The article deals with a new product in the Czech market that is quickly getting to awareness of potential clients and gaining a significant place in the local real-estate market. Until recently, the inspection of immovable properties was an unknown concept. Nevertheless, in recent two years such assistance service is being more and more popular. Pertinent specialised inspection companies assist the real property buyer in eliminating potential risks that are related to selection and purchase of a given building. A competent certified inspector checks up to about 200 items of the building and compiles an expert report to help the client to correctly decide whether he should buy the given building or not. The inspector will acquaint the client with a real purchase price, precisely describe all the defects and how to correct them, and finally, he will hand over to the client a complete budget to cover the cost of necessary repairs.
In 2013 the inspection of real properties comes to one of the fastest growing segments of Czech economy. The people intending to buy any real property are more cautious and, now at the time of an economic uncertainty, they begin using the above relatively new assistance service in a large extent.
Archiv článků od 22.4.2013 do 9.12.2013
Moisture in moist buildings can be limited by the most different methods. Problems are divided into two papers. The author of paper analyses the conditions of moisture-spread in building in the first part of paper and he solves the selection of sanitation method with less frequent technology of realization. The concrete cause with utilization of air – insulation system then will present in the second part.
The purpose of this paper is to inform about research and development results of special composite materials with enhanced capacity to accumulate infrared radiation. The aim of this project was to create an adjustment for wall and ceiling surfaces enabling good conduction, absorption and storage of thermal radiation with subsequent slow release of heat energy stored during periods of intermittently heating. This proposed solution in conjunction with infrared heaters and air conditioning equipment provides sufficient thermal comfort in heated spaces during winter season and thermal stability of rooms in summer. The main emphasis was on cost saving and increased efficiency of heating systems and cooling units.
The article presents one possible solution and principle for increasing absorption of infrared radiation and accumulative ability. The emissivity and surface temperatures of the developed sample were measured within the frame of the experimental works on real laboratory models in cooperation with specialists from Brno University of Techology (BUT) in Faculty of Mechanical Engineering (FME) and Faculty of Civil Engineering (FCI). The analysis of thermal comfort and energy balances including the assessment of the suitability in summer and winter was performed as well.
Thin-walled composites made of fine-grained cement-sand matrix reinforced by alkali-resistant glass fibres are currently used for the range of applications in the building industry, especially as architectural elements and cladding panels. Their advantage is mainly low weight as well as resistance to mechanical and weather impacts. These preconditions led to an innovative solution of cladding elements for accumulation and consecutive utilization of solar energy. Solar energy is transformed into heat energy by the means of an integrated pipe system and the heat achieved is deposited by the means of a heat water reservoir. Element surface can be set with photovoltaic cells. This material is possible to use as a roof panel as well. On the contrary to standard robust photovoltaic panels a difficult superstructure is not necessary and roof structure assembling is much easier. A wide range of simulation trials in interior as well as real tests in exterior was carried out with cooperation of a renowned company from the photovoltaic branch.
The weakest part of concrete high-rise block are their envelopes, so most of regenerations are dealing with reconstruction of existing envelopes. It related of the replacement of window openings, the installation of additional contact thermal insulation or modifications of projecting structures, including loggia glazing and, last but not least, changes in the colour shading of the surface façade layer. These adjustments can improve energy efficiency of the building, but secondary negative effects on the interior environment in terms of the daylight level must also be considered. In this study we tried to take account of both width and shape of jamb of the window with taking into account the effect daylight inside the room.
Measurement of short term water absorption and thermal conductivity was carried out on samples of traditional insulation and the insulation samples from natural fibers. Further, the measured change in thermal conductivity after soaking and subsequent drying of the original weight.
The results showed that the thermal insulation of natural materials retain their original properties – thermal conductivity, shape, compared to conventional insulation.
The term “ancillary materials” covers a wide range of products (mouldings, profiles etc.) which significantly influence the overall quality of works. As legislation normally does not require any verification of performance and no relevant standards exist, verification and declaration of performance is usually omitted. In reaction to that, we have specified characteristics and verification methods for adequate and consistent verification of relevant characteristics in the framework of voluntary certification.
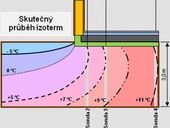
Existing procedures for determining heat transfer in the soil. Temperature measurements in the soil under the floor of the experimental house MSDK at the Technical University in Ostrava. The difference between the calculated temperatures and actually measured. Theoretical and real temperature field in the soil.
Blocks for masonry with integrated insulation material are known over 30 years. Especialy hollow clay bricks have low U value due to optimalization of their geometry with low thermal conductivity of ceramic body. Finaly integrated insulation material into the holes in bricks results to increasing of thermal insulation properties. Article is focus on behavior of hollow clay bricks with and without integrated insulation material in dynamic heat load.
The paper focuses on the description of construction technology of concrete shell blocks with the system of internal thermal insulation. The emphasis is placed on the building envelope. There is described construction technology of external walls and implementation of internal insulation. Another part deals with description of the main details that must be resolved differently than a normal brick house. In conclusion are compare advantages and disadvantages of internal insulation.
Change of the standard ČSN 73 0810/Z1 (valid from 1st June 2012) introduces a new term - so-called „equivalent DP1“.This represented an exception in the classification of non-combustible components for some products. This exception was cancelled by the Change ČSN 73 0810/Z3 valid from 1st July 2013.
In relation with the implementation of the revised EU Directive 2010/31/EU on the energy performance of buildings are currently changing some of Czech legal regulations and new methodology for energy performance assessment is introduced . This article focuses on an example rating the standard family house with conventional solution of building envelope and technical systems, using the new evaluation method. For this object will be also an obligation to issue an energy performance certificate as required by the Consolidated Act No. 406/2000 Coll., as amended.
In the second half of the last century the village changes in terms of demographics. First, the outhouses lose their importance, later, the living houses got empty. At best, the homesteads are used for weekend recreation. As a result of these changes, and due to improper construction impacts the houses dilapidate. There is material destruction and creation of static structural failure of the house.
zpět na aktuální články