This article explores the potential for rental housing in existing single-family home areas in the suburbs of Prague through soft densification. It opens a discussion on the possible incremental transformation of these unsustainable locations, responding to their circumstances, including the current housing affordability crisis and demographic aging of the population. The aim of the research is to quantify the spatial reserves in the built-up areas of municipalities that would allow for the development of housing units without the need to occupy new land. Through GIS analysis, more than 31,500 plots in 40 municipalities strongly affected by suburbanization were examined. The results show significant spatial reserves for the creation of additional housing units, either on the plots or inside family houses within their spatial reserves. The study confirms that the adaptation of the existing stock of family houses represents a significant and yet untapped source of housing units,that would lead to increasing population density, supporting social sustainability, and more efficient use of infrastructure in satellite municipalities.
Archiv článků od 29.8.2025 do 20.2.2026
The growing use of combustible façade materials and the expansion of multi-storey timber buildings increase the demand for effective passive fire protection. Façade fire barriers (fire belts) limit vertical fire spread, but their design in tall timber structures is challenged by non-combustibility requirements. The paper reviews European approaches and the Czech regulations, including Annex K of ČSN 73 0802 ed. 2 + A1 (2025), which permits DP2-type fire barriers for timber buildings above 12 m fire height. The Envilop Fire façade panel was experimentally assessed as a DP2 barrier in three medium-scale MiniFUR furnace tests under ISO 834 exposure. Timber-frame temperatures were monitored with a 350 °C limit, supported by visual evaluation. The DP1 reference panel passed. The first DP2 variant with a single lining failed due to unsealed joints causing local charring and smouldering, while the second variant with a double lining met all criteria. The results demonstrate DP2 barriers as a viable norm-compliant option for high-rise timber façades, provided that joints and detailing are properly executed.
Building with earth is gaining increasing attention, partly because there are many high-quality historical and contemporary earthen buildings in our country. Documenting the extent of the earthen building heritage has the potential to strengthen the perception of earthen construction as a valuable part of cultural heritage and as a promising tool for sustainable construction. This article presents the research framework, methodology, and starting points for the upcoming map output Historical Earthen Buildings in the Czech Republic, which aims to systematically map the occurrence, frequency, and typology of these structures.
The article presents research focused on a detailed analysis of cement-bonded particle boards modified with waste dust. This dust is produced during the grinding and cutting of cement-bonded particle boards. The emphasis was mainly placed on the behavior of boards with a modified composition with regard to their hygroscopicity and useful properties. The properties of three types of boards were analyzed – reference (Portland and blended cement) and dust-modified (filler and matrix – based on Portland and blended cement, substitution with waste dust in an amount of 8%). The boards were exposed to an environment with variable relative humidity (0% to 96%), with a gradient of increase and decrease of 10%. The output of this measurement is sorption curves. Subsequently, the mechanical properties (strength characteristics and modulus of elasticity) were tested on the test specimens. The obtained sorption isotherms confirmed the different behavior of individual composites in response to changes in ambient relative humidity. The results indicate that the composition of the mixture has a significant influence not only on sorption processes, but also on the stability of the wood filler itself, specifically spruce chips contained in the material. However, the behavior of the analyzed types of boards in terms of hygroscopicity is very similar. An increase in strength and modulus of elasticity was observed in all tested board variants. This finding is a positive sign for the further use of stabilized alternative raw materials in cement-bonded particle boards. The use of waste dust has significant potential to positively impact the environment, i.e., by consuming waste that would otherwise be a burden on the environment.
This article outlines the assessment and market placement of External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems (ETICS) in the Czech Republic and the EU. It compares national (STO) and European (ETA/EAD) procedures, focusing on manufacturers’ duties in quality management and conformity assessment. Key changes include the new EAD 040083-01-0404, the phase-out of ETAG 004, and the forthcoming harmonized standard EN 17237. Selected test methods—hygrothermal performance, water absorption, mechanical resistance, adhesion, and pull-through resistance of anchors are presented. The paper describes the role of certification bodies.
