The paper describes the changes that has been introduced in the new version of the ČSN 73 0532:2020, all the changes are described in details.
Archiv článků od 6.2.2019 do 5.10.2021
To properly understand the meaning of standardization of daylight, it is necessary to think in general about the reason for the existence of standards and the means of their creation. Such a consideration may have its current significance at this time, when the European Commission for Standardization (CEN) unified standards for daylighting of buildings throughout Europe and when the Chamber of Deputies of the Parliament of the Czech Republic approved a new building law.
This article focuses on theory of thermal bridges of ventilated facades and deriving approximate formula to include effect of ventillated facades with fixing elements MFT-FOX (type HT and VT) on heat transmittance of construction by means of modeling 3D calculations of 3D constructions and analysing data of point and linear thermal transmittance.
The Helmholtz resonator is one of the most widely used low and medium frequency attenuation acoustic absorbers. While commercial products usually offer efficiency across almost the entire spectrum under consideration, in many cases only the specific natural resonance of the room needs to be suppressed. In such cases, it is necessary to proceed with your own design. This paper presents one of the possibilities of calculating a perforated resonator using the electro-acoustic analogy and the transfer matrix method. This method is not demanding on computing power, but nevertheless it is rarely used in current building-acoustic practice. This paper focuses on the comparison of the calculation of the sound absorption coefficient by this method with the data measured in the reverberation room.
The European standard ČSN EN 17037 Daylighting of buildings has been valid in the Czech Republic since August 2019. A year and a half is enough time for the first evaluation of its functioning in project practice. The author of the article deals intensively with this practice and in this paper he would like to share some of his findings concerning the assessment of solar exposure of buildings according to this new European standard. On the edge of this problem, the relationship between accuracy and uniformity in normative requirements is also discussed.
Panels for openings in structures have always been an essential and integral part of buildings. Their importance in terms of a building´s functionality was not recognised. However, the general view on this issue has changed from focusing on big planar segments and critical details to sub-elements of these structures. This does not only focus on the forms of connecting joints but also on the supporting systems that keep the panels in the right position and ensure they function properly. One of the most strained segments is the threshold structure, especially the entrance door threshold structure. It is the part where substantial defects in construction occur in terms of waterproofing, as well as in the static, thermal and technical functions thereof. In conventional buildings, this problem is solved by pulling the floor structure under the entrance door structure and subsequently covering it with waterproofing material. This system cannot work effectively over the long term so local defects occur. A proposal is put forward to solve this problem by installing a sub-threshold door coupler made of composite materials. The coupler is designed so that its variability complies with the required parameters for most door structures on the European market.
This paper deals with the content of prepared review of ČSN 73 2902:2020 External thermal insulating composite systems (ETICS) – Design and application of mechanical fastening for fixing of ETICS in the base material. It specifies modifications made in content of standard and in particular the addition of new provisions for correct assessment of the stability of the ETICS.
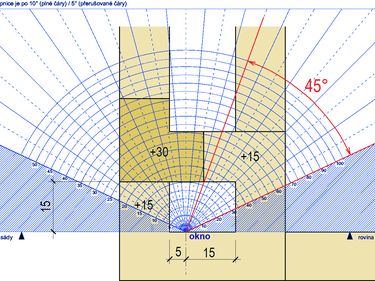
The article deals with an acceptability assessment of a building extension from the point of view of daylighting in the case when daylighting of a neighbouring building is obstructed not only by the extended building but also by balcony and wing belonging to the neighbouring building. The results are confronted with the provisions of the Czech Standard ČSN 73 0580-1 and the Prague Building Regulations.
In modern building systems, sound insulation of walls is often made of multi-layer structures. This article deals with the acoustic operation of such structures and discusses the importance of proper implementation. It also warns against limited sound insulation at low frequencies, which is often not given enough attention. Software for calculating sound insulation - INSUL - was used to compare the acoustic behavior of structures and for simulations.
The article pays attention to the importance of daylight and sun exposure of apartments for public health. The daylight of apartments must be given the same attention as the daylight of workplaces and schools. The way in which the daylight factor Dw (%) of the exterior window plane was introduced into the Czech technical standardization as a criterion is described. The results of a study regarding daylight of living rooms in connection with the limit values of this factor and in connection with the so-called distance angle and window area determined as 1/10 of the floor area of the living room are presented.
