The paper deals with the effect of all-metal anchors of suspended facades on the heat transfer coefficient of double skin walls. The thermal properties of the anchors are described by means of the point heat transfer coefficient, which can be obtained using a derived formula or calculation aid.
The data for the derivation of the formula and the calculation aid were obtained by three-dimensional modelling and analysis of the calculated data in the framework of the thesis [2]. The input data and the necessary documents used for the calculation were provided by H&B delta. The thesis thus provides a simple calculation and possible comparison of several material and design variants of the used all-metal anchors.
Archiv článků od 26.10.2020 do 1.3.2023
Contemporary architecture often works with glass facades, roofs or even glass columns and beams. The problematic part of a glass structure design is usually a connection between the glass elements and the rest of structure. In order to achieve as much transparency as possible, various mechanical point fixing systems, adhesive connections and their combinations were developed. Although being widely used, the design procedure is mostly based on experiments. There is ongoing research at the Czech Technical University in Prague focusing on characteristics of an embedded laminated connection under various types of loads. Within the initial phase of experiments, small scale specimens consisting of different glass and foil types were tested. The experiments revealed the tensile, eccentric shear and compressive short-term load-bearing capacity of the connection and a dominant mode of failure. Data obtained from the tests are going to be used for further numerical simulations and a parametrical study.
The article deals with sealing of cement-based materials and tensile properties of the sealed joint. Aquapanel cement board was chosen as the base material, which was treated with a primer. Then two sealants were applied, one representative of acrylic and one of polyurethane sealants. After curing, the resulting test specimens were tested according to the valid European standard ČSN EN ISO 8340, which defines the parameters of the test specimen and subsequent test procedures. The evaluation of the test, which took place visually and with a caliper measurement, showed that only polyurethane sealant could be recommended for sealing Aquapanel. This putty, unlike acrylic putty, did not show any defects after the test, so it can be stated as suitable for sealing Aquapanel cement board.
Ukraine has a strong influence on prices and availability of some construction materials. Steel products are the most hit by the war. Rising prices of energies and fuels are influencing the prices of construction materials, too. These unfavourable conditions are seen not only by small investors, but also by municipalities when announcing public tenders. The original price that won the public tender usually rises during the project’s preparation phase and subsequent construction phase. The author of this article analyses the construction materials’ price developments during a period of several years. In the article you can find a pricing of a particular public tender by indicative prices of construction materials and work in different periods.
Producers and suppliers of construction materials are dealing with rising prices of raw materials, semi-finished products and lots of different types of products. Insecurity of input raw material supplies for production is on the rise as well. This is due to the concurrence of many unfavourable circumstances.
Plastics are now being directed primarily to healthcare, mainly for the production of protective aids against virus transmission. A large amount of plastics is used for disposable food containers or packaging of goods, which is now more than ever ordered online. The outage of production capacity of global plastics producers in the USA has the biggest impact on plastics prices. Lack of plastics in the US influences significantly the quantity of plastics available on European markets. The subsequent withdrawal of plastics from China and Europe significantly contributes to logistics complications. Insufficient capacity of transport ships, aircraft and rail transport makes delivery times longer.
Reduction or termination of production of some smelters in Europe, rising emission allowance prices, tariff restrictions and a shortage of metals from Asia are contributing to raise metal prices. It is seen on the London Metal Exchange.
Although the long-term bark beetle calamity is not at its end yet, foresters have succeeded in stopping it in many places in the Czech Republic. Logging of bark beetle timber is decreasing and its price increases. The increase is caused not only by the decrease in logging, but also by export of this timber abroad, particularly to China, which is a phenomenon of the last two years.
Pandemic restrictions have impact on availability of workers for materials production, products logistics, sale and on-site assembly. There was a slowdown in construction output in spring and summer 2020. However, a recovery phase has been seen recently and demand for many materials exceeds supply.
This article deals with the manufacturing process of inorganic foam glass with utilization of waste diatomite as a raw material. The waste diatomite was first subjected to an analysis of chemical and mineralogical composition. The foam glass was formed by a powder sintering method by pressing into pellets with the addition of a foaming agent. After firing, the properties of the foam glass were investigated using an X-ray diffraction analysis, scanning electron microscopy, bulk density, and compressive strength. The possibility of utilization of waste diatomite in raw material mixtures was investigated in accordance with the influence of firing temperature and the resulting properties of inorganic foam glass.
