The concept of sustainable development is becoming increasingly popular worldwide. The intensive debate on sustainability issues in the construction industry has led to the development and implementation of various systems for defining and assessing the sustainability of buildings around the world. Concrete is one of the most important and useful materials in the construction sector, which, unfortunately, has an adverse impact on the environment, it is evident that correct procedures for designing concrete structures need to be created. In this paper is an indicator expressing quality, with regard to sustainability, is determined using information on concrete performance characteristics, service life and environmental impact, enabling the quantification and comparison of various cases.
Archiv článků od 6.1.2020 do 22.5.2020
The present paper deals with the measurement of the thickness of the coating on wood using the ultrasonic method, which is based on the measurement of the ultrasonic pulse passage time through the layer. One of the biggest advantages of this method is non-destructive measurement, which allows online quality control during operation, eg when checking paint thickness on window or door frames. During the experiment, the deviations of the coating thickness measured by the destructive and non-destructive method were recorded, however, these deviations were in most cases smaller than the inaccuracy of the optical microscope measurements. The results clearly showed that the accuracy of the described method is sufficient and can therefore be used to measure the thickness of the coating on porous and diamagnetic materials such as wood.
The newly developed jointing grout is designed not only for normal conditions, but also for environments with higher chemical stress. For this reason, one of the key endpoints was also a chemical resistance of the grout. The jointing grout is based on a polymer basis, in particular with epoxide binder used, and also hazardous wastes are used as fillers. As is well known, the epoxy thermosets are very resistant to inorganic acid solutions. However, they can be easily degraded by the action of organic solutions. Within this fact, the aggressive environments and their concentrations were selected and their influence on the developed grout was assessed. Specifically, the effect of action of 60% sulfuric acid, then the influence of the action of vapours of this acid (at a concentration of 96%) and immersion of 10% acetic acid solution were assessed. After exposure to these aggressive substances, the visual changes of the samples were assessed primarily. Colour change, blistering, cracking, flocculation, gloss change, etc. were monitoring. The influence on microstructure, change of bulk density and flexural and compressive strength of the polymer jointing grout materials was studied.
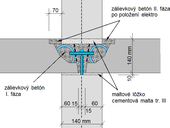
White tanks are structures which, in addition to the load-bearing function, must also have the function of watertightness. Watertight of the concrete is ensured by adherence to design, production and technological measures. The width of the early-age cracks that former in the structure is controlled by the reinforcement. During construction, however, joints (expansion, construction and control) are created in the structure, which must also be watertight. The joints are the most sensitive place of the white tank and therefore the most leaks are created at the point of the joints. The correct choice of the joint sealing system is the basis for the design of the watertight joint. The paper deals with the description of various joint seal and pipes through of the white tank.
One of the main characteristics in the concreting of massive, waterproof and dam structures is the prediction of crack formation. This prediction is connected with the understanding of mechanism hydratation temperatures development in concrete that affects in particular the selected parts of binder. Suitable combination of cement and mineral admixtures, as well as the usage of shrinkage reducing admixtures appears to be an effective tool for influencing the dynamics of development and maximum values of hydration temperatures. Appropriate selection of the concrete formulation can significantly extend the mentioned structures lifetime.
The article is focused to a monitoring of influence of different mineral admixtures on influence of volume changes of cement pastes. Furthermore, in this article was monitored connection between volume changes and hydratation temperatures development of cement pastes. With the target of minimalization both these phenomena were used shrinkage reducing admixture.
The elementary aim of the described research is to prove the necessity of creating an additional impermeable layer acting as moisture insulation of historical structures by means of undercutting technology. From a technological point of view and also based on known research, it is obvious that this technology is one of the most effective remediation methods. Unfortunately, the use of this technology is from the point of view of Regional Monuments Authorities, which, due to adherence to the uncompromising Venetian Charter, is considerably limited, because, despite considerable efficiency, this technology disrupts the integrity of historical vertical structures. The methodology of research into undercutting technology consists in verifying and demonstrating the effectiveness of this technology in various historical buildings and recording individual moisture values in situ before and after the implementation of the technology. The results measured in this way should objectively prove the necessity of using the technology of undercutting masonry as a remediation method of wet historical structures, provided that this does not compromise the statics of the object and this intervention is necessary.
The mass construction of apartment buildings using the technology of large-format prefabricated prefabricated elements in the former Czechoslovakia took about 40 years. The lifetime of these buildings is approaching their planned value. A common problem of prefabricated buildings is the creation of new openings in load-bearing structures without prior expert appreciation. The important details of the joints of the support elements have changed not only between the individual assemblies, but also during the development of the particular assembly. The article describes some problems of load-bearing structures of prefabricated buildings, which designers have to consider in their assessment.
This paper is a theoretical research of semi-rigid timber connections using modern fasteners Rothoblaas Alumidi. These connectors allow for semi-rigid behaviour. The aim of the research is the examination of the real behaviour of structural connections with real constants of rigidity. The rotational stiffness is calculated according to [1] and it is verified by the method of deflection of virtual bending moment. The results of the numerical calculation will be confronted with experimental verification of the connections. Concurrently with the experiment, the axial loaded grip nails will be examined in order to determine the value of slip modulus.
