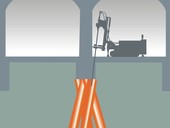
The paper deals with the constructions from jet grouting (JG), which is one of the most modern methods of special geotechnical works. JG is the technique of mixing in-situ soil with the energy of high-pressure jet of slurry. The definitions and types of JG are given in the first part: single fluid, double fluid and triple fluid. The second part concerns JG implementation technology and also lists the necessary activities in designing and implementing JG elements and structures. In the third part, examples show the field of use of JG, including deep foundations, for which the example of static load test is given.
Archiv článků od 4.12.2017 do 17.2.2020
In this paper, the authors consider the aspects of routine procedure compared to the expert approach in solving construction defects and failures. For better orientation in the issue the basic terminology of defects and failures sphere is given. Also, the authors describe in details the course of both solutions, contemplate their specific aspects and point out their consequences. An essential part of the article is presentation of the potential benefits of the expert approach, the advantages of the expert approach are emphasized in the conclusion.
The paper deals with a case study of building defects inspection of Lužánky Free Time Centre in Brno. It is described the history of the building and the building diagnostics. There were used the survey methods of visual-defectoscopic inspection, semidestructive diagnosis and diagnosis of foundations and foundation soil. The conclusions contain recommendations for immediate and long-term solution of the object's static problems.
This work is focused on the verification of the possibility of using specially modified hazardous waste, solidification product, formed from selected secondary raw materials as solidifying agent and hazardous waste (end-product) as a filler in polymer grout joint material. Totally, two solidification technologies were verified, the first one was wet granulation of raw materials and another one was dry homogenization. It is more advantageous to use dry homogenization technology, which is economically less demanding. The possibility of using a specially modified filler was verified by the appropriate tests, and results showed that the grout joint showed high compressive strength of approximately 50 MPa, flexural strength up to about 20 MPa. Developed material can also be characterized by very good cohesion with the cast basalt.
Fibre-reinforced concrete is increasingly used in structures where its properties can be utilized - especially tensile and residual strength after cracking. For applications in load-bearing fibre-reinforced concrete structures, it is necessary to ensure the uniformity of the steel fibres distribution in its structure. The paper summarizes the current knowledge of fibre-reinforced concrete production and test methods, which can be used to monitor the uniformity of fibres distribution in both fresh and hardened fibre-reinforced concrete.
Oak wood is characterized by good durability against biotic damages. However, its surface treatment by coatings is problematic, especially in the exterior expositions. In most cases, there is a rapid degradation and damage caused by weathering. Transparent variants of coating systems suffer from this phenomenon even more than pigmented ones. The article contains the results of practical experiments that lead to some general recommendations, which use leads to surface treatment of oak wood in exterior with longer durability and better colour stability.
The mechanical properties of earthen building material have been intensively investigated for the last fifty years. Different earth mixtures are used for different building technologies, such as walls, bricks or plasters. Therefore, it is almost impossible to set a specific numerical value for a parameter in general. These values may vary significantly and are listed within range. The properties of each earth mixture are dependent on the clay content (type of clay minerals), filler, water and additives. Depending on the building technology several tests can be performed to determine the mechanical properties. This review article discusses mechanical properties of earth, the tests and limit values. These properties include density, binding force, compressive strength, tensile strength, bending tensile strength, bond strength, resistance to abrasion, modulus of elasticity and impact strength of corners.
The paper summarizes latest research on the influence of natural clay materials and earth structures on the quality of indoor microclimate regarding relative humidity. This laboratory research has been carried out at FCE CTU in Prague and UCEEB CTU in Prague and focuses on the dynamic sorption properties of building structures based on natural clays compared to building structures based on common building materials.
Due to increasing amount of construction and demolition waste (C&DW), new recycling methods and applications of secondary raw materials are searched. The biggest part of C&DW is old concrete and mortar which can be used for production of recycled concrete aggregates (RCA). To protect the nature and decrease amount of mined natural aggregates, RCA could partially or totally replace natural aggregates used for production of new concrete. This article presents the factors which have influence on the RCA properties. Properties of three different types of RCA were analysed and results compared with properties of natural aggregates. Description of connection between factors and properties of RCA are discussed. Results showed that not only origin and amount of impurities has influence on applicability of RCA as a replacement of natural aggregates for new concrete production.
In contemporary architecture, straw is used marginally, mostly in do-it-yourself construction. Although the convenient qualities of straw have long been known, it has not gained the trust of builders and designers. Construction companies have not learned to work with straw on a regular basis. In the scope of green technologies, an opportunity is emerging to use straw in professional building systems suitable for sustainable architecture. If we want to apply it in our architectural designs, we have several possibilities. The common small straw bales are suitable for many ways of structure and do-it-yourself process. This way of building process can be interrupt by logistic problems or weather disaster. Contemporary building market offers professional products made of straw: universal strongly pressed boards or system of modular units for external walls. All these ways of application are able to gain the high building quality. The innovative straw technologies enable to design and erect the energy passive house with considerable percentage of straw in constructions. Although the advantages of straw are indisputable, the next success of straw building materials depends on the interest of architects and builders.