The new Eurocodes for basis of design and actions are almost completed and the final phases of their minor modifications are underway within the working groups of technical subcommittees SC1 and SC10. Their national availability for translations and preparation of national annexes is planned between 2023 and 2025, their implementation and withdrawal of the current Eurocodes in 2028. For the operational implementation of the new generation of Eurocodes, it will soon be necessary to prepare new national annexes and optimally set the values of nationally determined parameters, including calibrations of partial factors for loads and material properties, to ensure reliability, safety and economy of our buildings. It is expected to use the potential of our experts, as well as the considerable financial resources will be needed for the national implementation of the new Eurocodes and the publication of new manuals with practical applications.
The article presents a structural survey of the historic building of the Imperial Hospital at Prague Castle. The aim of the survey was to determine the functional capability and durability of the building, including an assessment of its usability and evaluation of the condition of historical materials. The research was focused mainly on the issue of inappropriate interventions performed in the past and the associated increased moisture of structures.
Greening of the cities (Green Architecture) is one of the current trends in the development of urban architecture. Apart from the system elements of facades overgrown or planted with vegetation, which are a question of the current century, the Green Architecture also includes the traditional use of plants - direct planting near building structures, with their gradual connection using climbing and attachment mechanisms of plants. The effects of such a surface on traditional and modern building surfaces have not yet been precisely defined. The paper presents the results of moisture measurement of the outer surface of traditional building structures in order to evaluate the effect of vegetation surface on the structure.
This paper deals with the diagnostics of a timber load-bearing structure before planned renovation of covering structures. The roof and facade cladding can also change the load conditions, therefore, the inspection static design in this case is necessary. The planned object renovation is an opportunity for elaboration of diagnostic inspection of the supporting structure.
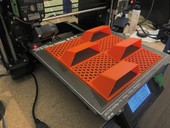
The article describes the development of a prototype vegetation facade panel using parametric modelling. Parametric modelling was then most used for the design of individual parts of the panel, especially the visual part of the panel, which consists of a mathematically generated mesh, and also to create a supporting structure for vegetation. The production of individual prototypes of panels, their parts and components was performed with the help of FDM 3D printing. Individual prototypes were further subjected to testing in real conditions to verify the functionality of the proposed prototype and to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the panel, which will be used for further development.
This article focuses on theory of thermal bridges of ventilated facades and deriving approximate formula to include effect of ventillated facades with fixing elements MFT-FOX (type HT and VT) on heat transmittance of construction by means of modeling 3D calculations of 3D constructions and analysing data of point and linear thermal transmittance.
This task deals with the properties and the possibility of recycling of thermal insulation materials such as polystyrene and mineral wool, not only from buildings after demolition but also from discarded materials left over after the construction of new buildings. This newly developed material is being tested as a filler for ultra-lightweight concrete where it fills the cavities of ceramic hollow bricks, as a filler for self-compacting concrete (SCC) and for the production of acoustic facing.
The paper offers an overview of the performed analyses, which evaluated the leakage into underground garages in the densely built-up area of the Prague city centre. Only after a comprehensive reassessment of geological conditions, the project and other available information was it possible to determine the probable causes of leakage into large underground parking spaces.
This contribution deals with damage to buildings and building materials due to bad manage of rainwater regime. Effects are divided according to location of damage. First, the damage of roofs and roof trusses is presented, which are followed by examples of damage to the enclosure walls. The most attention, including numerical 3D modeling, is devoted to damage to foundation structures and foundations.
This paper deals with the test results of shear characteristics of thermal insulation boards based on MW with longitudinal orientation of fibres of thickness 200 mm and more according to ČSN EN 13162+A1, documents serious faults in test procedure according to current ČSN EN 12090, reasons included, and proposes possible way of their solution.
In the expert business, the usual requirement is to find a possible fault, its cause and a proposal for how to eliminate it. More and more often, however, in expert practice I encounter the requirement to simultaneously assess the current state of the flat roof and especially the waterproofing layer and comment on its possible further functionality and durability.
The present paper deals with the assessment of several realized construction details within the renewed flat roof of the multifunctional building. The new roof structure has the composition of a single-layer flat roof with a classic order of layers, which is mounted on the original roof structure. The problematic details are closely related to the incorrect realization of the waterproof membrane and its fitting to the individual building structures within the detail. Individual factors play a significant role in the assessment: absence of additional elements (cover and anchor strips), improper drainage of rainwater from the roof surface and improper handling of accessories within the waterproof membrane. The assessment of the individual details revealed significant shortcomings that can cause rainwater penetration into the roof structure and thus endanger the reliability and durability of the roof.
zpět na aktuální články