The article explains the differences between the invention patents and utility model from the perspective of Czech legislation. Also highlights the confusion individual categories and purposeful fraud by producers and sellers of equipment.
Archiv článků od 31.8.2015 do 8.3.2017
Natural building materials are in recent years used still more often in civil engineering. One of these materials is also the straw. By its crushing and cutting into small pieces it is formed so-called crushed straw. The properties of this material, which are important for civil engineering, were not published yet unlike the properties of the straw in bales. In the Czech Republic there exist a many objects built from straw bales. In this paper there are described partial results of research which is implemented on Faculty of Civil Engineering, VSB – Technical University of Ostrava since 2013. The aim of this research it is to set fire resistance, thermal – technical properties and acoustical characteristics of crushed straw. There are described results of fire tests – flammability test and tests of single burning object (SBI). Subsequently there are referred results of thermal conductivity measurements, which were provided for different bulk densities of crushed straw.
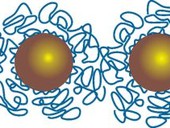
The removal of unwanted material from the surface of historical artefacts is one of the most important and also the most delicate operations in the restoration of cultural heritage. In the Center for innovations in the field of nanomaterials and nanotechnologies a novel design concept of the cleaning microemulsions was developed based on a combination of the two functions, implemented by two components, namely a micellar solution or microemulsion of nonionic surfactants with the addition of co-surfactants and the specific solvents, which are selected according to the respective substances to be removed. The patented cleaning compositions can very effectively and selectively remove coatings of many substances important for the restoration practice, such as waxes, resins (e.g, Damara), paraffins, oils, water acrylate dispersions, hydrophobization coatings (both monomeric and polymeric) etc. Besides the efficient cleaning, the developed procedures have wider applications, such as in a new method of the hydrophobization of sandstone and limestone materials with a thin hydrophilic surface layer, which has been certified by the Ministry of Culture of the Czech Republic.
Non-aqueous dispersions of nanoparticles of calcium hydroxide and magnesium are principally suitable means for the consolidation of wall paintings and limestone materials because they are compatible with the material of historical artefacts. They are also suitable for the deacidification of paper and wood. In the Center for innovations in the field of nanomaterials and nanotechnologies procedures were developed which provide nanoparticles of calcium hydroxide and magnesium ranging in size from about 10 nm to about 200 nm. The procedures are relatively experimentally challenging and put them into practice will require further technological research. Thanks to the good stability of the dispersion a sufficiently long shelf life is ensured and premature aggregation on the surface or just below the surface of treated materials is prevented. There are several alternative methods of the consolidation stone, as exemplified by the use of alkoxides of calcium or magnesium. In converting the alkoxide to calcium carbonate, the sole by-product is alcohol, which naturally evaporates from the stone.
For more than a year, a nearly zero-energy standard has applied to certain buildings. In the Czech environment, specific technical parameters for such buildings have been known for three years. And for over six years, the Directive on energy performance of buildings has been in force, imposing the obligation upon EU member states to introduce this standard.
Nevertheless, it seems that for many experts, including those in the field of energy, this term is still quite unclear. Many imagine buildings coated with photovoltaic modules from the ground to the roof, buildings which are better than passive ones or buildings which are self-sufficient, i.e. completely independent of public energy networks. Given the fact that the concept of a nearly zero energy building is very distant from such notions, and because this standard will soon become obligatory for all buildings, including small family houses, let's have a look at what a nearly zero-energy building really is.
The paper presents an example of solving the propagation of noise from an air/water heat pump installed in the basement of an apartment building. Air intake and exhaust are brought out on the façade of the building, where it is calculated the noise situation in the protected exterior of the building. In the interior it is solved the propagation of sound from the plant room to the protected interior space. In conclusion, the results are compared with the data from the report on measurement at the realized work.
Since year 2000 up to now a similar classification of roof safety waterproofing layer was valid in Czech Republic and in western countries, while in Slovakia is still valid.
In 2011 so-called working group of ROOF CRAFTSMEN ASSOCIATION CZ (Řemeslná rada Cechu KPT ČR) was established, and new Rules for design and construction of roof (Pravidla pro navrhování a provádění střech) (hereinafter „CZ RULES“) were created after 3 years of hard work. These „CZ RULES“ were approved on 28.3.2014 and officially published on 12.9.2014. By these „CZ RULES“ the roof safety waterproofing layer - „PHI“ (pojistná hydroizolace), was renamed to roof additional waterproofing layer - „DHV“ (doplňková hydroizolační vrstva).