Recycling materials is an effective way to reduce the consumption of primary resources in construction. However, challenges arise when integrating recycled materials into construction products, primarily due to the variability of their quality, which can impact production processes. This paper explores the balance between recycling and decarbonization goals in the manufacturing of ceramic materials, examining both legislative pressures and environmental objectives. The paper emphasizes the need for optimized recycling strategies and innovative solutions that align with circular economy principles to meet sustainability targets in construction.
This paper deals with methods used for estimation of masonry moisture contens as part of building technical survey. General description comes from WTA 4-11 Recomendation and Czech standard CSN P 730610 “Waterproofing of buildings. Rehabilitation of damp masonry”. Different practise, used during survey, caused by unspecified procedures, is discussed. Also misinterpretation of measured values, caused by waterproofing and water repelent layers on masonry is being shown.
This article concludes a series of studies on the use of OSB claddings as passive fire protection for steel structures. Based on furnace experiments and numerical simulations (CFD and FE), OSB has been shown to significantly slow down steel heating and extend the time to reach critical temperature by up to 45 minutes. The summary highlights a paradoxical yet effective approach, where a combustible material provides protection through the formation of a char layer. The discussion addresses the main limitations, including cladding detachment, joint performance, and sensitivity to moisture. Practical applications are outlined with respect to current standards and fire codes. Finally, the article suggests directions for further research and the potential integration of wood-based materials into the normative framework as an alternative fire protection system.
The third part of the series focuses on numerical modeling of a steel beam protected by OSB cladding using the Finite Element (FE) method. The first stage involved thermal analysis, which described heat transfer in detail, included the material properties of OSB, and accounted for condition-dependent cladding detachment. The subsequent mechanical analysis, based on the thermal results, enabled assessment of deformations and load-bearing capacity of the steel member at elevated temperatures. Simulations were carried out in ANSYS Mechanical, showing good agreement with experimental data, particularly up to the moment of cladding failure. Deviations appeared in later stages, as the models did not incorporate viscoplastic steel behavior or explicit simulation of cladding failure. The study confirms that FEA modeling is a suitable tool for designing fire protection, but requires further development with advanced material models and dynamic failure simulation.
This review describes Phase Change Materials (PCMs) as an advanced solution for improving building energy efficiency and thermal comfort. It synthesizes insights into their evolution, categorization, and practical construction applications. It discusses PCMs history, operational principles, diverse typologies, and classification, including composite PCMs. It elucidates specific building applications, illustrating their integration based on recent research. The aim is to provide an overview of PCMs development and underscore their significance as a sustainable instrument for mitigating energy operating costs and elevating thermal comfort in contemporary construction. Concurrently, it delineates current obstacles and proposes strategic research directions, focusing on thermophysical property optimization, economic viability, and ecological sustainability.
Fire Protection of Steel by Timber and Wood-based Materials: Part 2 – Fire Experiment and CFD Models
The second part of the series presents a comprehensive approach to evaluating the effectiveness of OSB claddings as passive fire protection for steel beams. A large-scale furnace test demonstrated that OSB boards significantly delay steel heating until the moment of cladding failure. A single-layer cladding extended the time to critical temperature by about 17 minutes, while a double-layer system achieved up to 30 minutes. The main weakness of the system was identified at the panel joints, where premature failure occurred. A CFD model developed in FDS successfully reproduced the heating trend, especially for unprotected members and protected profiles up to the loss of cladding integrity. Deviations appeared only after cladding detachment, highlighting the need to incorporate mechanical failure into future models. The findings confirm the protective potential of OSB claddings and provide a foundation for developing design methods that account with cladding stability, joint-gaps, and time-dependent failure prediction.