Contractors tend to ignore design solutions to reduce the cost of construction. Change of materials, absence of building elements, adjustment of layer composition, application of cheaper alternatives – these are common situations in construction practice. In certain cases, these modifications are without consequences, but in such a situation it is necessary, among other things, to take into account the laws of physics. This article deals with the case in which the structure was replaced – instead of the reinforced concrete ceiling slab, the contractor chose a wooden structure. Wood has significantly different properties than reinforced concrete, so it is necessary to take into account several aspects such as statis, thermo-technical properties and last but not least – with whitch this article deals with – moisture conditions in the structure. The relationship of wood and moisture is specific, the article assesses a specific case of such a structure, lists the possible consequences and finally suggests the most appropriate solution – adjusting the composition of this particular ceiling structure to meet the requirements.
The issue of calculating summer overheating is less known in the field of civil engineers, although it is becoming more and more current. In the first part, the paper deals with current standard requirements in this area. The following is an example of computational programs. It further addresses the problem of climatic boundary conditions and other significant factors affecting the result of the calculation of summer overheating such as ventilation and internal heat gains. The second part of the paper will be devoted to the impact of the method of internal heat gains application on simulation results. The paper concludes with a model daily schedule of internal heat gains for the dwelling unit, created from the taken over actual statistical measurements.
The paper discusses the importance of water absorption of traditional building materials and the ability of traditional non-insulated buildings to withstand rising damp. It also draws attention to some of the risks involved in reducing the water absorption of building materials designed for remediation of moisture and salts problems of traditional buildings.
Increasing the thermal insulation properties of walls, roofs, floors and windows has a positive effect on reducing heat loss and energy need for heating. However, when assessing the energy need for cooling in buildings with conditioned indoor environment, this tendency to increase the thermal insulation capability may lead to an increase the energy need for cooling, when measures to reduce heat gains by transparent structures are not applied.
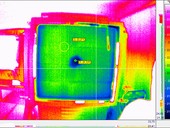
Nowadays, when the demands on the thermal insulation envelope of buildings are increasing, the importance of thermal bridges on the overall thermal loss of the envelope increases. Point thermal bridges are often neglected in the calculations but can lead to an increase in heat loss by an envelope of up to 35%. Significant point thermal bridges are, among other things, elements which ensure anchoring of structures protruding in front of the façade fulfilling the supporting function, since the main emphasis is placed on the bearing capacity of such an element. Several variants of anchoring systems with thermal bridges are available on the market. This paper deals with the thermal-technical assessment of the selected anchoring system and its experimental verification during loading in the climatic chamber.
The application of external wall insulation systems is frequent today due to the increasing demand for energy saving in buildings. The structures attached in front of the facade fulfilling the supporting function must be sufficiently anchored to the external load-bearing structures. The thermal bridges solution in the anchoring system is an important factor beyond the bearing capacity. Several variants of anchor systems are available on the market to deal with thermal bridges. This article introduces the currently available solutions and presents experimental results of the selected anchoring system.
The paper deals with the emission of noise from chimneys and air-conditioning exhausts in the free space. Chimneys in general are vertical flue ducts designed to remove flue gases from combustion devices. The paper does not only address these cases, but extends to the termination of vertical piping systems into the atmosphere in general, addressing also the case of the discharge of degraded air into the outdoor environment through a pipeline of a certain dimension.
Construction and renovation often brings thermal-technical challenges in certain details of certain structures. These details often place strict limitations on the thickness of thermal insulations. This is where the so-called superinsulations (i.e. materials with exceptionally low thermal conductivity) can find good use. The paper focuses on the use of these superinsulation materials in the remediation of thermal bridges in door and window jambs.
In the case of building management, innovation is mainly used to improve the quality of the indoor environment and the comfort of people in the bulding. The role of the energy management of buildings is getting to a whole new position, where each measure is considered not only by looking at money and financial savings, but also by performance and above all health of people.
zpět na aktuální články