stress and abrasion of fast-flowing water. At present, several reconstructions of concrete overflows, chutes of dams or weirs are underway or have already taken place with the requirement for increased resistance to abrasion. From the point of view of ČSN EN 206, abrasion-resistant concretes are determined by exposure class XM, but the evaluation criteria and testing methods are insufficient. The article deals with a closer presentation of the requirements for the properties and development of concrete with high resistance to abrasion and frost and its subsequent testing.
The benefits of BIM are discussed at almost all the conferences concerning the construction industry. Better quality project documentation is one of the most often referred assets of projects modelled in BIM. Unfortunately, it is not clear whether this benefit was realised in the projects or not. So, there raise following questions:
- How exactly was the declared better quality measured?
- What exactly is meant by the better quality documentation in practise?
- How can a contracting authority assess the quality of the project data processed by BIM models?
This article will try to answer all these questions and introduce the reader into the elementary principles of the quality measurability of the project information.
The article is intended for all clients (contracting authorities) who would like to choose a quality BIM contractor for their future project. It is based on the experience of implemented tenders (small-scale public contracts) and procurement procedures pursuant to Act No. 134/2016 Coll. on Public Procurement, as amended (“PP”). The article is an introduction to the system of qualitatively oriented selection of the BIM model contractor and related outputs – i.e. 2D drawing, quantity take-off, etc. This article applies to the Czech law.
This paper deals with the test results of shear characteristics of thermal insulation boards based on MW with longitudinal orientation of fibres of thickness 200 mm and more according to ČSN EN 13162+A1, documents serious faults in test procedure according to current ČSN EN 12090, reasons included, and proposes possible way of their solution.
The paper deals with the issue of emerging defects and failures in the construction of industrial floors in relation to concrete technology. The effects of deficiencies in concrete recipes on the occurrence of defects or failures are described, as well as the effects of treatment of the finished structure, laying of concrete and methods of its compaction.
In the expert business, the usual requirement is to find a possible fault, its cause and a proposal for how to eliminate it. More and more often, however, in expert practice I encounter the requirement to simultaneously assess the current state of the flat roof and especially the waterproofing layer and comment on its possible further functionality and durability.
There are many factors affecting the internal fire. The important thing is the dimension and the geometry of space, the existence of openings, accidental, and still fire load and other. In large-space objects, to design structures under the fire load often proceeds through a performance-based approach. Advanced methods can be used in all parts of the design - in predicting of the scatter of temperature field, in calculating of the heat transfer to the structure and in assessing of the mechanical behavior of the structure or its part under the fire load. The prediction of the gas temperature in the fire compartment is crucial for the structure design. The paper describes the worst fire scenario in the large-space building. The problem is solved by using FDS (Fire Dynamics Simulator).
The present paper deals with the assessment of several realized construction details within the renewed flat roof of the multifunctional building. The new roof structure has the composition of a single-layer flat roof with a classic order of layers, which is mounted on the original roof structure. The problematic details are closely related to the incorrect realization of the waterproof membrane and its fitting to the individual building structures within the detail. Individual factors play a significant role in the assessment: absence of additional elements (cover and anchor strips), improper drainage of rainwater from the roof surface and improper handling of accessories within the waterproof membrane. The assessment of the individual details revealed significant shortcomings that can cause rainwater penetration into the roof structure and thus endanger the reliability and durability of the roof.
The article presents the possibilities of computational estimates of selected characteristics of fires of accidentally escaping gases and liquids, namely jet fires, instant fires (flashes), pool fires and fireballs. It divides fire and explosion models into empirical, phenomenological and CFD with examples of specific types of available models and categorization of buildings according to standard classes of consequences. Finally, the importance of these calculations for the quantitative assessment of the risks of explosions and subsequent fires is emphasized.
This paper deals with the content of prepared review of ČSN 73 2902:2020 External thermal insulating composite systems (ETICS) – Design and application of mechanical fastening for fixing of ETICS in the base material. It specifies modifications made in content of standard and in particular the addition of new provisions for correct assessment of the stability of the ETICS.
zpět na aktuální články