The construction of precast hous consists of prefabricated concrete walls and floor slabs. These elements through joints form rigid spatial (so-called box) load-bearing system. The prefbricated elements of this system were designed for certain layout and static possibilities of the panel system. All additional interventions in the load-bearing structure must be thoroughly investigated. If necessary, it is also necessary to propose a suitable way of strengthening the weakened parts of the load-bearing system.
This article is focused on current situation in preparation of new generation of European standard for design of concrete structures prEN 1992-1-1. This article deals with main features and development in design principles involved in new standard. In these days there is available the 4th draft of standard for comments of national authorities and experts. The final draft of prEN 1992-1-1 should be finished this year (2020) and provided to formal vote in CEN.
This is a case study of a multifamily residential building that has been environmentally assessed in terms of greenhouse gas (GHG) production using a simplified life cycle assessment (LCA) method. The results of total GHG emissions were compared to the emission limit value, which was set based on the climate objectives of the Paris Agreement and the scientific report The Emissions Gap Report. In response to the non-compliance with the emission limit, a number of emission-saving measures have been proposed and have been suitably designed into variants meeting the emission requirement.
The paper briefly specifies the possibilities of computational estimates of the magnitude of accidental leakage of gases and liquids from tanks, pipelines and equipment under pressure, the rate of evaporation of not boling liquid from a pool created by the discharge and adiabatic flashing vapor of liquefied gas during its discharge into the environment. It presents three examples of these calculations using SW Excel. The seriousness of the issue is demonstrated by the selection of statistics on fires and explosions in the Czech Republic for the period 2017–2018 and by a picture of a prefab house in Prešov after the gas explosion in December 2019, which attracted a lot of attention from the general public. With regard to the growth trends of production and consumption of dangerous chemicals and preparations in the world, EU and the Czech Republic, the conclusion of the article emphasizes the need for further development of preventive measures to prevent accidents, including methods of risk analysis.
This is a case study of a multifamily residential building that has been environmentally assessed in terms of greenhouse gas (GHG) production using a simplified life cycle assessment (LCA) method. The results of total GHG emissions were compared to the emission limit value, which was set based on the climate objectives of the Paris Agreement and the scientific report The Emissions Gap Report. In response to the non-compliance with the emission limit, a number of emission-saving measures have been proposed and have been suitably designed into variants meeting the emission requirement.
Eurocodes EN 1991 for the basis of structural design and EN 1991 for actions, currently under development in the Technical Committee CEN/TC 250, should be more user-friendly in the 2nd generation of Eurocodes. They will provide basic design procedures, new types of actions and improved theoretical models which will be applied for the design of structures. For effective and economic implementation of 2nd gneration of Eurocodes into the systém of Czech standards, correct decision on National Determined Parameters is needed.
The article presents the basic criteria in the evaluation of structures of historical buildings. The whole procedure is described in detail in EN 13822, Annex I. The intention is also to provide additional guidance on the application of this International Standard for the construction of cultural heritage buildings. The instructions given here are to be followed in conjunction with all other clauses of the internationally applicable standard EN 13822 and other regulations.
The paper deals with the constructions from jet grouting (JG), which is one of the most modern methods of special geotechnical works. JG is the technique of mixing in-situ soil with the energy of high-pressure jet of slurry. The definitions and types of JG are given in the first part: single fluid, double fluid and triple fluid. The second part concerns JG implementation technology and also lists the necessary activities in designing and implementing JG elements and structures. In the third part, examples show the field of use of JG, including deep foundations, for which the example of static load test is given.
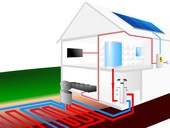
The issue of calculating summer overheating is less known in the field of civil engineers, although it is becoming more and more current. In the first part, the paper deals with current standard requirements in this area. The following is an example of computational programs. It further addresses the problem of climatic boundary conditions and other significant factors affecting the result of the calculation of summer overheating such as ventilation and internal heat gains. The second part of the paper will be devoted to the impact of the method of internal heat gains application on simulation results. The paper concludes with a model daily schedule of internal heat gains for the dwelling unit, created from the taken over actual statistical measurements.
Methods and instrumentation for injection quality measurement in heat pump boreholes including measurement of groundwater flow through the borehole outside the partly grouted borehole exchanger tubes have been developed in the Czech Republic. A Semtex charge has been developed for the rock massive repair, which reliably disconnects the ground exchanger tubes without serious impacts on the surrounding rock environment and buildings. The resulting hole can then be used for re-grouting, thus preventing undesirable vertical water flow through the borehole.
In this paper, the authors consider the aspects of routine procedure compared to the expert approach in solving construction defects and failures. For better orientation in the issue the basic terminology of defects and failures sphere is given. Also, the authors describe in details the course of both solutions, contemplate their specific aspects and point out their consequences. An essential part of the article is presentation of the potential benefits of the expert approach, the advantages of the expert approach are emphasized in the conclusion.
The paper discusses the importance of water absorption of traditional building materials and the ability of traditional non-insulated buildings to withstand rising damp. It also draws attention to some of the risks involved in reducing the water absorption of building materials designed for remediation of moisture and salts problems of traditional buildings.
zpět na aktuální články