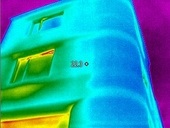
The exact determination of emissivity and the following determination of surface temperature of glossy materials can be carried out e. g. after applying a material with a known value of emissivity on the surface (e. g. self-adhesive foil or spray tint). The contribution deals with other possibility of determination of surface temperature and the influence of emissivity of glossy materials using a metal shield that reduces the negative influence of the reflected radiation during the termographical measurement.
Archiv článků od 4.11.2013 do 26.1.2015
The article deals with the determination of thermal conductivity mineral insulation. Mineral Insulation Manufacturers Association conducted a survey on this topic between building designers and describes the various possibilities of calculation and determination of these values and the differences between them.
The practical determination of surface temperature and emissivity of glossy materials using the infrared thermography is carried nowadays in the way that the surface is covered with a material which has a known value of emissivity. The mentioned values are, however, possible to be determined even without the materials which havae a known value of emissivity: using the infrared radiation, which is reflected by the glossy surface and is detected by the termographical device afterwards. The contribution deals with the possibility of determination of surface temperature and emissivity of glossy materials by the mentioned method.
There are two possibilities how to place the ETICS on the market of the Czech Republic in this time – the national and european certification. Against the european certification valid all over the European Union the national one entitles manufacturer to sell the product just in Czech Republic territory. This contribution further mentions the basic specifics for each type of these certification processes.
Prague building regulations currently represent debated and controversial topic among both professionals and the public. This is a new concept of law to which they are greatly implemented basic knowledge of urban theory and practice. The article summarizes the basic principles of the new regulation in the field of building requirements.
The importance and popularity of wooden houses in the Czech Republic has been rising in long term. It is due of the speed of construction and low energy intensity of the finished house. For laboratory measurements key acoustic parameter – airborne sound insulation – the construction of wood-made wall was designed, so that it accomplished requirements of respective standards. Two different types of material were used, mineral and wood-fiber insulation, for comparison of its influence on the observed property of wall. Tested constructions were placed between the transmission and monitor chamber in accredited laboratory and all needed parameters were determined by appropriate measuring equipment, so the calculation of airborne sound insulation could be made. The influence of individual layers of the wall on airborne sound insulation was stated from altogether eight measurements of different parts of construction.
Hidden defects of buildings, which may become evident only in winter, are one of the biggest problems of any real property purchase. The article gives some advice how to detect them in advance so that the buyer may be prevented from submitting time consuming, expensive and often ineffective claims in face of the previous owner.
This paper discusses a long time measurements inner surface temperatures of different construction methods during summer season. The investigation was carried out on test building location at branch Holzforschung Austria in Stetten – Lower Austria in years 2011 to 2013. Inner surface temperatures were measured for different used construction methods of timber and masonry houses in quantity 44 samples. In this paper are presented the most significance results of measurement. The samples of construction methods were divided by specific characteristics: construction, core insulation, internal cladding and colour of facade. The measurement values inner surface temperatures were processed by statistical methods.
The airtightness measurements of building are important for construction of low energy and passive houses nowadays. It is very effective method to control quality of building envelope and look up for air leakages. These defects of building envelope is a source of wasted energy, because conditioned air heated or cooled is what is leaking out. It is better to find and seal the air leaks, and keep that conditioned air inside.
This study deals with investigation of research sample – 69 family single wooden houses. This amount includes multiple measurements. The construction method of building envelope is based on timber frame. Family single houses are located in Slovakia and border Lower Austria. The year of construction varies from 2011 till 2013. Airtightness measurements were conducted according standard STN EN 13829 (2011). For this investigation, there was Q 46 Blower Door Test equipment used, manufactured by Retrotec Inc., USA. The investigation of airtightness measurements of building was processed by statistical methods. Outcomes are the expressed value air change rate at 50 Pa. The results are divided to a few parts by significance. The first part describes air change rate at 50 Pa dependdant on number of storey and shape of the tested buildings. In the next part of investigation there is significance of difference between method B and A compared. The most interesting part is presented by percentage frequency of air leakages through building envelope. Analysis confirmed improving requirements airtightness of building.