In the paper the refurbishment of riding`s hall roof structure is presented. The combined steel-timber load-bearing structure had visible and high horizontal deformations and the gable wall was pushed out of the building.In the frame of refurbishment the diagnostic survey, structural calculations of the original and the new stage of the structure and the proposal of refurbishment works were worked out.
This paper shows the process of restoration, of a historic wooden ceiling, using a “dry method” – interaction between historic timber joists that are mechanically jointed with wood-based boards.The paper describes reasons for choosing the method and principles of a good design. The experience of using this method on site is also described in this article.
Wood and the materials on its basis fulfil the requirements of an ever-evolving and accelerating society. In addition to naturally grown wood, wood-based materials are frequently used as a basic material for production of furniture and for building constructions as well. Looking at changes in waste management, a significant shift from the waste to the circular economy can be observed. The valuable raw materials are kept in the production cycle instead of landfilling or burning. Wood and wooden products can be efficiently separated in waste management, reused and recycled. The so-called wood waste – old furniture, wooden pallets, window and door frames, demolition wood, used lumber, bark and other wood residues can be reused in particleboard production. Particle board manufacturers in the Czech Republic have adopted progressive waste management and currently use 60% of recycled wood into particle boards. A completed life cycle analysis (LCA) of OSB demonstrates that replacing of 50% of natural fibres with recycled wood has significant environmental benefits. The objective is to push furthermore on effective legislation to promote waste material utilization and thus lead to a more sophisticated waste wood collecting.
Wood and the materials on its basis fulfil the requirements of an ever-evolving and accelerating society. In addition to naturally grown wood, wood-based materials are frequently used as a basic material for production of furniture and for building constructions as well. Looking at changes in waste management, a significant shift from the waste to the circular economy can be observed. The valuable raw materials are kept in the production cycle instead of landfilling or burning. Wood and wooden products can be efficiently separated in waste management, reused and recycled. The so-called wood waste – old furniture, wooden pallets, window and door frames, demolition wood, used lumber, bark and other wood residues can be reused in particleboard production. Particle board manufacturers in the Czech Republic have adopted progressive waste management and currently use 60% of recycled wood into particle boards. A completed life cycle analysis (LCA) of OSB demonstrates that replacing of 50% of natural fibres with recycled wood has significant environmental benefits. The objective is to push furthermore on effective legislation to promote waste material utilization and thus lead to a more sophisticated waste wood collecting.
Wood and the materials on its basis fulfil the requirements of an ever-evolving and accelerating society. In addition to naturally grown wood, wood-based materials are frequently used as a basic material for production of furniture and for building constructions as well. Looking at changes in waste management, a significant shift from the waste to the circular economy can be observed. The valuable raw materials are kept in the production cycle instead of landfilling or burning. Wood and wooden products can be efficiently separated in waste management, reused and recycled. The so-called wood waste – old furniture, wooden pallets, window and door frames, demolition wood, used lumber, bark and other wood residues can be reused in particleboard production. Particle board manufacturers in the Czech Republic have adopted progressive waste management and currently use 60% of recycled wood into particle boards. A completed life cycle analysis (LCA) of OSB demonstrates that replacing of 50% of natural fibres with recycled wood has significant environmental benefits. The objective is to push furthermore on effective legislation to promote waste material utilization and thus lead to a more sophisticated waste wood collecting.
The paper deals with the experimental analysis aimed at function verification of fiber optic sensors (Fiber Bragg Gratings). The sensors are used for mechanical stress measurement in wooden load-bearing structures. Glued laminated timber beam with built-in fiber optic sensor system was mechanically loaded during two bending tests. The data obtained using the fiber optic sensors were compared with the results of reference measurement method and analytical calculation.
Sintering activity (dependence of porosity, flexural strength and firing shrinkage on the firing temperature) of feldspar dust (Casial) which is generated during the milling of potassium feldspar in Halamky quarry was determined. Potassium industrially milled feldspar Z75K13 as a reference material with similar granulometry and mineralogical composition with Casial was used for comparison. More intensive sintering activity showed dry pressed samples based on Casial in comparison with feldspar Z75K13 (about 30 °C lower sintering temperature – 1180 °C). Casial created red body after firing thanks to higher content of Fe2O3.
In December of year 2016 has been finished the extensive reconstruction of the multi-family house built in the thirties of last century, located in the district Žabovřesky of the city Brno. Investor with architect desired the modern appearance of interior and facade of the house, which involved a number of difficult renovations and new structures that had to be consulted with structure engineer. The significant steps of the reconstruction of the multi-family house are described in detail in this contribution.
In the last two decades, the US hardwood industry has experienced an important increase in their exports to key markets in Southeast Asia, and Western Europe. However, the export to Easter Europe is currently limited. In these emerging economies, production of furniture and many different kinds of wood products are on the rise. Favorable labor costs, progressive design, and available material resources are key factors that sustain the growth of these industries. The forest products industry is also significant consumer of hardwood lumber. Despite the fact that Easter European countries have its own hardwood material resources, the rapid industry growth, increased sustainability practices, and increased demand of high quality material may require the need for additional material sourcing.
zpět na aktuální články