This article addresses the issue of passive fire protection of steel structures using wood-based board materials, specifically OSB panels. Although steel is non-combustible, it rapidly loses its mechanical properties at temperatures above 400–600 °C and therefore requires effective fire protection. The study demonstrates that timber claddings, despite being combustible, can paradoxically slow down steel heating and extend load-bearing capacity due to the formation of a charred layer. In the experiment, beams with different OSB claddings were tested, showing that multi-layer systems can increase fire resistance by several tens of minutes. These findings were further validated by numerical modeling (CFD and FE analyses), enabling a detailed description of heat transfer, pyrolysis processes, and structural response. The study provides a methodological basis for the design and assessment of timber claddings as an alternative fire protection system for steel members, emphasizing safety, architectural integration, and sustainability.
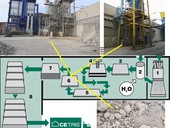
The paper focuses on the issue of returnable dust content generated during the production of hot asphalt mixtures in asphalt plants, which represents a long-standing unresolved problem in waste material management. It describes the current state of solutions to this issue, including an overview of legislative and technical requirements related to the utilization of returnable dust. The article deals with the specification of returnable dust quantities in individual narrow aggregate fractions and their potential usability. The next part includes verification of the applicability of returnable dust in cement mortar used for grouting layers partially stabilized with cement mortar. Laboratory tests were conducted to examine the mechanical properties of these mortar mixtures and their suitability for construction applications.
The second generation of the design standard, FprEN 1992-1-1:2023, allows for the use of fibre-reinforced polymer (FRP) reinforcement in structural concrete for the first time in Czech design practice. Reinforcement made of glass (GFRP) or carbon fibre (CFRP) is a promising alternative, especially in environments with high demands for corrosion resistance. The reinforcement is non-conductive and non-magnetic and is therefore suitable for areas with shielding requirements against the electromagnetic waves. Compared to steel, however, GFRP has a lower modulus of elasticity and a linear response to imposed loads up to failure, which requires a different approach to structural sizing. The new standard defines a relationship for determining the design punching shear capacity of a slab with longitudinal FRP reinforcement but does not allow the FRP to be used as shear reinforcement. This paper presents experimental results from slabs reinforced with both traditional steel and FRP reinforcement. Selected specimens also included FRP stirrups to assess their effect on punching shear capacity. The experimental results are compared with predictions based on both the first and second generation of the Eurocode.
Reducing the environmental footprint of concrete is crucial for sustainable construction. This paper explores circular economy strategies such as reusing existing structures, recycling concrete and mineral waste, and substituting cement with secondary raw materials. A case study evaluating over 100 concrete mixes (C10/15–C30/37) compared natural and recycled brick aggregate, as well as six types of blended cements (CEM II). Mechanical properties and environmental impacts were assessed using LCA in five impact categories. Results highlight the effectiveness of secondary materials in reducing CO₂ emissions and overall environmental burden.
Pre-demolition audits help identify materials suitable for reuse or recycling, thereby reducing the volume of construction and demolition waste and supporting the principles of the circular economy. The article presents the legal framework, audit methodology, and the environmental and economic benefits of such audits. It also includes current insights and practical examples from the European project CIRC-BOOST (Horizon Europe), which tests and implements circular solutions in construction through pilot projects in five countries.
This article addresses the issue of the effect of moisture on the characteristic manifestations of plasterboard. It first summarizes the processes of plasterboard in fire. It then highlights the influence of fire-fighting water. Second, it describes an experiment carried out in which fire-degraded plasterboard samples were exposed to water. Their subsequent natural drying was also measured.
The article summarizes aspects of fire safety in hybrid structures using wood. It highlights the limited applicability of existing standards when combining materials with different thermal and mechanical properties and emphasizes the need for a fire engineering approach. Based on casestudies, including the Moen-Wood system from the Japanese company Takenaka, approaches such as layered structures and controlled charring are presented. The article provides an overview of current design options and identifies challenges faced by Czech design practice in the design of fire-resistant timber structures for higher buildings.
The paper deals with the numerical calculation of a steel joint at elevated temperature. The Sheffield experiment, well known and described in the literature, has been studied. The study of the shell model has been carried out using the (CBFEM). The validation of the model shows good agreement with the experiment. A summary of the sensitivity study is included in the paper.
zpět na aktuální články