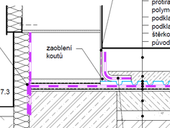
This paper deals with the determination of linear thermal transmittance for buildings with rounded shapes. Introduction deals with typlogy and examples of the buildings containing organic shape. Subsequently is described the theory of determination of linear thermal transmittance. It provides information applicable for buildings assessment in engineering practice.
The contribution deals with particular causes of excessive damp of wooden constructions in objects of the civil engineering. It concerns for instance the matter of water condensation on the surface of wooden elements and on the inside of constructions that contain wooden elements, of incorrect construction design, of constructions with wooden elements and leaking water in places wth wooden elements.
The article deals with the determination of effects of heat radiation on the quality of the indoor environment in winter season, while insulating by double and triple glasses. Effect of radiation through the fillings of the panels and building structures has been evaluated on the basis of knowledge of the mean radiation temperature and operative temperature in the given indoor environment. Isotherms of mean radiation and operative temperatures for different cases of application of insulated glasses having different coefficients of thermal transfer have been presented.
One of the most discussed questions during the last few decades is the functionality of inverted roofs, with the thermal insulation of low water absorbing extruded polystyrene.
The main question is the one of heat loss caused by the cold rain water penetrating through the joints between the boards of thermal insulation itself and going towards the water outlet system beneath this insulation, respectively directly on the waterproofing. The snow melting period seems as the most serious from this point of view.
Two test sample frames were prepared for the purpose of investigation of this phenomena. One of them simulating the rain water outlet above the roof edge flashing and the second one for the simulation of outlet through the inner roof gully. The ratio of undergoing water in the various roof slopes in condition of artificial rain was measured. The ratio of undergoing water was actually high and that it decreased with the increasing slope, depending also on the scheme of water outlet. In case of installation of standard breathing membrane with the low equivalent diffusive thickness placed in the position of separation layer between the XPS insulation boards and the gravel ballast layer ratio of undergoing water became to be nearly inverted. This breather membrane took the function of certain rain water barrier in the structure.
In October 2013 in Orange County Great Park in city of Irvine, California, took place the sixth edition of the prestigious international competition of universities U.S. Solar Decathlon 2013. This round took part also Team Czech Republic from the Czech Technical University in Prague, which finished at overall third place. The article describes in detail rules of competition and technical solutions used in the AIR House.
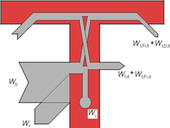
The comparison of different calculation methods for airborne and impact sound insulation between rooms is given in this paper. Theoretical influence of flanking transmission on total sound transmission between rooms is done, based on calculation results for reference set of residential buildings. New simplified methods are also introduced for estimation of corrections for flanking transmission in common cases.
The article describes the reasons for verification of moisture content of substrate layers and draws attention to illogicality of current approach, where moisture content in only very thin surface layer of 10 to 20 mm thickness is verified, but the influence of moisture held in entire thickness of the substrate layers is fully neglected. The article recommends use of in situ methods of measurement of dynamic moisture content of substrate layers, as it is for example described in American norms ASTM F1869-11 and ASTM D4263-83. Only moisture content measured by such methods, allows the contractors and investors to avoid many times fatal consequent failure of surface treatments.
Article presents the results of expert authors work to address the critical situation associated with a negative opinion of the authority concerned czech KHS and impending ban trial operation structures associated with adverse acoustic impacts of construction traffic on the surrounding buildings object. Technical modifications and methods to prevent the reported results were described in Article Equivalent sound pressure level outside space in practice. Text contains the results of measuring the noise level around buildings and not just before and after the implementation of modifications to reduce the acoustic parameters, but also the results of control measurements on site and in the surrounding area. The purpose of this article is to assess the contribution made arrangements for acoustic comfort.
zpět na aktuální články