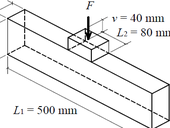
Despite efforts to maintain quality during the construction of reinforced concrete structures, it is relatively common for improper reinforcement to be used contradicting the project, which can lead to serious structural defects. It is then up to non-destructive testing methods to prove these defects. The key is to choose the appropriate method and device for the task.
Archiv článků od 1.5.2017 do 11.9.2017
The article discusses the defects and failures of synthetic foil waterproofing, which show manufacturing defects, which then lead mainly to shorten the lifetime of waterproofing system, but also their own waterproofing due mainly manufacturing, but structural faults. The article gives examples of analytical, non-destructive methods that can be documented defects in material and demonstrate. At the end of the article is included as a legal commentary on the defects and malfunctions and legal information about how to resolve this issue in terms of the legal system.
The paper describes the technology of liquefaction and stabilization of soils that are created in the excavation works of engineering networks. Liquefied grout could be used to fill even the less accessible spaces of utility networks. For the re-use of the excavated soil in a liquefied form, is necessary its pre-treatment, which consists in stabilizing by the suitable stabilizing additive. The mixture is furthermore required the liquefaction by using a suitable liquefying additives. Suitable for stabilization and soil liquefaction it seems the use of fly ash, as is mentioned below in the paper.
The mutual joint waterproofing aspfalt strips can in practice be done in different ways. But not everyone is the correct one. Also important is the width of the overlapping associated strips. We will deal with strongholds in the modified stress and oxidized asphalt strip and compare the strength of the joints. If the bitumen is used as additional waterproofing is necessary, select the types of bitumen sheets with matching suitable bearing insert. As a waterproofing type we should use the modified asphalt strip. The issue of reliability of waterproofing is associated with a high quality of work performed. This quality is affected not only the human factor, but also the technology used for implementation of waterproofing layers. Another influencing factor is the type of applied asphalt waterproofing strip.
Between 1975 and 1985, many gyms of T18 type were built in Czechoslovakia. These gyms were mostly intended for schools, specifically primary schools. The manufacturer of these structures was Bučina Zvolen. The index T18 relates to the span of the load-bearing structure which amounts to 18 meters. The ground-plan measurements are 18,8 by 41,15 m.
The gyms were designed as low-cost structures, which also affected the length of their useful life – 20 to 25 years. In the present, many of these structures are still in use even though they are over 40 years old. Since there has been no refurbishment of these structures to this day, they fail to meet any normative criteria, especially concerning the thermal protection of the structure. Due to unsystematic maintenance, defects have in many cases occurred on the load-bearing members. These can result in limits to the structure’s usage and eventually to its complete shutdown. Under some conditions, it is possible to lengthen the useful life of the gym and it should be in the interests of its owners to be able to continue using it. Based on the diagnostics performed on the specific structure in Želiezovce (Slovakia) and the data collected from other gyms of this type, the authors of the presented contribution have elaborated the static calculation of the load-bearing timber structure for the case of enhancing the heat insulation properties to meet the European standards.
The cause of moisture in the masonry could by different. By old historical buildings is the problem in absence of hydro-insulation, which was made by flat stones or clay backfill. New buildings have a lot defect by application (for example: pipes penetration, join) or wrong design of hydro-insulation, which are the point infiltration of water in to the construction. This problems are made by wrong projection of hydro-insulation in the project. The project does not reflect all influences of the water. But they are also another cases, which can happened like river floods, flood by the neighbour. In those cases it is demanding to dry the building as soon as possible, to protect the property from the mold and return the function of the building. One of the method, which is suitable for this solution is microwave dehumidification, which realize all conditions in one. This aim include also the practice example of the microwave sanitation technique, used by dehumidification masonry, and the positive results.
At present, there is growing interest in the realization of multi-storey wooden buildings. In the case of multi-storey wooden buildings, their safety, stiffness and acoustics are of key importance. The submitted paper focuses on the issue of fire safety of multi-storey wooden buildings, which is currently the subject of major discussions.
The definition of what is a common part of a residential building is essential especially when modifying the building structures and eliminating defects that affect both a common part and residential units. How common parts are defined affects who finances the modifications and reconstructions of such structures and parts. The definition of common parts is based on the new Civil Code (No. 89/2012 Coll.) and on the already abolished Act on Ownership of Housing (No. 72/1994 Coll.).
A growing environmental awareness and desire for sustainable solutions and healthy living conditions, especially in Europe, lead to an increasing demand for timber structures. High speed, excellent cut quality and accuracy of CNC processing allows an effective produce of timber structures by traditional carpentry procedures. This article responds to current problem of load bearing capacity calculations of traditional carpentry joints. This way of structural joints has not sufficient support in current standards and therefore design relies on simple empirical relationships based on experience. This paper presents the experimental and calculation methods for investigation of static behaviour and load bearing capacity of carpentry joints.
The contribution dealst with the problematics of statical defects, or more precisely with the formation of cracks in the brickwork caused by the effect of technical seismicity. It further deals with the construction principles which can be used when designing reconstruction of buildings which are located within the reach of the effect of technical seimicity. The problematics of historical buildings and conservation areas is also mentioned.
For excessive wet masonry rehabilitation, except for other methods, the method of air cavities is used. These can be wall or floor cavities. The wall cavities may be situated either on the internal or the external side of the wall. From the height point of view, internal side cavities can be located under the floor or above the floor level. This contribution only deals with the cavities above the floor level. In the projection practice, the air cavities usually are designed only empirically. But it is necessary to carry out their thermal-technical evaluation for their correct capacity. The matter of the evaluation is the topic of the following contribution.
Computing models for structural behaviour and determination of traditional timber butt joints using analytical relations are presented in this paper. A component method is a base of the computing technique introduced herein. This method is usually used for steel joints design. The component method is based on dividing a joint into individual components. These are defined by partial joint component stiffness. An analytical solution includes a subsidence effect of wooden material in a close proximity of compressive loading. Analytical computation results are compared with the experimental outputs. A design procedure according to Eurocode 5 for a load capacity determination of perpendicularly loaded structural element is stated in the paper.
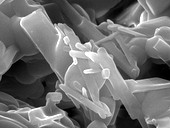
The article presents research into the effect of carbon nanotubes in the blended polymer-silicate matrix containing raw materials from alternative sources. The intention was testing of several variations of mixture composition at the laboratory and also extreme temperature ambient. Assessing the suitability of the matrix composition was carried out by using both basic physico-mechanical parameters and then microstructural analysis methods (on selected samples).
zpět na aktuální články