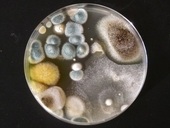
These series of articles focuses on the issue in terms of microbial purity level in internal environment, ventilation and heating systems of residential buildings. The issue relative to its scope is divided into several parts, following: Microbial microclimate of buildings and its limits, Collection and cultivation of samples from the family houses, Rating of family houses, Microbial microclimate in educational establishments, Heating surfaces and microbial environment.
The aim of this set of articles is to present methods and results of the subsequent mapping of microbial contamination of the interior of buildings to technical specialists and readers. The questionnaire survey will enable us to evaluate an impact of the MEP systems for indoor environmental quality, especially its microbial component. Those articles will present the work and the results processed in the framework of the specific research Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Institute of technical equipment of buildings under project FAST-S-15-2620.