The article gives information on the requirements of sunlight in buildings in the European Union and gives a brief historical overview of the normalization of sunlight in our country. On the concrete realization of the residential complex built around 2000 in a closed blocks line is demonstrated the satisfactory insolation in these conditions. From this perspective provides a comment on current events about the preparations of Prague building regulations.
Archiv článků od 22.6.2015 do 2.11.2015
This article deals about tropical hardwood species used for commercial purposes. These kinds of wood have more advantages like better natural durability against bio-degradation caused by high amount of extractives and good mechanical and physical properties. But their using is also connected with some questions – ecological and economical aspects and stability of supposed properties for each delivery. Not solved problem is protection against weathering and mainly decreasing of colour changes of tropical wood surfaces in the exterior till now.
Wilful attack targeted on strategic buildings and critical infrastructure can pose significant thread to property and human lives. By modification of the material traditionally used in building industry, in particular by addition of randomly dispersed fibre reinforcement in currently most spread building material – concrete, the enhancement of the blast and ballistic resistance can be effectively achieved without high additional costs. Within the research works presented in this article, the influence of several types of fibre reinforcement on the blast resistance of the concrete panel was assessed. The results of real blast tests indicates, that incorporation of any type of fibre brings enhancement of the blast resistance of the concrete, but the level is highly affected by strength and shape characteristics of the fibre.
The thermal performance of any building component is the result not only of its thermo-physical properties but also of a way of final installation and connections altogether of their all elements. In addition, thermal leakage and bridging in buildings can eventually contribute to a multitude of problems. The thermal bridge is the place in the building envelope through which heat transfer has a multi-dimensional nature. That is why in recent studies, the issue of heat transfer phenomena in the building components has been taken as a multi-dimensional into account more frequently. One of the specific details that create thermal leakage is located in balcony slabs. This paper is focused on advanced analysis of thermal performance of thermal break element applied in balcony slab with parametric correlation to the thermal properties of wall building envelope. Particular cases of commonly used balcony systems in buildings are observed related to multi-dimensional and parametric approach of modeling. Finally a finding of many aspects, such as building geometry, thermal properties variation and structural type importance are observed as certain influence to thermal bridges magnitude and final thermal performance of balcony slab detail.
The article deals with basic knowledge about the thermal storage mass of energy passive buildings in relation to the summer thermal stability under the climatic conditions of Central Europe. Article lightly touches on the issues of heat storage of buildings with lightweight construction system like a modern sandwich wooden houses.
The recast of the Directive on Energy Performance of Buildings defined all new buildings will be nearly zero-energy buildings by the end of 2020. However, the transformation of the EU’s building stock will not be completed until well after 2020 and this target can only constitute an intermediate step. The renovation of existing buildings stock offers significant potential for both cost-effective CO2 emissions mitigation and substantial energy consumption reduction. Therefore energy efficiency can be seen as Europe’s biggest energy resource. The cost optimal methodology may be a useful tool able to identify the more appropriate retrofit measures in order to launch the renovation of the existing building stock on a large scale.
The article describes floor surfaces and form of their determination in construction and other fields, such as services, real estate, valuation, facility management and more. In Europe, each country has a different technical standard. This means that when we are determining the type of floor area for buildings with these technical standards, we can conclude that they differ by up to 30 %. Therefore, we chose a sample idea of building on which we symbolized each floor type. We tried to make clear, which constructions and types of floor are creditable and which are not. To demonstrate the importance of correct identification of floor surface we give an example calculation of cleaning services where savings could be seen in the correct determination of the floor surface.
The article deals with concrete production and its control as interrelated issues, describing in detail the various types of inspections of concrete plants, as well as ČSN EN 206-1, the standard relevant for concrete. Explained here are the mandatory inspections for road construction supplies according to TKP 18, which contains stricter requirements for the equipment and operation of concrete plants, concrete composition, and for control and testing. The process of the initial inspection by a compiled questionnaire is described, where the individual specific essential requirements and the documents issued during inspections are arranged in logical subject units.
The paper deals with complex solution of heating and economy measures regarding ecology of heat sources and preservation of architectural values of the Volyně college-complex. This solution also includes padding warm and exchange of windows in all complexes. New technology in boiled room was installed with application of boiler for fytomass-burning, gas condensation boilers, thermal pump in system air/water and cogeneration unit for supply electric energy.