The new „CZ RULES“ were made due to changes in building standards in Czech Republic and newly approved version of Rules for design and construction of roof by „ZVDH“ in Germany. The new „CZ RULES“ don´t fully correspond with the German rules, but are very similar.
External Thermal Insulation Composite System (ETICS) still plays an important role in increasing the energy efficiency of buildings – the bigger is the demand, the thicker is just the insulation layer. In August 2016, a new version of basic fire safety Czech standard ČSN 73 0810 comes into action. Changes stated in this document are related, among other, to ETICS and it significantly changes the use of combustible and incombustible thermal insulation on facades. This article intends to point out the essentials of the mentioned problematics.
Presented text discusses the use of RPAS (Remotely Piloted Aerial System) in the building industry and heritage preservation. It provides information of various case studies and shows examples. For the purposes of building industry and technological area monitoring multicopter systems are mainly used. They have more complex control, but they can be successfully navigated in very low heights and low speeds around and above the object. Safe handling and ensuring the area after agreement with the owner or facility manager is crucial for their use.
In early September, the administration building Aviatica was inaugurated and officially unveiled, which is the flagship of a large development in the former factory Walter in Prague. Use of abandoned industrial sites, called Brownfields has been the great theme of Planning and Development during the last few years. Vast territories with dilapidated buildings have a negative impact on their environment, in terms of the degradation of the environment, environmental stress, negative social phenomena or reduction of the economic potential of the site. These lucrative localities are connected to existing technical and transport infrastructure. The transformation has a positive impact on the surrounding areas and instead of spatial expansion of cities into the countryside is one of the ways to exploit their intrinsic potential.
In October 2015, it was one year from when the new polyfunctional building Quadrio in the center of Prague above the metro station Národní třída was opened. It incorporates not only business and office space, but also residential building, a public passage and exit from the metro station. After almost thirty years a big scar of the historic city was healed. It was caused by the construction of the metro station Národní třída, which was accompanied by the demolition of the original buildings and the replacement with single-storey ground lobbies that suit rather to the suburb than the city center. At the same time a new public urban space was created, a stone plaza, which is in the case of similar projects rather rare exception than the rule.
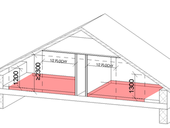
The basement of a castle greenhouse, so called catacombs, and a terrace with air shafts above them are located to the east by the Palm greenhouse of a state castle Lednice and they are connected with it. Catacombs used to serve as depositaries for storing plants from castle park in a period of winter month. Preservation of greenhouse’s catacombs began in 2004 and was carried out in phases till the end of 2007 when the work was interrupted. In 2012 the investor decided to proceed to finish the second part of a planned reconstruction connected with a reconstruction of basements under the greenhouse terrace. The vital part under the project documentation is also dealing with a rehabilitation of damp masonry including necessary constructional and technical research with respect to dampness and its elimination.
Revision of ETAG 004 brought a change in the assessment of noise protection external thermal insulation composite systems (ETICS). Under this revision ETICS may have positive or negative influence on airborne sound insulation of wall on which was applied. The article deals with calculation method of airborne sound insulation, including concrete calculations, and measurements on ETICS with mineral wool.
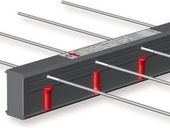
The thermal performance of any building component is the result not only of its thermo-physical properties but also of a way of final installation and connections altogether of their all elements. In addition, thermal leakage and bridging in buildings can eventually contribute to a multitude of problems. The thermal bridge is the place in the building envelope through which heat transfer has a multi-dimensional nature. That is why in recent studies, the issue of heat transfer phenomena in the building components has been taken as a multi-dimensional into account more frequently. One of the specific details that create thermal leakage is located in balcony slabs. This paper is focused on advanced analysis of thermal performance of thermal break element applied in balcony slab with parametric correlation to the thermal properties of wall building envelope. Particular cases of commonly used balcony systems in buildings are observed related to multi-dimensional and parametric approach of modeling. Finally a finding of many aspects, such as building geometry, thermal properties variation and structural type importance are observed as certain influence to thermal bridges magnitude and final thermal performance of balcony slab detail.
The recast of the Directive on Energy Performance of Buildings defined all new buildings will be nearly zero-energy buildings by the end of 2020. However, the transformation of the EU’s building stock will not be completed until well after 2020 and this target can only constitute an intermediate step. The renovation of existing buildings stock offers significant potential for both cost-effective CO2 emissions mitigation and substantial energy consumption reduction. Therefore energy efficiency can be seen as Europe’s biggest energy resource. The cost optimal methodology may be a useful tool able to identify the more appropriate retrofit measures in order to launch the renovation of the existing building stock on a large scale.
zpět na aktuální články