This paper describes an own development of a curtain wall panel system. The leading idea of the project was to prepare an alternative solution for replacement of old metallic curtain walls during the refurbishment of nonresidential buildings from the 1960ies – 1970ies. Presented solution use wood and wood based materials (laminated veneer lumbers) for construction of panels, with clear preference to non-oil based materials for thermal insulation. System allows for different type of external cladding (cement based boards, wooden claddings, integrated PV, support for greenery). Integration of other technical components, like venetian blinds, decentralized ventilation units, is possible. Thermal performance, noise protection and fire safety of this new envelope together with environmental oriented assessments are discussed.
Archiv článků od 13.4.2015 do 22.6.2015
The article describes one of the key factors affecting the lifetime of a wooden building – moisture. It shows the most common causes and effects of increased moisture inside a wooden construction. Methods of determining moisture level in it are listed and particular one suitable for continual monitoring is presented. The suitable method is measuring of the resistance and conversion to a moisture level. Corrections of the moisture level for temperature effects and wood type are included.
The Czech landscape is predominantly a cultural landscape changed for the centuries. It is the cultural heritage connected with the landscape framework – with the terrain relief, water areas, rivers and vegetation. The absence of restriction of the building activities and changes in the use of the territory might cause decline of the historical cultural landscape values and disruption of the landscape cultural identity. The formulation of the cultural landscape value and the method of treatment with it are embodied in the European Convention on the Landscape, in the Preservation of Monuments Act and in the tools of territorial planning. It particularly concerns the designation of the landscape parts as the landscape monument zones, which brings possibilities of the concentrated cultural values protection. It also brings valuable information on the principles of protection for designers and investors. The preservation of the landscape values is embodied in the territorial planning tools. It concerns the principles of territorial development, where the goal characteristics of the landscape are defined; further it concerns the territorial analytic documents of municipalities and a conception of the landscape arrangement in the territorial plans.
In buildings registered in preservation zones the preservationists require keeping of the division and shaping of the opening pane girts and respecting of the original look of the facade. Keeping the girt profile, it is nowdays permitted to glaze the window wings using insulation glass. The manufacturers of windows still make many mistakes affecting not only physical characteristics of the opening panes but also their durability – life time.
In 2013, the World-Green-Building Council (WGBC) made a study to address the influence of sustainable buildings on the international real estate market. In the study, it was revealed that in comparison to normally-built buildings, sustainable buildings
- have a higher selling value
- are rented at a higher price
- can be used more widely.
There are certification systems used to evaluate quality and sustainability of buildings. Besides already renowned systems, e.g. BREEAM and LEED, others have started gaining popularity, for instance DGNB (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Nachhaltiges Bauen) and BNB (Bewertungssystem Nachhaltiges Bauen) in Germany. In the Czech Republic, SBToolCZ (Sustainable Building Tool CZ) was introduced by the Faculty of Civil Engineering of Czech Technical University in Prague in 2010. As part of this study, created on the basis of cooperation between Hochschule Zittau/Görlitz and Czech Technical University in Prague, the BNB (partially similar to the DGNB system) and SBToolCZ systems were compared on an office building.
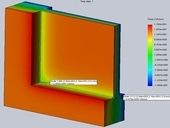
The surface temperature as one of the most watched parametres of the opening panes and light enveopes not only in the Czech Republic is being assessed in a view of risk of water vapour condensation, or more precisely in a view of their health and a hygyenic flaws and ecologically sound environment where inbuilt. The mening is determination if the structure is suitable for the marginal conditions or whether is necessary to choose another structure.
This article deals with the assessment of applicability of OSB boards as the main airtightening layer. Different material thicknesses and various kinds of surface modifications of boards were tested. Measurements were performed with blower-door test in an airtight chamber, which is located in the experimental wooden structure EXDR 1. The article describes a procedure of the experiment and its results.
The paper presents the basic characteristics of fiber reinforced concrete (FRC) that affect its durability and allow to increase service design life of load bearing construction from FRC. This effect is in more detail demonstrated on the test results of the test samples, i.e. strength characteristics, obtained homogeneity and carbonation. The paper focuses on the SFRC, i.e. FRC when using metallic fibres.
The surface temperature as one of the most watched parametres of the opening panes and light enveopes not only in the Czech Republic is being assessed in a view of risk of water vapour condensation, or more precisely in a view of their health and a hygyenic flaws and ecologically sound environment where inbuilt. The mening is determination if the structure is suitable for the marginal conditions or whether is necessary to choose another structure.
