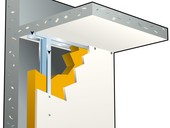
In connection with the implementation of the revised European Directive 2010/31/EU on the energy performance of buildings, certain legislative provisions such as Decree No. 148/2007, Coll. Replaced by Decree No. 78/2013, Coll. are currently amending. This article is focused on the changes associated with the energy certification of buildings, the "ENB", from the perspective of changes in the evaluation ENB.
Archiv článků od 24.9.2012 do 8.4.2013
This paper examines the occurrence of extreme boundary conditions in the internal microclimate in the context of the intended use and structural design and technical equipment of the building. It refers to the occurrence of extreme conditions of the internal microclimate and the effects on constructions of buildings.
After 35 years the requirement for the lowest internal surface temperature of opening panes was left out from the obligatory standard. The makers will probably like this change because they will be able to reject the complaints related to this problem. However, is it correct to think like this and intentionally degrade the quality of the buildings?
Floors are made by construction layers of different materials with unequal functions and characteristics. This formation creates functional unit. According to the material of bearing layer dry and traditional floor systems are distinguished. In dry floors the bearing layer is made by board prefabricated element, e. g. gypsum fiber board, cement bonded particle board or oriented strand board.
Floors must be designed in accordance with legislative and technical requirements. Thermal and technical requirements are of basic significance. Guarantee of required contact temperature decline value presents a significant parameter for ensuring the thermal comfort.
This article compares an influence of three materials of dry floors bearing layer and two materials of wearing layer on the value of contact temperature decline.
This article summarises the results of research on work intensity in special greenhouses based on measurement of heart rate in correlation with microclimatic environmental working conditions in these greenhouses during the summer period of the year. According to the results of measurement the indoor conditions represented by operative temperature value were higher than value required by low in Czech Republic. In order to these facts, the general conclusion of this study is proposal appropriate operation mode for workers in so specific environment conditions.
External thermal insulation composite systems (ETICS) are commonly used in the Czech Republic for thermo-retrofitting of old multifamily buildings as well as for proper insulation of new buildings constructed presently. Additional insulating layer radically improves thermal performance of a wall but at same time reduces its sound insulation in certain frequency range depending on the resonance frequency of the system. This problem becomes important in the case of noisy locations. This contribution presents a revision of the European Technical Approval Guideline No. 004 and describes suitable test methods and single value characteristic ΔRw including relevant national requirements.
Czech Technical Standard ČSN EN 12464-1 entered into force on April 1st. This standard is closely related to healthy light. It establishes rules for correct (and healthy) illuminating of workplaces. A number of changes occurred in the standard, small but important. Since the analysis throughout the standard would be impossibly large, I will assume that readers know the "old" version, and I will focus mainly on the kind of changes.
Czech Technical Standard ČSN EN 12464-1 entered into force on April 1st. This standard is closely related to healthy light. It establishes rules for correct (and healthy) illuminating of workplaces. A number of changes occurred in the standard, small but important. Since the analysis throughout the standard would be impossibly large, I will assume that readers know the "old" version, and I will focus mainly on the kind of changes.
This paper deals with predictions of reverberation time of sports buildings in the phase of project preparation. On the set of nine buildings, the comparison of calculated results with in-situ measured data is done. Different prediction methods and computer simulations have been included in this work.
The article describes unbiased comparison between two different methods of building protection against subsurface water and moisture – the foundation structure of waterproof concrete and waterproofing envelope based on the bitumen or plastic continuous sheet water proofing. The confrontation of properties and risk factors of the methods is made from the perspective of waterproof concrete structure which is the main content of the article. The comparative analysis is supplemented with the photos from field surveys and the results of independent laboratory tests.
The aim of this article is to highlight the ever increasing importance of a comprehensive evaluation of the energy balance of buildings and present a set of results of student work in this field which can be used for explanation the basic relations and ideas about the current impact of the Czech residential buildings on the environment.
The comparison of different approaches to the evaluation of airborne sound insulation between rooms is given in this paper. Based on the described advantages and disadvantages, the most appropriate approach is chosen. Emphasis is laid on the uniformity of assessment for different types of building elements and users of buildings, so that the values of objective quantities for airborne sound insulation should correlate with subjective evaluation.
This paper deals with the issue of comparing simulations for steady and unsteady thermal state at the massive structures. In this paper, computer simulations are compared with real measurements and measurements of climatic data. The evaluation showed that the steady-state temperature can be comparing with real model used after the end of the accumulation phase. It is evident that the requirements for the temperature factor of the internal surface of the solid structures, set by legislation, are a safe assumption.
Series of articles discusses the way of determination of setting the limits of the building envelope air-tightness and its influence on the total value of air permeability, and analyzes the influence of including the elements inside the building to the total value of air permeability. Analysis included 6 experimental houses and proofed the influence of calculated border of building envelope and above all the influence of inside elements like furniture or inside structures.
The behaviour of real structures in some cases differs from the structure modeled in computational program. Article deals with the influences that can affect the characteristics of the structure, so that they affect the surface temperature of the structure. In particular, the moisture inside the material and air humidity.
The behaviour of real structures in some cases differs from the structure modeled in computational program. Article deals with the influences that can affect the characteristics of the structure, so that they affect the surface temperature of the structure. In particular, the moisture inside the material and air humidity.
The analysis of influence of integrated phase change materials (PCM) in light building constructions
This paper deals with the impact of using phase change materials (PCM) in light building constructions. It describes how these materials react during the whole year, how they impact the summer temperature stability of a room and how they react in the transtition period and in the heating period. Measuring was carried out in the experimental and reference room in the attic of the Institute of Building Structures. The layout of these identical rooms enables to compare the measured values. The measuring of the indoor climate which had been carried out during the whole year in the reference and experimental room was analysed. The analysis was used to create the basic methodological procedure for using PCM in light building constructions. These materials proved to be efficient in the summer time. During the heating period the power consumption was monitored in relation to the application of the phase change materials.
Today, besides standard insulation products reflective thermal insulations can be purchased on the market. This may for example be a combination of closed air layers with several layers of metallized foil. Dealers of reflective insulation often claim that the thermal conductivity of reflective insulation reaches values lower than 0,01 W/(m‧K). One dealer introduces this fact to consumers in another form: three centimeters of reflective insulation are equal to twenty centimeters of mineral wool. However, are such properties physically possible?
zpět na aktuální články