As a consequence of the growing production and use of asbestos and inorganic fibres, measurement of their concentration in indoor air is of great importance. The relevant legal regulations require the measurement. Various methods were developed for the purpose, based on collecting airborne particles in capillary membrane filters and subsequent determination of their number concentration. Remediation of buildings with fiber-containing construction elements is an essential part of any reconstruction.
Archiv článků od 24.8.2020 do 27.3.2024
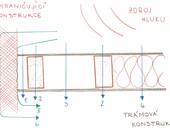
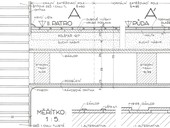
The article is focused on the issue of traditional timber joist floor structures and floor compositions from the period up to the first half of the 20th century. In building practice, we very often encounter these structures in residential buildings that are the subject of structural changes. During these interventions, the basic ideas of the original technical solution are not always respected and some physical parameters of building are degraded. The article describes the principles that were devoted to these types of structures in historical legislative and standard regulations and further in professional literature. The original historical solutions are presented on a practical example. In relation to building interventions in historic timber joist floor structures, current legislative and standard regulations are described, as well as examples of modern solutions and their limitations.
The article is focused on the issue of traditional timber joist floor structures and floor compositions from the period up to the first half of the 20th century. In building practice, we very often encounter these structures in residential buildings that are the subject of structural changes. During these interventions, the basic ideas of the original technical solution are not always respected and some physical parameters of building are degraded. The article describes the principles that were devoted to these types of structures in historical legislative and standard regulations and further in professional literature. The original historical solutions are presented on a practical example. In relation to building interventions in historic timber joist floor structures, current legislative and standard regulations are described, as well as examples of modern solutions and their limitations.
Textile and leather wallpapers are an integral part of the interior of historic buildings. These types of wallpaper are specific in their construction, where they are stretched on wooden frames and form a membrane in front of the wall. Verification of diffusion properties is one of the steps to elucidate the thermal-humidity behaviour of these historical structures. Knowledge of diffuse properties is important for architectural and historical surveys and for the reconstruction of historical buildings. Based on this knowledge, we can assess other properties of wallpaper construction, such as moisture and microbial climate.
The standard “ČSN 73 0527 Acoustics – Acoustical design of rooms – Rooms for cultural uses – Rooms in schools – Rooms for public purposes” was revised after 18 years. In the framework of this revision, the regulations for determining the optimum reverberation time were updated, especially in relation to commonly used technologies and trends in the use of the spaces in question. A new methodology for determining the standard of acoustic treatment for spaces with lower acoustic requirements was developed and, last but not least, a code for occupancy calculations for measuring reverberation time in unoccupied spaces was defined.
In the past, natural stone was among the most used building materials in the Renaissance and Gothic periods. On the territory of the Slovak Republic, sandstone was used for its suitable properties, good compressive strength, appearance, and good machinability. Sandstones still form the supporting elements of sacral and public historical buildings. These building structures are exposed to the weather because the surface finish consists of capillary-active materials or none. From the point of view of monument protection, it is not possible to propose hydrophobic modifications and therefore water coming from driving rain can be absorbed into these structures of historical buildings. This article describes the absorption and redistribution of water in structures using one-dimensional computational simulations of liquid water transfer in selected sandstones from eastern Slovakia using a simulation tool. The results are compared with German sandstones.
In connection with the natural disaster that hit the Břeclav and Hodonín regions in June last year, more than a thousand houses, buildings, halls and other structures were damaged or completely destroyed. Real estate was owned by both natural and legal persons, as well as by cities, municipalities and state institutions. Several state and non-state, for-profit and non-profit organizations came with financial help. To determine the amount of support, subsidy or loan, it was required to document the estimated costs of compensation. The estimated costs were determined on the basis of several methods, taking into account the type and type of real estate, ownership, and the extent of damage. The methods used to determine the estimated costs of compensation are described below.
Producers and suppliers of construction materials are dealing with rising prices of raw materials, semi-finished products and lots of different types of products. Insecurity of input raw material supplies for production is on the rise as well. This is due to the concurrence of many unfavourable circumstances.
Plastics are now being directed primarily to healthcare, mainly for the production of protective aids against virus transmission. A large amount of plastics is used for disposable food containers or packaging of goods, which is now more than ever ordered online. The outage of production capacity of global plastics producers in the USA has the biggest impact on plastics prices. Lack of plastics in the US influences significantly the quantity of plastics available on European markets. The subsequent withdrawal of plastics from China and Europe significantly contributes to logistics complications. Insufficient capacity of transport ships, aircraft and rail transport makes delivery times longer.
Reduction or termination of production of some smelters in Europe, rising emission allowance prices, tariff restrictions and a shortage of metals from Asia are contributing to raise metal prices. It is seen on the London Metal Exchange.