In the article, I would like to draw attention to the issue with an outside window lintel on existing double glazed windows. The lintel is mounted below the other lintel and can therefore when replacing windows in modern window to form a problem. The article presents possible solutions window lintel. The most appropriate way is a solution that includes the total renovation of the building envelope with the replacement of windows.
Paper introduces the energy study for old building retrofit for future Centre of Low Energy Buildings in Pisek. Design of the energy efficient buildings with nonuniform user structure (combined residential, administration and technology use) requires the detailed dynamic simulations of buildings and energy system to develop the optimum concept meeting the comfort demand on one side and energy efficiency on the other side with minimized investment costs. Energy study of building retrofit for the Centre has shown how important could be knowledge on future building use in the design stage and has clarified the questionable issues for further design process (high fraction of fan power on electricity demand, suitable extent of PVT collectors use, optimum storage capacity for heat and cold and its cost benefit).
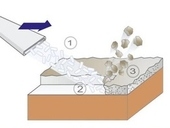
The article presents a technological procedure and possibilities for surface treatment of different materials by using compact parts of CO2dry ice. A purifying medium is accelerated in the nozzle of the SDI Select 60 device by compressed air stream to a supersonic speed, and so it reaches high kinetic energy. The impact of CO2 at the temperature −78.8 °C rapidly cools down the surface; dirtiness becomes brittle and loses its base adhesion, causing temperature shock. Simultaneously with this temperature effect, dry ice intensively sublimates, increases its volume and removes, at high inner tension, the impaired surface of dirtiness without any formation of abrasion waste. The device is applicable to the removal of contamination from elements which cannot be saturated with water or when it is necessary to modify elements with no need to dismantle them. The report introduces the technology when removing contamination on the surface of wooden construction elements, artefacts and stone statues, as well as when forming a relief on the native wooden surface and at a surface treatment before the application of paint, or fungicidal and insecticidal agents.
Drying masonry building structures using high-frequency electromagnetic (EMW) radiation, so-called. Microwave technology in construction practice becoming more exercise. It is an innovative method which can be used to remove excess moisture significantly speed. This article focuses on the description of physical phenomena that occur during drying and comparison standard, the most commonly used, processes for drying buildings.
In the last few years the engineered building product cross laminated timber (CLT) has become very common in timber engineering applications. CLT is a cost-competitive wood-based solution that complements the existing light and heavy-frame options, and is a suitable substitute for some applications which currently use concrete, masonry and steel. This contribution deals with the analysis and design of CLT, used as floor elements. Different calculation procedures for plates loaded out-of-plane are discussed. Comprehensive 3D finite element models (ANSYS 14.0), which can be used to analyze the mechanical behaviour of the board of CLT, were developed.
The landscape character protection is nowadays widely used term within the nature and countryside protection processes that influences the architectonic and urban forms of many construction intentions. It represents some limitations for large construction intentions and also for the single building constructions. It is applied on the landscape protected territories and also on the already settled areas or directly in towns. This article presents different cases when the knowledge of this landscape and nature protection instrument is very important for the architect and shows us the examples when the knowledge can anticipate some unpleasant surprises during the approval process of different construction intentions.
The paper presents the design and construction of the wooden roof structure covering the Penny market building, which is located in the Czech Republic and was built in the summer of 2013. The building of the roof structure was based on the 26 m long elements consisting of 2 or 3 trusses assembled with punched metal plate fasteners and bracing members. The design philosophy, details and descriptions of choosen methods used in the roof design are part of the paper.
This paper is concerned with selected defects and failures of timber buildings. The paper is based on the findings of theoretical, implementation and realization work of loadbearing systems used for timber houses.
Due to the fact that the load-bearing capacity and deflections of timber structures are considerably affected by the load-bearing capacity of joints, it is desirable to verify the influence of structural design of connectors on the overall behaviour of structural systems.Findings from behaviour of structures after their rehabilitation are crucial for further research into real behaviour of timber structures. The paper contains authors, conclusions from designing, realization and exploration of selected building structures.
The article deals with the properties of concrete with two natural zeolites as a the supplementary cementitious material. The determined parameters bring the findings of basic mechanical propeties and frost resistance of aerated concretes with zeolites. The results of properties of concrete with two different kind of zeolite are compared to reference concrete without zeolite. Concrete with zeolite Z2 showed worse properties due to finer particles.
zpět na aktuální články