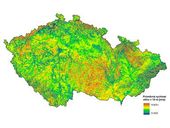
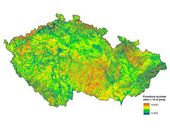
While an actual map of the mean wind speed at the height of 100 m above ground (i.e. at the height of state-of-the-art "large" wind turbines) was created and published in 2007 – 2008, only less accurate older data were available for the conditions closer to the ground. This gap is filled by presented article and concurrently published map of the wind speed at the height of 10 m. Furthermore, other important aspects of wind conditions over the area of the Czech Republic are discussed. These results can form a useful tool for those interested in construction of small wind turbines.
To calculate the average wind speed at a height of 10 m above the surface the same procedure and the same input data as for “wind map” at a height of 100 m above the ground were used. The resulting wind map is a synthesis of three calculation models used for long time at the Institute of Atmospheric Physics AS CR: VAS, WAsP and PIAP.