The effort is most builders to get the cheapest project documentation and stamp for start of construction. Little attention has been paid to its proper location. Construction practice is to sit as close to the fence with a neighbor to remain more space for the garden. It should be noted that, under the refers to the construction of any building works that arise construction or assembly technology, regardless of their technical construction design, used in building products, materials and construction, the purpose and duration of use. Under construction is also considered to be a product performing the function of the building. It does not matter if the building is connected to the ground as often by professionals and lay people hear.
Part I of the article is a general discussion of the current laws covering the institution called “smlouva o dílo” (the “contract for a work”). It discusses the issue of defining the work, which has changed relative to the old Civil Code in that the work no longer needs a material expression. It also discusses the options for setting a price for the work, as well as the concluding of such a contract without setting a price. There is a detailed section on budget-based price determination, which is especially useful in the construction industry.
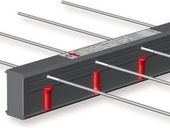
Utilization of steel fibre reinforced concrete (SFRC) during the design of load-bearing structures presupposes that manufactured SFRC will be classified into the strength classes. For static design, these stated strength in the strength class are necessary: compression, tension when the macrocracks open and agreed limit deflection during the bending test on beams. The paper shows the procedure of determining the strength class of SFRC under such prescriptions. Different arrangement of the test equipment, differences in the ranges of test beams and their modifications affects the procedure for evaluation of tensile strength, including those resulting strength classes. Compressive strength of SFRC is considered in accordance with the evaluation of common (normal) concrete (cylinder/cube). These strength classes, calculated by two methodologies, show the difference in classification of one type of SFRC, in this case by increasing strength of SFRC after formation of the macrocrack caused by higher concentrate of fibres.
Stabilization of roof waterproofing coating, which uses the technology of mechanical fixing, are among the most commonly used technology not only in the Czech Republic. With an increasing number of roofs which are realized in practice still appear defects in these types of roofs, which are often caused by failure of the fasteners.
The aim of this paper is introduce the reader to the results of experimental measurements and make the statistical analysis of resistance of chosen fasteners supplied to the Czech market, find the possible cause of the failure of mechanically fastened roofs and evaluate the potential impacts on the design of mechanically fastened system.
According to the statistics of the Fire Rescue Service of the Czech Republic, fires in apartment houses are among the most frequent tragedies. Therefore, it is necessary to pay them due attention. Their cause is often the incorrect execution of building construction disrespecting fire safety aspects.
The present study reveals the influence of typical wind permeability of connections at the eaves on thermal losses. Therefore, a laboratory test and a field test with different insulation materials and different typical geometries of the gap at the eaves were carried out. In order to show the influence on the heat flow rate dependent on insulation material characteristics, three insulations with different densities and air flow resistances were chosen. Furthermore, in the laboratory test the roof inclination, the insulation thickness and the fixation of the roofing underlayment were varied.for the laboratory test, a part of a roof was constructed in the climate chamber. Hence, an influence on the heat flow rate depending on the insulation material has been detected. Where as cellulose insulation and the heavy mineral wool show no significant reaction of the heat flow under different wind velocities and different gap sizes, the investigated lightweight mineral wool insulation shows an important variation of the Uvalue. For the field test, a typically pitched roof was constructed, the eaves placed in the main direction of the wind. It was shown, that the influence of wind on the heat flow rate is negligible if the gaps at the eaves are masked by a projecting roof. The outcome of the research project will lead to a modification of a national construction standard.
The increased moisture of the building materials causes the change of its mechanical and physical characteristic. In particular the high amount of loose water in construction is harmful to human beings, increase the economic expenses of usage of the building and shorten the lifetime of the building. One of the direct techniques to restore damp proofing and to increase the utility value of the building that have undergone rapid progress in last few years is the injection procedure.With use of experimental methods in my work I deal with evaluation of two injection compounds used in Czech Republic and with its impact on the mechanical characteristics of the mortar.
The paper presents the Acoustic Pack device which can record sound emitted by wood-destroying insect larvae while eating wood mass. It records the sound with up to eight sensors at once in several-hour records using high quality acoustic signal recording system. While detecting, it is also possible to hear an activity on a certain element in the structure. This makes it possible to obtain a complete view of the condition of elements with a graphic output of the activity and sound records. Thanks to these advantages, the acoustic system has become a great helper in the detection of damage and in the status analysis of attacked elements in the structure.
zpět na aktuální články