It is necessary to perform fire tests of wood-concrete structures of them trying to get as much knowledge that would allow the develop computational models. This paper focuses on describing the problem of composite wood-concrete structures and an overview of new knowledge about their behaviour under fire.
Archiv článků od 20.12.2010 do 19.3.2012
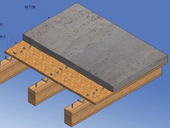
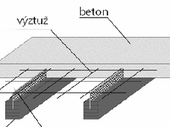
In recent years we can observe in the Czech Republic increased interest in the buildings of wood and wood-based materials. One of the technologies by which the Czech Republic is growing interest is the designing of composite wood concrete structures. So far, they are mainly used for reinforcement and strengthening of the old roof structure. But their use may also find the construction of residential and commercial multi-storey buildings or for the design of bridges and footbridges.
Adhesives used for timber are more rigid and more durable than wood, but also have much greater resistance to water. Despite this fact the way of using of different synthetic resins influences design of these members in different service classes. Phenol-formaldehyde (PF), resorcinol-formaldehyde (RF), phenol-resorcinol-formaldehyde (PRF) resins are generally used as a binder for exterior grade members production. Melamine-formaldehyde (MF) and Melamine-urea-formaldehyde resin is slightly less durable than these above. Products bonded with polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) and protein-based adhesives will not withstand prolonged exposure to water or repeated high–low moisture content cycling in bonds of high density woods. Some isocyanate, epoxy, polyurethane, and cross-linked polyvinyl acetate adhesives are durable enough to use on lower density species even under exterior conditions. This paper deals with different types of adhesive from the durability point of view by comparing strength properties, and considering the possibility of IR analyzing.
In last time popularity of wood-based structures is increasing. Most parameters in the design phase can be calculated using known procedures, but the acoustics is a problem with the theoretical determination of sound reduction index of wooden structures just, because there are the only reliable methods to determine transmission loss of silicate-based structure. In this paper is presenting the calculation method used to determine the sound reduction index of timber floor structures with visible beams.
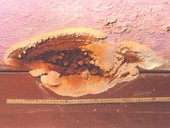
Excessive moisture may be the objects of wooden folk buildings have a negative effect on all the wooden structures, which are these objects formed. This is because if any of the wooden elements has excessive humidity, there is a risk of assault at his wood-destroying biological pests (wood-decaying fungi, wood-destroying insects, rot and mold).
Within the grant project "Multi-storey buildings made of wood" in the laboratories of the Academy of Sciences in Prague and TAZUS performed number of tests of wooden skeleton joints with steel plates, which confirmed the theoretical assumptions and calculations, and demonstrate their reliability and functional and economic advantages for use in practice. Here are a few of the results of experimental tests.
Comparison of knowledge in the field of wooden buildings between the CR and abroad is especially based on the author's many foreign visitors of completed buildings, businesses and universities, the knowledge of the extent and quality of especially American and German literature and participation in many international conferences, including the last World Congress of timber engineering WCTE, held in June 2010 in Italy.
This paper is focused to the fire resistance of multi-storey buildings with light wooden skeleton. Computational procedures in Eurocode are applicable simply and only for a limited number of building elements. For scientific work in this topic are indispensable fire experiments and their subsequent evaluation by means of numerical and analytical models.
This paper is based on the results of theoretical and implementation work in the development of mechanical connections with steel plates and steel elements in timber structures. The analysis of the slip of joints and support details ranks among important issues from the point of view of designing timber structures. The influence of joint stiffness on structural behaviour should be considered in modelling assumptions.
Wood pieces, even locally damaged exhibit useful stiffness and strength parameters with which they can help continue to meet current requirements - after repair. Experience with old wooden structures such as roofs of church towers demonstrate the ability of timber stored in a suitable environment to retain its material properties for many centuries.
Durability and functional reliability of buildings and structures of wood and wood based materials is significantly influenced by moisture content of these materials. In the article we report the results of measurement of moisture in the wood samples mounted between the outer walls with air chambers and comparing the measured values with values calculated by us in the recommended way of moisture balance in the construction according to ČSN 73 0540.
The hot-air treatment of the roof truss of the Upper Church in the village of Velká Lhota at Dačice is documented in stepwise details as a graphical and textual presentation with supporting charts and photographs. In addition to a mycological analysis, a project preparation plan and the main heat treatment technology, a detailed operations schedule is introduced as well as temperature measurement, supporting constructions and heat penetration. The writers’ utmost objectiveness towards this method is demonstrated by thermal camera images of the critical sites and cavities attacked by fungi. The article provides a comprehensive overview of application practices with all necessary recommendations, including the final application of chemical preservatives on the already heat-treated wooden framing.
The paper is focused on some new types of timber structures made from solid timber, glued laminated timber and wood based materials. Especially glued laminated timber is a highly engineered material, because large sizes of structural members and the possibility of various shapes in beams, frames and arches are available. The analysis of intensive loaded structures with large spans shows clearly that to the most advantageous types of connections belong those made by means of steel elements. The analysis of the slip of joints and supports ranks among important issues in designing timber structures. The paper summarises some experience and conclusions from the construction of timber systems with steel-to-timber joints.
There’s still big potential to make building cheaper, including building of passive houses. If the passive house building is optimalised and uncomplicated, It can be much cheaper than classic building. This paper analyses the building of family passive house in the Czech Republic step by step by the author himself.
Development of buildings with wooden structures in the Czech Republic relates to development of low-energy buildings. But there is still general public that is affraid of these constructions because of the fire danger. It is seldom known that wood is fire resistant very well, especially in the point of wiev the static resistance and solidity. In case of fire, in contrast to steel, wood does not lose its static resistance and solidity. The rest of a profile is usualy still able to care the waighting.
The land designated for the construction of the house is located in the PLA zone of the Jizera Mountains. Although it is not part of the protected area itself, it was necessary to design a house that will comply with a large part of the regulations related to constructions of buildings within a PLA. When buying the land the builders realised that the regulations will determine the appearance of the building with quite some detail and they will have to be followed. At the same time, a very energy efficient house had been requested, even if that meant that certain restrictions would be manifested in its appearance.
Defects in inbuilt wooden structures usually start as a small damage, which then increases in proportion to our neglect. Early detection and intervention at the right time will solve the problem for a long time and for an affordable price. Leaving those defects unattended increases de risk of deterioration of the interior parts of buildings or even the distortion of load-bearing structures with the subsequent rapid rise in the costs of sanitation works.
zpět na aktuální články