Although the long-term bark beetle calamity is not at its end yet, foresters have succeeded in stopping it in many places in the Czech Republic. Logging of bark beetle timber is decreasing and its price increases. The increase is caused not only by the decrease in logging, but also by export of this timber abroad, particularly to China, which is a phenomenon of the last two years.
Pandemic restrictions have impact on availability of workers for materials production, products logistics, sale and on-site assembly. There was a slowdown in construction output in spring and summer 2020. However, a recovery phase has been seen recently and demand for many materials exceeds supply.
The article presents a structural survey of the historic building of the Imperial Hospital at Prague Castle. The aim of the survey was to determine the functional capability and durability of the building, including an assessment of its usability and evaluation of the condition of historical materials. The research was focused mainly on the issue of inappropriate interventions performed in the past and the associated increased moisture of structures.
The paper deals with the monitoring of deformations during the completion and reconstruction of the Hotel Evropa in Prague. Part of the implementation design documentation was the detailed design of geotechnical monitoring of deformations of the foundation pit. This article presents the main features of the measurement outputs in the form of the vertical and horizontal deformations. Monitoring is one of the most extensive and detailed of all that has ever been implemented in our republic, both in terms of its scope and its duration.
The determination of the bearing capacity of the micropile from the tensile bearing capacity is based on a comparison of the results of compressive and tensile loading tests of micropiles, which were performed on an external test load frame. The micropiles were first tested with compressive forces and later after about one year the same micropiles were tested with tensile forces. Four grouted micropiles with a length of 3 m, which were installed in loess clays, were tested. The result of the tests are graphs of the dependence of the settlement and extraction of the micropile on the applied forces. These graphs are compared and it is looked for a dependency that would make possible an estimation of the bearing capacity of a micropile in compression from the tensile test.
Example of rehabilitation of sewerage facilities, shafts and chambers in an environment of the historic city center with increased loads of chemical-biogenic corrosion. Possible causes and consequences for both, original and newly constructed, building structures. Modification of the proposed solution, including the design of an appropriate construction structure and installation technology solution.
This contribution deals with damage to buildings and building materials due to bad manage of rainwater regime. Effects are divided according to location of damage. First, the damage of roofs and roof trusses is presented, which are followed by examples of damage to the enclosure walls. The most attention, including numerical 3D modeling, is devoted to damage to foundation structures and foundations.
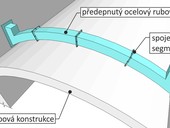
Many historic buildings are located in areas where there is a specific type of earthquake activity, the so-called earthquake swarms, during which a series of thousands of weaker tremors take place for several days or months. Sometimes these shocks are strong enough to be felt by people, and in some cases they can even cause material damage to buildings. Knowledge of the response, especially of vaulted structures of historic buildings to dynamic loads, is the basis of remediation interventions on monumental buildings exposed to these effects. Due to the increasing intensity of wheel and rail traffic, there is also an increase in the effects of the so-called technical seismicity on structures located near roads and tracks. The proposed system of additional stiffening of barrel, cross or of spherical vaults by means of prestressed flexurally rigid segmental ribs contributes to the increase of their resistance to the natural and anthropogenic dynamic effects.
Within the research project NAKI DG16P02M055, an extensive experimental and theoretical research of the influence of grouting on the physical and mechanical properties of brick and stone masonry is carried out. The focus of the research is to verify, in particular, the strengthening effect of selected grouting mixtures based on hydraulic lime (nano-lime), resins and silicates. The influence of grouting on the change of porosity, pore distribution, absorptivity and strengthening effect of grouting of historical brick, marl, sandstone, trachyte, limestone and mixed masonry with lime binder using various types of grouting mixtures in comparison with ungrouted masonry is evaluated. Particular attention is paid to the masonry damaged by cracks and cavities.
The present experience has shown, that the most serious effect of the accidental load on prefabricated panel buildings in our conditions is a gas explosion. In addition to the explosion of gas, the effect of elevated temperature during a fire is also significant. During a fire, the mechanical properties of building materials may change. These may not return to their original value at the end of the temperature load. The article describes the design of repair of the load-bearing members the panel building after fire on the 11th floor of the panel system type T-06.
The aim of the study was to determine the functional reliability of the historic wall of the Hvězda summer house and to assess its applicability. The article presents the possibilities of freestanding wall renovation design using optimal technologies, analysis of solution proposals and evaluation of risk factors. The actual design of the renovation was preceded by a detailed structural survey. At the end of the article, the course of implementation work is described, including the selected material solution of restoration. The Klokner Institute of the Czech Technical University participated in the material analyses and the renewal proposal was consulted with the National Heritage Institute.
zpět na aktuální články