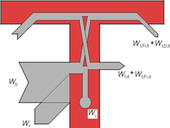
If you selected a high-quality windows and doors for your construction, the overall success depends only on the quality of installation. The most important is quality of the gap between the window frame and jamb. The basic three parts of this gap are inner and outer seal and thermal insulation.
Archiv článků od 25.11.2013 do 3.2.2014
Asbestos is often mentioned in connection with the construction industry, especially with the school buildings. Wrong way of asbestos removal meant a multimillion cost of cleaning the property. Unfortunately, these cases do not cause a change in legislation that would regulate working with asbestos.
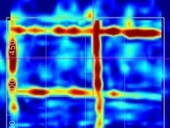
An integral part of a building survey is determining the location of steel reinforcements in building construction elements made of reinforced concrete. In the last decade, GPR came as one of the standard diagnostic methods. However, the equipment used until recently was characterized by its complexity and lengthy measurements, evaluation of which required a considerably professionally knowledgeable staff. The turning point was Hilti PS 1000, a GPR intended for use by common technicians during building surveys. This contribution evaluates the first experience with its use.
Cement-chip boards are construction elements which merge suitable wood and cement properties with the synergic effect designed for all-round use. The disadvantage of these boards remains the relatively high price. The price can be decreased by partially replacing initial raw materials. The paper addresses the option to modify the composition of cement-chip boards using alternative raw materials. Representatives of organic and inorganic materials were used (e.g., hemp, straw, waste products from production of mineral insulations and textile fibres). Alternative materials were used in the production of cement-chip boards under laboratory conditions in two various percentage ratios for the substitution of the wood component. In particular, 100 % and 50 % of wooden chips were replaced in the basic receipt of the boards. Testing bodies were produced using a mechanical press and basic properties were tested after 28 days of maturing. The results of individual board parameters – density, coefficient of elasticity and bending strength were compared with the normative requirements for cement-chip boards which are specified by standard EN 634-2.
The comparison of different calculation methods for airborne and impact sound insulation between rooms is given in this paper. Theoretical influence of flanking transmission on total sound transmission between rooms is done, based on calculation results for reference set of residential buildings. New simplified methods are also introduced for estimation of corrections for flanking transmission in common cases.
The article is focused on description of behaviour of the sandwich load-bearing panels with polystyrene core and OSB boards from the both faces. The interaction of the each component is provided by glued area connection. The panels are suitable for small and medium spans, walls and roofs. The benefits of the sandwich panels are high bending stiffness, good insulations properties and lightweight. The behaviour of the panel is mainly influenced by reinforcing, which is performed mostly by means of the I-beam ribs or rectangular profile ribs. The most important is the joint between sandwich panels and anchoring of the shear walls. The results of the racking shear wall experiments of the sandwich panels and capacity shear wall, which is significant for design of the timber structures, are presented in this article.
The concrete built in the structure is difficult to determine the static modulus of elasticity. One possibility is to measure the dynamic modulus of elasticity and subsequent conversion to static modulus of elasticity. This paper deals with mutual relationships between static and dynamic modulus of elasticity including practical examples of the determination of reduction factor.
The article describes the characteristics of claims for defects from contract for work according to the new Civil Code. The new Civil Code unifies the provisions on contract for work currently contained in both Civil and Commercial Code. The article describes the defects founding the liability of a contractor, reporting the defects and warranty, the rights resulting from the defects and the specifics of claims for defects when the subject of a contract is a building.
It is important for the work to be clearly specified in the contract. Differences from the contract are considered defects. It is vital to inspect the work after the handover for any differences from the contract. The ordering party has to report the defects to the contractor without undue delay. The statute of limitations for claiming the rights from defects is 2 years. The rights resulting from sales contract defects apply analogously to the contract for work. In case of substantial breach of contract the ordering party can ask for the delivery of a new work, repairs or resolution of a contract. Unsubstantial breach of contract allows for repairs or discount.
The last part of the article concerns specifics of claims for defects when the subject of a contract is a building. The ordering party cannot refuse to accept the building for minor defects. The statute of limitations for reporting hidden defects is 5 years in case of a building. The responsibility for defects in shared between the contractor, the maker of the documentation and the construction supervisor.
Steel fiber reinforced concrete (SFRC) with higher concentrations of fibers are still unattractive for investors. The paper presents the possibility of using metal waste to produce of wires, still suitable for the production of SFRC, but with a lower price than the known types of wires offered by current producers.
Moisture in most of buildings can be limited by different methods. Problems are divided into two papers. The author analyses the conditions of moisture-spread in building in the first part of paper and he solves the selection of sanitation method with less frequent technology of realization. The specific cause with utilization of air insulation system is presented in this part.
The article deals with a new product in the Czech market that is quickly getting to awareness of potential clients and gaining a significant place in the local real-estate market. Until recently, the inspection of immovable properties was an unknown concept. Nevertheless, in recent two years such assistance service is being more and more popular. Pertinent specialised inspection companies assist the real property buyer in eliminating potential risks that are related to selection and purchase of a given building. A competent certified inspector checks up to about 200 items of the building and compiles an expert report to help the client to correctly decide whether he should buy the given building or not. The inspector will acquaint the client with a real purchase price, precisely describe all the defects and how to correct them, and finally, he will hand over to the client a complete budget to cover the cost of necessary repairs.
In 2013 the inspection of real properties comes to one of the fastest growing segments of Czech economy. The people intending to buy any real property are more cautious and, now at the time of an economic uncertainty, they begin using the above relatively new assistance service in a large extent.
Moisture in moist buildings can be limited by the most different methods. Problems are divided into two papers. The author of paper analyses the conditions of moisture-spread in building in the first part of paper and he solves the selection of sanitation method with less frequent technology of realization. The concrete cause with utilization of air – insulation system then will present in the second part.
The submitted paper primarily informs about specific fire requirements for wooden houses in the Czech Republic and, due to its total size, it is divided into two parts. The first part is focused on combustibility of building products, i.e. classes of reaction to fire, types of load-bearing and fire separating structural elements (DP1, DP2 and DP3), assessment of construction systems for buildings (incombustible, combustible, mixed) and fire resistance of wooden houses in total. The second part is consequently focused on the issue of space separation of external timber walls with various material arrangements that can noticeably limit location of wooden houses on building sites.
The paper contains basic information on the relationship between the contractor and the client as introduced by the new Civil Code. Firstly, it points to a fundamental difference in the concept of ownership of land and buildings which will not be, unlike the current state, separate. Yet the law allows exceptions to this rule, which are briefly explained in the article.
The main part of the text deals with the issue that is most pressing in construction of buildings. It is the responsibility for the quality of the work or project documentation. The paper deals with the obligation of a client to accept work in stages, addressing liability for latent defects, acceptance of the finished with reservation of latent defects and etc. In this context it should not be overlooked, that the general liable for defective work are together the contractor, subcontractors, maker of the documentation and construction supervisor. These entities may waive liability only if they demonstrate that they did not cause the defect themselves.
zpět na aktuální články