Emergency lighting is one of the most important species of fire safety equipment which determine the fire safety of buildings or other facilities. Emergency lighting is established for use in the event of failure of normal artificial lighting and is therefore supplied from the second independent source. Properly designed, highly functional and operational installation of emergency lighting is essential to ensure a quick and safe escape of people in case of emergency.
Archiv článků od 30.5.2016 do 12.9.2016
The annual total losses caused by fires in the Czech Republic (direct and indirect) are not negligible. The total amount of these damages is to a large extent also involved in fires caused by the operation of electrical wiring and equipment. In terms of fire protection in these cases remains a key issue rate of compliance with fire safety requirements in design, construction, and especially in the operation of these facilities. Currently, in addition to the system of Czech technical standards implemented a lot of new European standards which transpose the international requirements for testing, design, operation and maintenance of electrical wiring and equipment, which requires often the direct modification of existing CSN, in those parts which are contrary thereto. This situation logically caused societal need to address this issue in order to protect public interests, and comprehensively, using available European technical documents, specifications and national standards of EU member states, according to the current state of science and technology.
During the assessment of existing structures of monuments made from reinforced concrete is always necessary to verify the properties of concrete and placement of reinforcement. The paper deals with testing of concrete by non-destructive methods – especially by hardness test method and ultrasonic method. For testing of historical structures seems to be the most suitable ultrasonic method.
Structure created from solid wood wall and deck panels is characterized by a high spatial stability and rigidity. Results of ongoing research have shown that adding concrete layer to the wood deck creating the composite floor structure allows us to receive the structural wall system with increased efficiency.
The aim of this article is to compare 3D numerical models of traditional timber joint. Numerical model of the subjected carpentry joint includes material nonlinearities. Material model of wood presume elasto-plastic behaviour and has orthotropic – transversal isotropic property. The finite-element meshes introduced herein differ one from other by element type and their quantity applied, type of mapping and local density of mesh. Number of nodes and elements, calculation convergence speed, FEM solution exactness, symmetry and mapping of elements are observed.
Building materials contains natural radionuclides, which comes from the earth's crust. In using secondary energy products as raw materials for production of building materials can increase the content natural radionuclides of products. This study focused on practical verification procedures proposed of radiation protection to optimize radioactivity of building materials. It measured the content of natural radionuclides in feedstocks and in final concrete mixtures. Measured values of natural radionuclides of concretes were compared with theoretical calculations.
External Thermal Insulation Composite System (ETICS) still plays an important role in increasing the energy efficiency of buildings – the bigger is the demand, the thicker is just the insulation layer. In August 2016, a new version of basic fire safety Czech standard ČSN 73 0810 comes into action. Changes stated in this document are related, among other, to ETICS and it significantly changes the use of combustible and incombustible thermal insulation on facades. This article intends to point out the essentials of the mentioned problematics.
The article is focused on ambivalent features of systems intelligent building management from the obligatory requests on fire safety point of view. It insists that reliable and functional detection is the basic predetermination to effective solution in fire case but it is not sufficient to the total fire protection provision. The complex solution of the problematics involves many further steps and provisions of both, technical and organizational character.
This thesis deals with the water vapor permeability of wood for the most commonly used types of wood for construction work - Norway spruce (Picea Abies). Diffusion of water vapor is solved according to the density of the material, which varies depending on climatic conditions tree growth. These different conditions are in the Czech Republic mainly characterized by different altitude growing zones. Water vapor permeability is solved in the thesis by a method of measuring the diffusion resistance of materials. Specifically, the method of wet cup and dry cup, which is carried out using EN ISO 12572 knowledge and advices of previous researchers of that method. The results were compared with values reported in the Czech standard and later used for construction project of the typical timbered buildings with respect to contemporary legislation.
Presented text discusses the use of RPAS (Remotely Piloted Aerial System) in the building industry and heritage preservation. It provides information of various case studies and shows examples. For the purposes of building industry and technological area monitoring multicopter systems are mainly used. They have more complex control, but they can be successfully navigated in very low heights and low speeds around and above the object. Safe handling and ensuring the area after agreement with the owner or facility manager is crucial for their use.
The airborne sound insulation of building structures is a subject of permanent interest of designing engineers and architects. Although the weighted apparent sound reduction index is in the final phase verified by measurements in already established buildings, semi-empirical methods have a potential of non-negligible financial savings in the building design phase. The paper presents a set of equations convenient for the calculation of the airborne sound insulation of single and double building structures which extends the Sharp’s method. The equations are derived by mathematical procedures but the purpose of this paper is to supply the reader with a prepared computational tool and that’s why the derivation is listed in different publications. The set of equations is compared with laboratory measurements and other methods both for single (EN 12354-1, Davy’s and Watters’ method) and double structures (Davy’s and Watters’ method).
Presented text discusses RPAS (Remotely Piloted Aerial System) in terms of history, legislation and its possible use especially in the civil sector. RPAS, often called UAV / UAS or “drones” in slang are a phenomenon of recent years. They present modern and popular technology that has undergone an unprecedented boom thanks to miniaturization of electronics, control and navigation equipment, high-performance battery development as well as individual components now available for affordable prices. Safe manipulation and current limits of applicability are indispensable and must be taken into account.
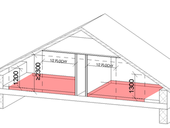
Within the reconstruction of town hall premises, the authorities of a district town decided to rebuild existing ramshackle group house radically. The house is located in a historic area of the city and therefore some parts of the house, namely the medieval cellars and street front, are listed. In addition, the adaptation of the underground spaces, facades and gable walls was necessary, too. In the course of designing process and also during the reconstruction works, the drawings had to be repeatedly revised, partly quite fundamentally.
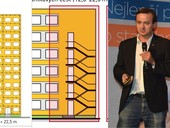
The paper describes a system of FBG (Fiber Bragg Grating) sensors and their integration into the beams of glued laminated timber for continuous monitoring and diagnostics of mechanical stress in building structures. The possibility of gluing the optical fibers into the timber structure and influence on manufacturing process of glued laminated timber on the glued fibers is studied. Laboratory tests including mechanical loading of examined samples were carried out to verify the correct operation of the sensors. Based on the measurement, a timber beam with embedded FBG sensors for the monitoring of the real construction have been manufactured.
The world exhibition EXPO 2015 proved from the creative and useful perspective that wood is a promising building material. We could see the use of wood on a number of exhibition objects representing countries from around the world. Even in the recent past that was not quite realistic. This was enabled by technological advances which created conditions for the implementation of bold ideas of architects associated with this renewable raw material. Along with the exhibition buildings, wood was used for the service utilities which provided comprehensive facilities of the exhibition grounds. In addition to wood, other natural materials such as rattan, bamboo and natural fibres were applied in some exhibition halls.
Energy-efficient buildings research is one chapter of General Programme for Research and Innovation Horizont 2020 (2014 - 2020) which helps reaching the aims of european energy policy. First part of the article deals with characteristics of private-public partnership called Energy-efficient buildings (PPP EeB) that was founded for this purpose during previous General programme (2007 - 2013) and sums up projects PPP EeB supported in both programmes so far. Second part of the article deals with Czech participation in this programmes and describes topics of nearest Programme Hotizont calls for the year 2017.
zpět na aktuální články