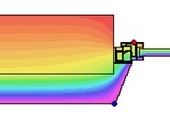
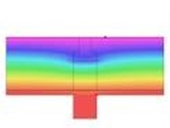
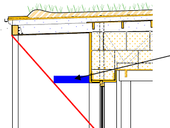
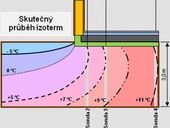
The weakest part of concrete high-rise block are their envelopes, so most of regenerations are dealing with reconstruction of existing envelopes. It related of the replacement of window openings, the installation of additional contact thermal insulation or modifications of projecting structures, including loggia glazing and, last but not least, changes in the colour shading of the surface façade layer. These adjustments can improve energy efficiency of the building, but secondary negative effects on the interior environment in terms of the daylight level must also be considered. In this study we tried to take account of both width and shape of jamb of the window with taking into account the effect daylight inside the room.
Archiv článků od 8.4.2013 do 14.10.2013
The paper is focused on hygrothermal performance of light pipes used in Kaprálův mlýn center. It is present an analysis the condensation risk in roof dome of light pipe and on surface of double insulated glass in cool part of light pipe. Insulated glazing is integrated to thermal insulation block made of extruded polystyrol.
This paper deals with the time period of condensation on the inner surface during the day and the severity of this phenomenon. Condensation on the surface structure occurs when the surface is cooled to or below the dew point temperature, which is a function of temperature, relative humidity and atmospheric pressure.
Thermal stability of rooms affects the local characteristic of the area, building geometry, orientation to the cardinals, the ability of heat storage, mean and intensity of ventilation, and also the size and properties of transparent parts of facade along with their shading. The most effective way to prevent the overheating of the room is to reduce heat gains through transparent structures by shading. Shading by overhanging structures is expressed by sunlit factor fs. This factor changes during the day, with the movement of the sun, and thus the determination for calculations is difficult. This paper deals with a comparison of two different methods of calculation, their comparison and the final comparison with the measured data.
The article deals with sound insulation of wooden house constructions, including the national requirements for sound insulation of walls. There is also a brief description of the laboratory measurement of the sound insulation of wall constructions and information about the sound insulation of single and double wood-based structures.
From the 1st January 2013 new legal and technical regulations are coming in force, which have an impact on higher requirements on energy use for heating and this way also on energy use for heating and cooling. These requirements are stricter not only on the new, but also on major renovated buildings. Proposed measures must fulfil hygienic and energy requirements set by STN 73 0540-2: 2012. Calculated thermal protection properties of building structures are influenced by the properties of used components. Conformity of achieved real properties with the design of building depends from the accuracy of components properties, their real quality and quality of the installation. The design values for construction materials (products) are set in STN 73 0540-3: 2012.
Existing procedures for determining heat transfer in the soil. Temperature measurements in the soil under the floor of the experimental house MSDK at the Technical University in Ostrava. The difference between the calculated temperatures and actually measured. Theoretical and real temperature field in the soil.
Blocks for masonry with integrated insulation material are known over 30 years. Especialy hollow clay bricks have low U value due to optimalization of their geometry with low thermal conductivity of ceramic body. Finaly integrated insulation material into the holes in bricks results to increasing of thermal insulation properties. Article is focus on behavior of hollow clay bricks with and without integrated insulation material in dynamic heat load.
The development of "national plan for increasing the number of nearly zero energy buildings" is a major task of the European Parliament and of the Council Directive 2010/31/EU of 19 May 2010 On the energy performance of buildings, which was transposed by Act no. 300/2012 Coll that amends and supplements Act no. 555/2005 Coll. On the energy performance of buildings, and amends and supplements Act no. 50/1976 Coll. Planning and building regulations (Building Act).
The paper focuses on the description of construction technology of concrete shell blocks with the system of internal thermal insulation. The emphasis is placed on the building envelope. There is described construction technology of external walls and implementation of internal insulation. Another part deals with description of the main details that must be resolved differently than a normal brick house. In conclusion are compare advantages and disadvantages of internal insulation.
Acoustic microclimate is an important part of shaping not only inside but also the outside of buildings. The article presents a case study problems associated with measuring equivalent sound pressure levels in outdoor spaces to be protected buildings. In the text of the methods to remove negative acoustic performance, or what building solutions can be used for treatment of non-compliant, measurement findings.
Acoustic microclimate is an important part of shaping the internal environment of buildings. The effect of noise on the listener is becoming an increasingly important issue that must be addressed. Great emphasis must be placed on indoor climate, not only in the home, but also in the work environment, where the interior acoustics greatly affects the quality and efficiency of operations carried out. Although the health consequences of excessive exposure effects do not show immediately, unlike expressions fluctuations in temperature that our body records almost immediately, long-term exposure to noise damages the health of the individual, not only physically but also mentally. Troubleshooting Sound microclimate has nowadays many ways, both active and passive, and becomes an increasingly important component in the search for optimal solutions and balance of all components of the internal microclimate.
zpět na aktuální články