Blocks for masonry with integrated insulation material are known over 30 years. Especialy hollow clay bricks have low U value due to optimalization of their geometry with low thermal conductivity of ceramic body. Finaly integrated insulation material into the holes in bricks results to increasing of thermal insulation properties. Article is focus on behavior of hollow clay bricks with and without integrated insulation material in dynamic heat load.
Archiv článků od 3.6.2013 do 22.7.2013
The paper is focused on the results of testing of a key segment of the tunnel lining, which is important for the capacity of the tunnel lining itself. Strength parameters of the designed structural steel fibre reinforced concrete (SFRC) element are described. SFRC key segment with fibres dosages 50 kg/m3 are compared with ordinary RC key segment.
The development of "national plan for increasing the number of nearly zero energy buildings" is a major task of the European Parliament and of the Council Directive 2010/31/EU of 19 May 2010 On the energy performance of buildings, which was transposed by Act no. 300/2012 Coll that amends and supplements Act no. 555/2005 Coll. On the energy performance of buildings, and amends and supplements Act no. 50/1976 Coll. Planning and building regulations (Building Act).
The article introduces the testing procedure of levelling instruments in construction. Generally described testing and validation procedure of levelling instruments (optical and digital as well) is supplemented by results and evaluation of four selected levelling instruments (Sokkia C40, Geo Fennell NO.10, Spectra AL100 a Leica Sprinter 150) used to work in technical levelling.
In order to assess the diffusion rate of solar and wind power plants in the Czech residential sector, we analyse data on licenses for business in the energy industries. We arbitrary set the maximum installed capacity for installations on residential roofs on 10 kWe and find out that the current number of such installations corresponds to 0.5 % of inhabited family houses in the Czech Republic, with most installations being in the Pilsen region and least in the Karlovy Vary and Liberec regions.
When compared with the overall development of solar power plants, it shows that the installations of up to 10 kWe accounted for about 35 % of all the solar power plant installations, but only for 1.9 % of the total installed capacity. Micro wind turbines are up to now not very expanded; we found only 20 installations of micro wind turbines.
The paper presented method of laboratory measurements for specifies air permeability of building board elements of wood- based. The aim of laboratory measurements was to designate value of air permeability of building board elements of wood- based. The results from measurement are in form protocols which indicate air permeability for differential pressure 50 Pa. The value air permeability decides about application and quality building board elements for airtight layer.
For reasons of failure to material detarioration have occurred to many premature or sudden failure of building structures. The quality of the design, execution and maintenance of building structures is a serious problem in the present. The paper presents probabilistic models of concrete deterioration that cause depassivation of reinforcement.
Energetics of structures in construction is a developing discipline that we nowadays encounter every day. Each structure rises and ends at its own life cycle period. In this article, the author evaluates an impact of the zoning plan and its studies on energetics of structures – lets save power from the beginning.
The paper focuses on the description of construction technology of concrete shell blocks with the system of internal thermal insulation. The emphasis is placed on the building envelope. There is described construction technology of external walls and implementation of internal insulation. Another part deals with description of the main details that must be resolved differently than a normal brick house. In conclusion are compare advantages and disadvantages of internal insulation.
Turbulent but often incompetent discussions about more stringent building-energy requirements are accompanied by calculations proving - often biased - what is needed. The article deals with the problem of reliability of building-energy calculations, especially when combined with financial evaluation. The stochastic calculation of energy performance of a large sample of buildings is used. Costs increase of low-energy solutions is discussed.
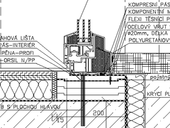
The current trend in the use of secondary raw materials, constantly growing demands to reduce the overall energy performance of buildings and the elimination of thermal bridges both in the design phase and in the implementation phase, helps solve a new element of the threshold coupling, combining the above mentioned requirements for construction. The threshold coupling is inserted in the form of plates under the frame fills of building hole which borders between the exterior and interior of the building. The variability is in the possibility of height and longitudinal adjustment to the exact size and greater range of boards with several kinds of geometrical modifications allowing waterproof closing of waterproofing made of the commonly used materials.
Forestry and forest management plays many roles in the landscape and in the socio-economic area. Forests represent a landscape stabilizer, the best preserved part of the landscape of predominantly natural character with significant application of natural, spontaneous process. It also serves as a source of material benefits to human society. The wood-producing function of forests was questuioned in this country in recent years. Above all, leaders of various environmentalist movement are demanding ever greater proportion of forests without economic activity. However, forestry is afflicted by such influences by decades and the aim of this paper is to demonstrate possible implications of these trends for forestry and subsequent economic sectors.
The paper analyses available data sources on the use of renewable energy in Czech households from which it is possible to derive the current distribution of these sources in the Czech residential sector. Available data provide information about biomass, solar and heat pump installations. The data indicate that the most frequently used renewable energy source among Czech households is biomass, which is the main source of heating in approximately 8 % of inhabited dwellings. Heat pumps are installed in 0.5 % and solar energy is used in at least 1 % of all the Czech inhabited dwellings. It also indicates that these renewable energy sources are far more used in detached family houses rather than in apartment houses. Overall, most of the renewable energy sources used in Czech households are in the Central Bohemian Region, the least in Karlovy Vary Region and the capital city of Prague. Although the datasets do not provide enough evidence to derive any reliable development trends, they provide useful information on the minimal distribution of these resources in the past 10 years and also the effect of selected policy instruments to support the use of these resources on Czech households in comparison with the situation before they came into force.
Change of the standard ČSN 73 0810/Z1 (valid from 1st June 2012) introduces a new term - so-called „equivalent DP1“.This represented an exception in the classification of non-combustible components for some products. This exception was cancelled by the Change ČSN 73 0810/Z3 valid from 1st July 2013.
zpět na aktuální články