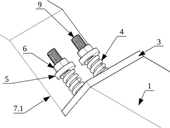
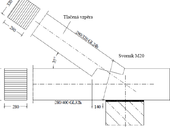
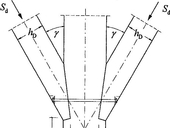
This paper presents a technical solution for bended timber beams and their strengthening. Beams exposed to bending are of the most common use as structural elements. King-post trusses, sling-braced trusses, tie-rod trusses or additional timber beams were assembled to cover large spans in the past. These structures required using additional structural members which limited the space above or underneath a subjected beam. The technical solution presented herein considers a tie-rod truss principle applied on a beam, similar to post-tensioning reinforced concrete structures.
Archiv článků od 28.12.2015 do 27.2.2017
Natural building materials are in recent years used still more often in civil engineering. One of these materials is also the straw. By its crushing and cutting into small pieces it is formed so-called crushed straw. The properties of this material, which are important for civil engineering, were not published yet unlike the properties of the straw in bales. In the Czech Republic there exist a many objects built from straw bales. In this paper there are described partial results of research which is implemented on Faculty of Civil Engineering, VSB – Technical University of Ostrava since 2013. The aim of this research it is to set fire resistance, thermal – technical properties and acoustical characteristics of crushed straw. There are described results of fire tests – flammability test and tests of single burning object (SBI). Subsequently there are referred results of thermal conductivity measurements, which were provided for different bulk densities of crushed straw.
The subject of this paper is a comparison of two experiments of timber-fibre concrete floors in fire, which consist of steel fibre reinforced concrete boards and glue-laminated timber beams. Main aim of this project is to assess the using of steel fibre reinforced concrete board, which work together with glue-laminated timber beams to increase fire resistance and investigate its behaviour in loaded construction.
Structure created from solid wood wall and deck panels is characterized by a high spatial stability and rigidity. Results of ongoing research have shown that adding concrete layer to the wood deck creating the composite floor structure allows us to receive the structural wall system with increased efficiency.
The aim of this article is to compare 3D numerical models of traditional timber joint. Numerical model of the subjected carpentry joint includes material nonlinearities. Material model of wood presume elasto-plastic behaviour and has orthotropic – transversal isotropic property. The finite-element meshes introduced herein differ one from other by element type and their quantity applied, type of mapping and local density of mesh. Number of nodes and elements, calculation convergence speed, FEM solution exactness, symmetry and mapping of elements are observed.
This thesis deals with the water vapor permeability of wood for the most commonly used types of wood for construction work - Norway spruce (Picea Abies). Diffusion of water vapor is solved according to the density of the material, which varies depending on climatic conditions tree growth. These different conditions are in the Czech Republic mainly characterized by different altitude growing zones. Water vapor permeability is solved in the thesis by a method of measuring the diffusion resistance of materials. Specifically, the method of wet cup and dry cup, which is carried out using EN ISO 12572 knowledge and advices of previous researchers of that method. The results were compared with values reported in the Czech standard and later used for construction project of the typical timbered buildings with respect to contemporary legislation.
The paper describes a system of FBG (Fiber Bragg Grating) sensors and their integration into the beams of glued laminated timber for continuous monitoring and diagnostics of mechanical stress in building structures. The possibility of gluing the optical fibers into the timber structure and influence on manufacturing process of glued laminated timber on the glued fibers is studied. Laboratory tests including mechanical loading of examined samples were carried out to verify the correct operation of the sensors. Based on the measurement, a timber beam with embedded FBG sensors for the monitoring of the real construction have been manufactured.
The world exhibition EXPO 2015 proved from the creative and useful perspective that wood is a promising building material. We could see the use of wood on a number of exhibition objects representing countries from around the world. Even in the recent past that was not quite realistic. This was enabled by technological advances which created conditions for the implementation of bold ideas of architects associated with this renewable raw material. Along with the exhibition buildings, wood was used for the service utilities which provided comprehensive facilities of the exhibition grounds. In addition to wood, other natural materials such as rattan, bamboo and natural fibres were applied in some exhibition halls.
The article introduces the new method “Lapped Scarf Joints for Historical Structures Repairs” that deals with design of the lapped scarf joint suitable for the reconstruction of valuable historical timber structures, with help of making the prosthesis for the damaged parts of the beams. The method is a result of the four-year research project supported by the Czech Ministry of Culture within NAKI program. Institute of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics AS CR, Faculty of Civil Engineering CTU and Faculty of Forestry and Wood Technology of Mendel University participated in the research.
Preface – Helping data (continuation): Compression design strength at an angle to the grain – Columns: buckling coefficients for solid timber and for homogeneous glued laminated timber – Stability of members: Beams subjected to bending without compression force – Tilting factors – Laterally loaded joints with dowel type fasteners.
In this research study we analyzed air permeation rate of oriented strand boards, OSB/3 and OSB/4 according to the ČSN EN 12114. OSB boards were manufactured in accordance with the ČSN EN 300 in the Czech Republic. We evaluated the influence of the board thickness (for the most used board thickness 12 and 18 mm) and the influence of the board type (OSB/3 and OSB/4) on air permeation rate values. We have proved that the groups of OSB/3 samples show lower resistance to air permeability than OSB/4. Furthermore 18 mm thick samples at both board types show higher resistance to air permeability than 12 mm thick samples.
Timber and glass are the materials that have excellent aesthetic qualities. In current architecture, glass, as well as wood, are increasingly used for the visually exposed structures. Since glass is a brittle material, various types of hybrid structures are developed. Glass in hybrid element is combined with other material (eg. concrete, timber, steel, aluminium etc.) to increase load-bearing capacity and stiffness of the element, achieve safe failure behaviour together with high level of transparency. Nowadays, several European universities and research centres deal with the glass-timber load-bearing elements. This article provides an overview of the developed hybrid timber-glass structures including an experimental analysis of adhesive timber-glass joints, which was performed at Czech Technical University in Prague.
The paper presents an overview of preservation methods based on professional, expert assessment and research activity of the Thermal Preservation Methodological Department. It reflects the suitability and usability of available methods for wooden elements of respective type of structure. The methods are represented according to currently available and applied preservation methods. The methods use thermal energy, namely the hot-air sterilisation of wood and microwave technologies. The presented paper specifies conditions under which the methods shall be used so that their application contributes to more efficient protection of the heritage fund. The field of biotic harmful elements includes wood-destroying insects and fungi with special regard to dry rot fungus (Serpula lacrymans).
zpět na aktuální články